Financial resources Material financial carriers. Financial resources - material carriers of financial relations. The budget system refers to
Financial resources are the material embodiment of finance, real carrier financial relations.
As an economic category financial resources - This is a state-generated monetary savings and cash funds in the production, distribution and redistribution of gross public Product and national income.
In economic literature, FR is often characterized as cashwhich the economy subject is disposed, i.e. Funds in the monetary turnover of the economic agent.
However, the category "Financial Resources" it is impossible to completely identify with money. At the same time, it is rather difficult to distinguish a clear criterion, on the basis of which the quantitative boundaries and the specifics of financial resources and the category "Cash" can be established.
In business practice, financial resources act as a totality of income, cash savings (cash reserves, depreciation deductions et al.), credit resources available to states, enterprises, households at a certain period of time.
This is a practical approach Based on commercial management practices. Indeed, the funds existing on a specific date of the enterprise in his account in the bank, regardless of whether they are their own or borrowed, make up all its real financial resources - its financial potential, in other words, is the "financial capacity" of Ek-th agent. Income and accumulation focused in state budgetwhether they are the result of the primary or subsequent distribution of the created cost protrude to each specific date as the financial resources of the state.
From the standpoint of economic theory, the concept of "resource" is usually interpreted as a stock, source and as a means to which are addressed in the necessary cases.
Target "reserves" of funds, as a rule, are "connected" in the funds (centralized and decentralized), which are used to meet certain needs.
The monetary fund is a targeted overhaul of funds (for targeted use).
State's monetary resources are mobilized to centralized funds by tax and non-tax methods.
Decentralized cash funds are formed at the level of economic entities and households. These include: authorized funds enterprises; Pay funds; working capital fund; Reserve funds formed from net profit of enterprises.
Some sources of money do not have a target orientation, they are not formed on funds. For example, a part of the funds entering the disposal of a business entity as fines, penalties, contest for violations of the terms of contracts, contracts from counterparties, partners, etc. Receipt of such funds can not be taken into account in advance and therefore are not planned.
Financial resources Measure all possible sources of cash, i.e. The possibilities of the economic entity in the formation of funds, that is, "power" in this regard, its potential.
Financial resources of the statemoreover, the overwhelming part is accumulated by the state with taxes.
The source of financial resources of the state is also funds attracted by state loan.
Part financial resources of enterprises Inventory, borrowed and attracted means. TO own financial resources enterprises include income depreciation, authorized and extra capitalAs well as so-called sustainable liabilities of the enterprise, including sources of financing that are constantly in the turnover of the enterprise, for example, reserves formed in accordance with the constituent documents of the enterprise or legislation. TO borrowed funds include loans of commercial banks and other credit organizations, Other loans, such as bonds. Attracted financial resources - these are funds attracted by additional output joint stock companies, budget allocations and funds of extrabudgetary funds, as well as funds of other enterprises and organizations attracted for participation And on other goals.
Part of financial resources invested by the enterprise in material and intangible assets and generating income is capitalenterprises.
The structure of FR enterprises varies depending on the organizational and legal form of the enterprise, its industry affiliation, etc. factors. For example, in the composition of the agricultural enterprise, there are budget allocations, enterprises with seasonal nature of production have borrowed funds, enterprises with high levels Technical equipment The high proportion is occupied by depreciation.
In economic literature, there is an opinion that short-term credit resources in the composition of financial resources include illegally, since their formation is not related to the creation of new material benefits, but occurs as a result of the redistribution of financial resources.
The savings of the population in the form of an increase in the contributions of the population in commercial banks on their economic entity are the source of financial resources, since in a material and real aspect (from the point of view of compliance with the effective demand of the population and resources of the commodity proposal and the volume of paid services) they correspond to them material resourcesequal to postponed demand in ND.
Thus, financial resources include funds that are "connected" in the funds, as well as those that do not have a target direction.
The main place in financial resources occupy the following elements of the cost: clean income (Profit), value added tax, excise taxes, customs payments, deductions to social needs and depreciation deductions.
An important factor in the growth of financial resources is productivity increase Public labor, which expresses a relative increase in national income in the process of reproduction, and also leads to growth financial results economic activity. Another indicator of the efficiency of social production is closely connected with labor productivity - FDO-report (Caidalotud). Raising FDOODODACK It is inevitably reflected on the formation of financial resources, namely, on the increase in their main source - net income, which increases both as a result of the increase in the production volume of products and due to saving current costs (primarily wages and depreciation deductions). Conversely, the reduction of fund-studies, reduces financial resources.
An important factor is the proportions of the division of gross social product on the refund fund material costs And the national income produced. Reducing the share of material costs in the social product consumption - contributes to an increase in the national income - the main source of financial resources.
The growth of financial resources also affects the material and real structure of social production in general and industrial production in particular. As is well known, the rate of the surplus product on production goods (the first division of social production) is lower than by consumer goods and consumer goods - the second unit (including excise taxes and possessing higher profitability). In addition, consumer goods turnover in the reproductive cycle occurs faster that for a certain period of time, for example, the reporting year, will allow to summarize the resources received from several revolutions. Therefore, the higher the specific gravity and the pace of development of the second division in public production, the greater the possible amount of financial resources may be.
The main sources of financial resources in the future will remain monetary savings (profit, value added tax, excise taxes), income from foreign economic activity.
Financial resources with temporary sources, such as revenues from privatization, the implementation of state-owned property - as they are exhaustion will decrease. Financial resources that have a source of special payments and taxes of subsoil users will increase: royalties, bonuses.
Further increase in remuneration, consumption funds will lead to an increase in the population of the population involved in financial resources.
Financial resources are in constant motion, part of the FR released from the turnover of an economic entity again involved in the circuit (for example, transforming into capital), the other part of them released, is distracted from the turnover and becomes the source of the financial reserve of this subject, or the overall process in favor of another economic Agent (states, etc.).
The trends in the dynamics of the volume and structure of financial resources of the state indicate that a significant increase in the efficiency of social production as a result of the implementation of the transition program to market relations will lead to the acceleration of the formation of financial resources and improving their structure to the direction of increasing the specific weight of those sources whose growth is due to intensive factors.
4.2. Economic content and essence of financial resources
It should be distinguished in the concept of "financial resources" his two parties:
1. In the practice of economic management, under the concept of "financial resources", a set of revenues and savings of all funds available to the state, enterprises, and so on in a certain period, are monetary funds, credit resources, cash reserves. This is a practical approach based on the commercial management practices. Indeed, the funds existing on a specific date of the enterprise at his bank account, regardless of whether they are their own or borrowed and make up all its real financial resources. Also, incomes, accumulations focused in the state budget are whether they are the result of the primary or subsequent distribution of the created cost perform for each specific date as the financial resources of the state.
2. If we proceed from the material and value structure of the total social product (C + V + M), its distribution and place in this process, then the concept of financial resources looks different. If you exclude a re-invoice element, then the concept of "financial resources" will express part of the gross social product and national income in value (monetary) form, which is concentrated directly from the state and enterprises to perform the functions assigned to them.
Sources of financial resources are all three elements of gross social product: "C", "V", "M".
For example, the element "C" is formed: depreciation deductions, working capital, deductions to the reproduction of the natural environment and the mineral resource base, payments included in the material costs in the cost of enterprise products. The element "V" is a source of such financial resources as state taxes from the population, deductions (taxes), on social needs, income on loans and lotteries. The element "M" includes net income (profit), indirect taxes, revenues and revenues from foreign economic activity (customs duties, fees for customs procedures).
Part of financial resources is formed comprehensively as part of several elements of the social product. Thus, from the elements "C" and "V", that at the level of economic entities corresponds to the cost of production and sales of products, works or services, resources are formed in the form of taxes, fees and deductions to special funds, payments for subsoil users - royalty, bonuses, tax on the vehicles, national tax, payments for emissions and discharges of pollutants, etc. And such a kind of proceeds from privatization have a source of national wealth, that is, the accumulated national income (V + M).
Determined essence of financial resources In our opinion, it is advisable to proceed from their functional purpose in the process of expanded reproduction of GDP and ND. This process is characterized by the movement of commodity and money masses, consists of several stages, on each of which commercial and cash flows Differently correspond to each other.
At the initial stage of movement (production) of GDP and the ultimate (its use), cash flows mediate commodity flows. At the stage of distribution and redistribution, the monetary form of expression of GDP acquires a relatively independent movement, since it is at these stages financial relations arise. As a result, they are formed by various cash funds, their rearrangement occurs and finite income are formed. This is how the scope and structure of national production and the needs of the national economy occurs, which in practice is calculated as GDP on costs and GDP in income.
Financial resources - This is a quantitative characteristic of the financial result of the reproduction process for a certain period. These are those cash that is legitimate to direct on the disposal of the disposal of fixed assets, industrial and non-productive accumulation, collective consumption. This macroeconomic indicator It has a balanced character because it can be represented as a sum of both income and expenses.
Part of the monetary turnover is rigidly agreed with the ingoing circulation, since it is implemented due to the exchange of equivalents expressed in the commodity form (from the seller) and the monetary (from the buyer). When excavating the equivalents, conditions do not arise for material and financial imbalance in society.
Another part of the money turnover is related to the needs of extended reproduction of GDP. They are provided in the process of its distribution and redistribution by finance. This part of the money turnover is financial flows, i.e. The movement of those tools that can be spent on the development of national economy and the satisfaction of national and social needs.
As noted earlier, a specific feature of financial flows (in contrast to the monetary) is their uncerevial \u200b\u200bcharacter. As a result, precisely finance in the process of distribution and redistribution of GDP generate an independent movement of money, in which the prerequisites of the material and financial imbalance of the national economy.
The specific content of financial resources is due to the fact that they act
1) as accumulative money funds,
which are formed as a result of the production, distribution and redistribution of gross domestic product;
2) as finite income, i.e. Cash, which are intended to exchange for goods and services;
3) as those incomes that have a material (real) coating, since they are formed as a result of the implementation of goods and services as sources of their formation (component elements):
Depreciation, profits, tax income, non-tax revenues, capital transfers, targeted budget funds,
State extrabudgetary social funds, other
receipts;
4) as the final financial result of the reproduction process, since are used to finance capital investments and overhaul fundamental funds, the increase in working capital, the acquisition of equipment and extension items for budget organizations, costs of social and cultural events, science, defense, the content of state bodies and management, etc.
So, the country's financial resources are part of GDP and may be presented as the sum of the following indicators of the National Accounts system (SNA): the gross profit of the economy, deductions to state extra-budgetary social funds, taxes on production and import taxes, taxes individuals, household savings, loans derived from foreign countries.
Thus, with the help of financial resources, the part of GDP is allocated, which can be directed to the expansion of the socio-economic system as a whole. With their help, part of the manufactured GDP delivers a part corresponding to the current costs consumed in the production process of materials and labor, and the advanced reproduction fund of industrial factors, including labor. From this point of view, the Expanded Reproduction Foundation is legally incorporated by society for health care, education, social policy, etc.
Financial resources are an objective macroeconomic category, the content of which is determined by the conditions for the material and financial balance of the economy. Equality of receipt and consumption of financial resources suggests that the effective demand of enterprises and organizations, which is formed as a result of financing the costs of the development of national economy and the functioning of government agencies, has material coverage, since it meets the established financial resources. Therefore, the condition of material and financial balance can be represented as in the form of compliance with the amount of financial resources and the volume of material goods (for example, reflected in accounting balance Enterprises) and in the form of balance equality of their receipt and spending (budgets of income and expenses of enterprises are drawn; the consolidated balance of financial resources of the state).
Consequently, the equality of the revenues and costs of financial resources is the necessary part of the general equilibrium. Being an internally necessary element modern economyFinancial resources not only characterize the potential of expanded reproduction, but also actively factor in economic dynamics.
The economy can develop efficiently and sustainably only by compaffying the main macroeconomic proportion (between consumption and accumulation) of the natural level, determined by the socio-economic conditions of social production (the development of productive forces, the specifics of the needs of society, etc.). In this case, the proportions of the redistribution of the gross domestic product are consistent with the proportions of its primary distribution and lead to the formation of finite income that correspond to the structure of its use, i.e. Provide a balance between the material and financial and cost aspects of the national production process.
Macroeconomic category "Financial resources" makes sense when society proceeds to regulation economic Development And there is a need to ensure the balance of material and financial flows.
The origins of the discussions about the monetary and not monetary form Financial resources lie, in our opinion, in determining the essence of the finance themselves and their borders. As you know, some economists believe that only cash relations can be financially relations, but they are all financially financial. Others believe that some non-cash relationships can be attributed to finance, for example, barter.
Task 41. The material carriers of financial relations are:
· Part of the national wealth
· Revenues from foreign economic activity
· All cash
· Financial resources
· Gross domestic product
Task 42. Financial resources are:
· Household property property
· Property State, organizations and households
· Cash
· Cash, revenues and accumulations owned and disposal of states, organizations and households
· Securities owned by organizations
Task 43. Specific features of financial resources are:
· Organizational and legal form
· Nephond form
· Monetary form
· Used to finance functions economic Subjects
· We are owned or disposed of households, organizations, state authorities and local governments
· Stock form
Task 44. The set of money incomes, revenues and accumulations owned or disposal of economic entities used on the purpose of extended reproduction, consumption and accumulation are called:
· Cash funds
· Property
· Financial resources
· Financial reserves
· Budgets
Task 45. Signs characteristic of financial resources:
· There are in monetary and natural form
· Are owned or disposed of states, organizations and households
· There are only in nephond form
· There are only stock form
· Exist only in cash
Task 46. Financial resources are:
· Instrument of payment
· Cash income, savings and revenues
· Money turnover
· Tool of circulation
· Material carriers of financial relations
Task 47. Compliance between the indicator and its characteristic:
· Financial resources - materialization of financial relations
· Financial funds - form of education and use of financial resources
· Finance as an abstract concept - a set of economic relations
Task 48. The sources of financial resources on the macro level include:
· Gross domestic product
· Part of national wealth
· Receipts from foreign economic activity
· Production funds
· Budget system funds
Task 49. Specific forms of cash income, revenues and accumulations, which are formed in the subjects of the economy as a result of the distribution - this is:
· Sources of financial resources
· Types of financial resources
· Financial obligations
Task 50. The correct statements are true:
· The stock form dominates with the organization of financial resources commercial organizations
· Financial resources are the material embodiment of finances
· Financial funds are material carriers of financial resources
· Funds always have special sources of formation and strictly target use
· Financial resources exist only in stock form
Task 51. Cash tools that a commercial organization receives as a financial result is:
· Depreciation deductions
· Profit
· Business income
Task 52. Cash tools that an individual entrepreneur receives as a financial result is:
· Depreciation deductions
· Entrepreneurial income
· Profit
· Revenues from sales
Task 53. Financial method Forming financial resources involves the formation of funds:
· On an irrevocable basis
· For free
· On the terms of payability
· Updated
· On the terms of repayment
Task 54. The credit method for the formation of financial resources involves the formation of funds to:
· Regulation conditions
· Freshly based
· Cost conditions
· Urgency conditions
· Intritable based
Task 55. Compliance of the subject and its main types of financial resources:
· Individual entrepreneur - Income from business activities
· Authority of state and local self-government - tax and non-tax revenues
· Household - salary, property revenues
· Non-profit organization - budget resources, gratuitous transfer of legal entities and individuals
· Commercial organization - profits, depreciation, reserve and similar funds
Task 56. The composition of the sources of financial resources of organizations affect:
· Field of activity
· The number of employees in the organization
· Public needs
· Monetary management processes of the organization
· Organizational and legal form
Task 57. The financial resources of households include:
· Wage family members
· Profit
· Entrepreneurial income
Task 58. Compliance of the subject of the economy and the main form of its income:
· State - taxes
· Organizations - Profit
· Households - wages and / or property revenues
Task 59. The arrivals of the commercial organization include:
· Insurance compensation in case of fire
· Profit
· Cash received from the maternal company
· Benefits
Task 60. The accumulations of a commercial organization include:
· Insurance compensation in the event of a fire obtained in current period
· Retained earnings of past years
· Profit of this year
· Depreciation deductions for previous periods
· Tax revenues
Task 61. The types of financial resources of commercial organizations are:
· Receipts from accommodation valuable papers
· Dividend paid shareholders
· Profit
· Value Added Tax
· Income tax
Task 62. The types of household financial resources are:
· Individual income tax
· Insurance compensation received due to the onset insurance case (fire)
· Salary members of the household
· Entrepreneurial income
· Pensions of household members
Task 63. Financial resources of commercial organizations can be directed to:
· Payment of fines for violation of tax legislation
· Pay taxes in Federal budget
· Payment of public security pensions
· Pay material assistance employees
· Payment of premiums to your employees
Task 64. A separate part of the financial resources of organizations, states and households, intended to replenish the lack of either the loss of financial resources in the event of unforeseen circumstances - this is:
· Fixed assets
· Financial reserves
· Cash funds
· Financial resources
· Distorting
The current interpretation of the concept of "financial relations" allows them to determine them as an organic component of the production relations, which express economic relations in cash between the state and individual business entities 46.
Financial relations are diverse. They are associated with cash relations that arise 47:
Between economic entities in the process of selling products, the provision of services, the acquisition of commodity and material values;
Between business entities and higher organizations when creating joint funds of cash and their use;
Between business entities and the state, local governments in the formation of budgets and extrabudgetary funds;
Within economic entities in the formation and use of target funds funds;
Between individual budgets extrabudgetary funds;
Between citizens and the state, local governments in the formation of budgets and extrabudgetary funds.
The subjects of financial relations are legal entities and individuals: the state, enterprises of all forms of ownership, various organizations (including credit banking), association, institutions, citizens and other participants in the reproduction process, which are at the disposal of cash funds target. Funds of financial relations are financial resources - cash funds, enterprises, institutions, organizations of all forms of ownership, individuals and other participants in the reproductive process.
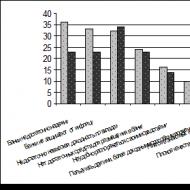
Financial resources are the material carriers of financial relations. As well as in relation to finance, in economic environment There is no uniform approach to determining the economic content of financial resources (Table 3).
Table 3.
Approaches to the definition of economic content of financial resources
| Author | Definition | Criticism |
| V.P. Dual | Financial resources are monetary resources regardless of whether they exist in a separate monetary form or are the monetary expression of certain material resources. | Some authors believe that only cash relations can be financially relations, others believe that some non-cash relations can be attributed to finance |
| Am. Bir- | Financial resources are defined as material, pronounced in money, which are formed by the state or in individual enterprises (organizations) as a result of the use of finance. Under the financial resources of socialist society, we understand the number of national income in the money, concentrated directly from the state or in socialist enterprises for use on the purpose of expanded reproduction and for general government spending. | The situation was actively criticized that only part of national income is the source of financial resources, which actually excludes depreciations from the composition of financial resources. |
| MK Shernya 50. | Financial resources - formed and used by enterprises, associations, organizations and state cash funds. | The definition does not fully disclose the content of financial resources and reduces their composition. Financial resources can exist not only in stock, but also in not stock form. |
| VC. Sencha | Financial resources national economy Present a set of cash savings and depreciation deductions and other funds in the process of creating, distributing and redistributing the aggregate social product. | The most accurate definition corresponding to the distribution concept of finances. Causes criticism of supporters of a reproductive concept. |
| Si. Lushin | Under financial resources are the part of the funds that can be used by their owner for any need for their removal | Too wide definition: In accordance with it, the entire revenue from implementation can be attributed to financial |
48 Dyachenko V.P. Commodity and finance in socialism. - M.: Science, 1974. - P. 129.
49 Burman A.M. Essays of the theory of Soviet Finance - M.: Uniti Dana - 1999 - 151 p.
50 USSR Finance: Textbook for universities / ed. MK Sheremen. - M., 1977. - 205 p. 35
51 Finance, money circulation and credit. Tutorial. / Edited by V. K. Senchagova, A. I. Arkhipova. - M.: "Prospekt", 1999.
| rhenium | resources | |
| Financially credit encyclop dICE | Financial resources - money generated as a result of economic and financial activities in the process of creating and distributing gross national product | Financial resources include all money generated as a result of economic activity, so it is too wide interpretation |
| A.G. Gryaznova, E.V. Mar | Financial resources - money income, accumulation and receipt of ownership or disposal of business entities or local government bodies and used on the goals of extended reproduction social needs Material incentives for working satisfaction of other social needs | There is no accent on the essence of resources. Any cash arrivals It can be attributed to financial resources, and, according to many, this is not true. |
Potentially financial resources are formed at the production stage, when a new cost is created and the transfer of the old one. But the real formation of financial resources begins only at the distribution stage, when the cost is implemented and concrete economic forms of the value implemented are made in the composition of revenue.
Based on the foregoing, it is possible to give a more advanced definition of financial relations as relations arising between business entities and the state in the process of accumulation, distribution and use of funds funds, as well as their use on expanded reproduction, material incentives for working, satisfying the social and other needs of society.
From the XVII century. Y. Krizhanich (1617-1683) and G. Kotoshikhina (1630-1667) reached us. In the works of Y. Krizhanich for the first time formulates finance management problems in a broad context, when the financial system is understood as one of the most important factors for strengthening statehood. In the manuscript of Gregory Kotoshikhina "About Russia in the reign of Alexei Mikhailovich", published in Russia in 1840, financial issues are not raised in a national scale, but from the position of the establishment of certain types of income and expenses on the example of royal orders.
Further formation and development of financial science is associated with the names of I.T. Pososhkov (1652-1726), I.Ya. Gorlova (1814-1890), V.A. Lebedeva (1833-1909), I.I. Janjula (1846-1914), I.Kh. Ozersov (1869-1942) and others. As in the West, formed in Russia by the end of the XIX century. The science of finance had an obvious focus on the state.
An important role for his time was played by the "Finance Plan" (1810) M.M. Speransky (1772-1839), which focused on the tax system (liquidation of wine sputters, refusal of non-production expenses). The next milestone in the development of finance in Russia was the work of N.I. Turgenev "Theory of Tax Theory", published in 1818. Turgenev gave a brief description of the history of the emergence of taxes, formulated the principles of tax policy, led various tax classifications, disassembled in detail economic meaning Each tax, gave definitions and interpretations of various types of capital.
The feature of the development of financial science in Russia within the framework of the classical theory of finance was that it, firstly, for a long time, closely corresponded to financial law. At the same time, the overwhelming majority of books on financial law and financial science in a substantial plan largely duplicated each other. Secondly, there were no universities in those years. special programs Training of economists and financiers - these specialties were preparing at the law faculties of universities.
S.Yu. Witte noted that "From the end of the XVII century, under the word" Finance "began to understand the entire set of state property and in general the state of all state economy. In the sense of the whole totality materialsThe state of its revenue, costs and debts is available - this word is understood and now. Thus, more precisely, the science of finances can be determined as a science on the methods of best satisfaction of the material needs of the state. "
In Russia, on the eve of the revolution of 1917, two independent directions were developed and successfully developed - the analysis of the balance (as part of the balance sheet) and financial computation. The bundled revolution contributed to the formation of financial science. In the 20s XIX century Finance is beginning to be treated as relations with the redistribution of social product and national income (MG Bronsky, A.K. Schmidt, K.A. Shmelev). MG Bronsky wrote that in the implementation of commodity-monetary relations, the financial system "is engaged in the redistribution of national income of the country according to goals and objectives economic Policy» .
In the conditions of state ownership of the means of production and planned system Management The theory of socialist finances was developed (V. Dyachenko, A.M. Alexandrov). In the future, the basic concepts of finance - distribution (L.A. Drobozin,
V.M. Rodionova, N.G. Sychev, V.G. Caneladze, etc.), reproductive (D.A. Aplachverdian, P.S. Nikolsky, V.K. Senchagov, etc.) and imperative (E.A. Voznesensky).
With the development of market relations, the term "Finance" goes beyond the scope of its narrow understanding only as state (public) finances. Accordingly, two relatively independent financial sciences were formed. public Finance Scienceand science of finance of enterprises, organizations, corporations,that is, economic entities. Recently, the methodological foundations of financial management are included in textbooks on the theory of finance as relatively independent direction of financial science. The current state of financial science in Russia, the logic of its structuring, the interpretation of basic sections, categorical and scientific instruments are set out in the teaching and methodological work last years Edited by L.A. Trobozic, A.M. Kovaleva, V.V. Kruglov, V.M. Rodionova, M.V. Romanovsky, O.V. Counselovoy, S.I. Lushina, V.A. Slepova. Financial management is represented by the works of such specialists as I.A. Blank, L.P. Pavlova, G. B. Pole, E.S. Stoyanov, etc.
10. Financial resources as material carriers of financial relations
Contemporary interpretation of concept "Financial relations"allows you to determine them as an organic component of the production relations, which express economic relations in cash between the state and individual business entities.
Financial relations are diverse. They are associated with cash relations that arise:
- between business entities in the process of selling products, the provision of services, acquisition of inventive material values;
- between business entities and higher organizations in creating joint funds for money and their use;
- between business entities and the state, local governments in the formation of budgets and extrabudgetary funds;
- within economic entities in the formation and use of target funds funds;
- between individual budgets, extrabudgetary funds;
- between citizens and the state, local governments in the formation of budgets and extrabudgetary funds.
Subjects of financial relationslegal and individuals are acting: the state, enterprises of all forms of ownership, various organizations (including credit and banking), association, institutions, citizens and other participants of the reproduction process, which are at the disposal of the target cash funds. Objects of financial relationsare financial resources - Cash funds, enterprises, institutions, organizations of all forms of ownership, individuals and other participants of the reproduction process.
Financial resources are the material carriers of financial relations. Just as in relation to finance, in the economic environment there is no single approach to the definition of the economic content of financial resources (Table 3).
Table 3.
Approaches to the definition of economic content of financial resources

Potentially financial resources are formed at the production stage, when a new cost is created and the transfer of the old one. But the real formation of financial resources begins only at the distribution stage, when the cost is implemented and concrete economic forms of the value implemented are made in the composition of revenue.
Based on the foregoing, it is possible to give a more advanced definition. financial relationsas a relationship arising between business and state entities in the process of accumulating, distributing and using funds funds, as well as their use on expanded reproduction, material stimulation of working, meeting social and other needs of society.
11. Financial system Russian Federation, its spheres, links and their relationship
On the basis of finance is formed financial system - form of organization of monetary relations between all the subjects of the reproductive process on the distribution and redistribution of the cumulative social product. The process of distribution and redistribution of the value of the cumulative social product is financial mechanismwhich is a "system of organization, regulation and planning of financial relations, ways to form and use financial resources." The financial system consists of financial institutions(organizations, institutions that implement and regulating financial activities, the Ministry of Finance, Treasury, central bank, tax inspectorate, tax police, stock and currency exchanges, financial and credit institutions) and financial instrumentscreating the necessary conditions Leaky financial processes.
The country's financial system forms a multi-level, hierarchical structure characterized by the presence of a number of parts, cuts, as well as species of different purposes of financial resources and sources of financing (Fig. 4).

Fig. 4. Spheres financial system Russian Federation
Depending on the methods of income generation economic entities financial system is customary to divide on spherescentralized Finance (Public Finance) and Decentralized Finance (Finance of Organizations and Finance of Households).
Via centralized financemobilize resources in the budget system, and their distribution and redistribution between the sectors of the national economy, economic regions, individual groups of the population occur. The main in this area are public Finance
which reflect economic relations on the formation and use of centralized funds for funds intended to ensure the fulfillment by the state of its functions. Decentralized financesused to regulate economic and social relationship As part of individual business entities and make up the basis of finance. The general financial position of the country largely depends on their state, since most of the financial resources are formed here.
Existing differences like in functional purpose These areas and methods, methods for the formation and use of financial resources make it appropriate to allocate separate systems of financial relations: (1) Finance of organizations (economic entities); (2) Public Finance (state and municipal finances); (3) Household Finance (households).
These subsystems, in turn, are divided into separate links (private subsystems), depending on the mechanism of formation and use of cash funds in specific economic entities. Given such a grouping, the financial system of the Russian Federation is divided into the following spheres and links (Table 4) (we note that other submissions of the financial system are possible with the separation of those or other components).
Table 4.
Financial Systems and Links

The financial system is not just the sum of the blocks, links and sodes. This is really a system that is a single whole, all components of this system are closely related to the numerous types of economic relations and relations, and the implementation of the objectives of individual spheres and links is the development financial Policy.
12. Institutional structure financial system of state
Institutional structure is a set of organizations operating in the financial sector of the economy. In fig. 5 The most general representation of the institutional structure is given. The financial sector of the economy can be viewed in a wide and narrow sense.

Fig. 5. Institutional structure of the financial system of the country
In the first case, it should be attributed to the financial institutions themselves; So control, observational bodies, as well as financial unions. The main tasks of the controlling and observational bodies within the framework of the financial system are to maintain its sustainable functioning, the implementation of state regulations and directly monitoring the activities of financial institutions. The main appointment of financial unions is to submit and protect the interests of groups of financial institutions before the state and the public.
Financial institutions within the framework of the financial sector itself (in a narrow understanding) include organizations related to banking systemse, as well as to non-bank financial intermediaries. In turn, in the banking system a special place is given to central banks. Distinguish the central emission bank responsible for credit-money policy In the country and emission of banknotes and other credit money, as well as central bankswhich perform regulatory functions within certain banking groups, such as central banks of a cooperative loan. The largest group of banks form commercial bankswhich can be viewed as the core of financial and banking systems.
As non-bank or other financial intermediaries allocate a large group of institutions that carry out only individual banking or "bank-like" functions. In the group of non-bank financial intermediaries, two subgroups can be distinguished:
1) institutions that are considered by the country's legislators as credit ( investment banks, depository banks carrying out storage, registration and re-registration of property rights on securities);
2) institutions that are not considered credit (insurance companies, pension funds, Real Estate Funds, Leasing Companies, Dealer Companies, etc.).
In economically developed countries, two main types of financial systems are traditionally allocated - segmented and universal. IN universal Financial Systemlegally is not limited to the implementation by banks of those operations of financial services that do not relate to banking. This is a fundamental sign. Banking operations are determined primarily established list, and their composition is periodically revised in accordance with the change in legislation. Universal systems are characteristic of the countries of continental Europe. The classic example of such a system is considered German. IN strictly segmented financial systembanks cannot be performed by non-banking functions. An additional feature, although not absolute, is the tougher distinction of the fields of activity and individual operations. Thus, with a segmented system bank operations At the reception of deposits and issuing loans, legislatively separated from operations on the production and placement of securities of industrial companies and a number of other types of services (insurance, trust operations). Typical representatives of segmented systems are US, United Kingdom and Japan.
13. Financial policies, its essence, structure and basic elements
Financial policy is a fundamental element in the Financial Management System. Depending on the management entity, state financial policies and financial policies of enterprises are allocated.
State financial policy - This is part of the state's socio-economic policy to ensure the balanced growth of financial resources in all units of the country's financial system. The main thing purpose of State Financial Policy Must be the creation financial conditions For socio-economic development of society, raising the level and quality of life of the population.
Subjectsfinancial policies are legislative (representative) and executive authorities, which determine and approve the main directions of development of financial relations, develop concrete ways to organize them in the interests of business entities, population and state. Objectsfinancial Policy is a combination of financial relations and financial resources forming the spheres and links of the financial system of the state.
Financial policy contentquite complicated, as it covers a wide range of events:
1) the development of the general concept of financial policy, determining its main directions, goals, main tasks;
2) the creation of an adequate financial mechanism - systems established by the state forms, species and methods for organizing financial relations;
3) management financial activities States and other economic entities.
In the target installations, financial policies are divided into financial strategy and tactics. Financial strategy- a long-term course of financial policy, designed for the future, and implies the solution of large-scale tasks that are determined by the economic and social strategy. In the process of developing a financial strategy, the main directions of development of finance are predicted, the principles of use and organization of finance are planned, the issue of the need to concentrate financial resources in those areas of economic development, which are developed and adopted economic politics. Financial tactic- solving problems at a certain stage of the country's development and ensuring this development through timely changes in the organization of financial resources aimed at solving the tasks of financial policies. Financial tactics are more flexible, as it is determined by mobility economic conditions and social factors. Financial strategy and tactics are interrelated. The strategy creates the conditions for solving tactical tasks, and also identifies the decisive areas of development and results in compliance with the methods and forms of the organization of financial relations and relationships. Financial tactics makes it possible to solve the tasks of the financial strategy at a more compressed time limit. Currently, the financial strategy includes the completion of tax and budget reform, the development of pension reform and social reforms. An example of financial tactics are the decline in the NDC and the ESN, streamlining budget process.
On the modern stage Known three types of financial policies:classical, planned - directive, regulating. The basis of each of them was the corresponding economic theories (Table 5).
TO financial policy elements1) Tax, 2) Budget, 3) Customs, 4) Social, 5) investment policies and 8) policies in international finance.
Table 5.
Types of Financial Policy

In the development of state financial policies in Russia, all branches of state power are involved. At the same time, due to "the peculiarities of the constitutional system, the priority in its development belongs to the President of the Russian Federation, who in the annual messages of the Federal Assembly defines the main directions of financial policies on this year and perspective.
Along with state financial Policy There is I. financial policies of enterprises,presenting the purposeful activities of financial managers to achieve business goals. The objectives of the financial policy of the enterprise can be: (1) the survival of the enterprise in a competitive struggle; (2) avoiding bankruptcy and major financial failures; (c) leadership in combating competitors; (3) maximization market value enterprises; (4) Sustainable growth rates of enterprise economic potential; (5) the growth of production and implementation; (6) profit maximization; (7) minimizing expenses; (8) ensuring profitable activities, etc. The priority of this or that goal of the financial policy of the enterprise is predetermined primarily by the objectives of business.
The role and importance of financial policies is that it fundamentally forms financial science and the practice of financial relations. Financial policies are subject to all in the field of finance and not only. It is subordinate and dissatisfied only in relation to the political course in the field of economics.
14. Financial mechanism, its role in the implementation of financial policies
Practical incarnation The financial policy finds in the financial events of the states that are implemented through the financial mechanism. Financial mechanism - an integral part of the economic mechanism, represented by a set of species and forms of organizing financial relations, conditions and methods of calculation used in the formation of financial resources, education and use of targeted funds. Financial mechanism is used to affect the economy and social sphere, holding a single financial policy of the state, regions, municipalities, business entities.
Influence of financial mechanismthe economy and the social sphere is carried out, on the one hand, through structure of financial mechanismand the focus of the various parts for solving specific tasks and the achievement of the real effect, on the other the magnitude of financial resourcesfood at the disposal of economic entities and states and sent (invested) to meet the needs of society (states, its territorial structures, business entities, citizens).
Structure of financial mechanismit is very difficult in connection with a huge variety of species and forms of organizing financial relations. Highlight three groups reflecting the economic content of finance: Mechanism of state and municipal finances; financial mechanism of the enterprise; Insurance mechanism.
Elements of the financial mechanism:
- Forms of financial resources;
- methods of their formation;
- system of legislation and standards, which are used in determining the income and expenses of the state;
- Budget system organizations, enterprises' finances and securities market.
In addition, the structure of the financial mechanism is distinguished functional links:financial planning and forecasting; financial indicators, standards and limits; financial management; Financial levers and incentives; financial control. Applies the division of the financial mechanism on organizational and managerial blocks:block financial planning and forecasting; operational management; financial control. The functioning of the financial mechanism is due amount of financial resourcesallocated to specific goals, methods for forming financial resources, as well as in which forms and in what channels are moving money, under what conditions they are allocated and used. Financial mechanism, which drives financial resources, affects social production through financial support and financial regulation. At the same time, the higher the level of development of society and its economy, the more significant the role of financial regulation. Financial support is implemented through self-financing, lending and irrevocable financing.