Proposals for improving real estate assessment. Thesis: Real estate assessment. Determination of the market value of real estate as part of an income approach
For the rights of manuscript of Akulov Evgeny Olegovna Improving the methods of analysis of the most efficient use of real estate for the purpose of value estimate 08.00.10 - Finance, money circulation and credit the dissertation author's abstract on competition of a scientific degree of the candidate economic Sciences Moscow 2015 2 The work was carried out at the Department "Evaluation and Management of Property" of the FGOs "Financial University under the Government Russian Federation»Researcher Candidate of Economic Sciences, Professor Ivanova Elena Nikolaevna Official opponents Sterztor Sergey Gennadevich Doctor of Economics, Professor, FGBOU VPO" Russian Academy of National Economy and public service Under the President of the Russian Federation, "Professor of the Department of Real Estate Management and Problems of Land Use Kamnel Dmitry Mikhailovich Doctor of Economics, Associate Professor, FGAOU WITH" National Research Tomsk State University ", Head of the Department of General and Applied Economics of the Faculty of Economics, Leading Organization of FGBOU VPO" Moscow State Construction University " The defense will take place on April 16, 2015 at 12-00 hours at the meeting of the dissertation council D 505.001.02 on the basis of the FGOVPO "Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation" at the address: Leningrad Prospect, d. 49, Aud. 406, Moscow, GSP-3, 125993. The dissertation can be found in the dissertation hall of the library information complex of the FGOBULPO "Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation" at the address: Leningrad Prospect, d. 49, room. 203, Moscow, GSP-3, 125993 and on the official website: http://www.fa.ru. The author's abstract is placed on February 10, 2015. Scientific Secretary of the Dissertation Council D 505.001.02 Candidate of Economic Sciences, Meshkov Associate Professor Elena Ivanovna 3 I. General characteristics of work The relevance of the topic of dissertation research. The modern stage of development of the valuation of property is characterized by a deeper understanding of the theory and methodology for determining it market value, consolidating the fundamental principles in the developed assessment standards, as well as the spread of the latest techniques in practice. The principle of the most efficient use (Further NEI), the practical aspect of which is being implemented using NEI analysis methods, refers to the most controversial and least developed provisions of the theory and practice of property assessment. It implies that the magnitude of the market value of the assessment object is formed by its unique characteristics, subject to the option of optimal use, ensuring the satisfaction of social and production needs, the maximization of the profits of its owner and, as a result, the greatest value of the object itself. The obligation to take into account the principle of NEI in the assessment of the market value of real estate laid in international standards Estimates, enshrined in adopted in September 2014 federal Standard "Real estate assessment (FSO No. 7)", but this does not stop the discussion in the evaluation community regarding its principled need and practical implementation procedures. The absence of a single conceptual apparatus, a transparent and systemic methodological instrumental, developed information infrastructure complicates the identification of an object NEA option for the purposes of assessing its market value. Thus, the obligation to implement the NEI principle in assessing the market value of real estate forms an urgent need to improve the methods of its analysis, concretization of existing methods and calculation algorithms adapted to the specifics russian market real estate. The degree of scientific development of the problem. The principle of NEI as one of the fundamental principles of value assessment is considered mainly in the labor assessment of foreign authors: Kinnarda V., Ordueya N., Reilie D., Ring A., Friedman D., Harrison G.S., Ecker . et al., and Russian authors: Alexandrova V.T., Artytemova I.L., Asaul A.N., Grabovaya P.G., Gribovsky S.V., Gryaznova A.G., Ivanova E.N., Korosteleva S.P., Kulakova, Yu.N., Level Lefera L.A., 4 Ozerov E.S., Petrova V.I., Sberry G.M., Siberiana S.G., Tarasewich E.I., Tepman L.N., Fedotova M.A., Fomenko A.N., Yaskevich E.E. et al. Highly appreciates the contribution of scientists to the development of approaches and methods of value assessment of real estate, it should be noted that the lighting of NEIs in their works is common, does not contain clear integrated methods of its practical implementation. The applied aspect of the principle of NEI, implemented by analyzing alternative use options, in the works of domestic and foreign authors is mainly reduced to the description of a short algorithm, does not contain justifying the feasibility and field of its application, as well as restrictions caused by Russian conditions of valuation. In the last decade, interest in the practical implementation of the NEI principle has increased in the Russian scientific literature. Conceptual issues of analysis in the context of the Russian real estate market are highlighted in the works of Grigoriev V.V., Ozerov E.S., Smolyak S.A., Fomenko A.N.; Applied aspects of solving the problems of analysis in the conditions of the closedness of the market, the undeveloped information infrastructure, the high degree of uncertainty are considered by Alexandrov V.T., Korostelev S.P., Munermann I.V., Ozerov E.S., Pupenzova S.V., Yaskevichi E .. They developed recommendations for improving certain stages of NEI analysis, aimed at improving the quality of assessment services. In the dissertation works of GRANNS S.V. and Gubareva E.V. The issues of NEA analysis in the context of the problems of general economic management and the efficiency of resource use are studied. Practical significance represents the work of Petrova M.N. in which quantitative and qualitative methods of NEI analysis are investigated. However, the proposed economic and mathematical models have a number of restrictions, require adaptation to the modern realities of the real estate market and evaluation activities in Russia, as well as installations in a complex algorithm. Thus, the existing interpretations of the NEI principle require comprehension and clarification in accordance with the main trends in the improvement of standards and methods of valuable real estate assessment, modern level The development of which dictates the need to develop a comprehensive analysis algorithm using the actual assessment of methods. The purpose and objectives of the study. The purpose of the study is to improve the methodological instrumental analysis of NEI analysis, ensuring an increase in 5 correctness of the valuation valuation. To achieve the goal of the study, the following tasks were delivered: clarify the content of the concept of the principle of the most efficient use and procedure for its practical implementation, argued the need for its mandatory implementation in the value assessment of real estate; consider the existing classification of real estate objects and analyze the possibility of introducing a new feature that grinds objects as necessary and the degree of NEI analysis detail; to analyze the specific features of the real estate market of Russia to identify its most acute problems in order to improve the algorithm for analyzing NEIs and methods of its practical implementation; Develop guidelines, taking into account the specifics of the Russian real estate market, on the practical assessment of basic analysis criteria: legal admissibility, physical feasibility and financial feasibility; Explore NEI analysis methods, develop recommendations and assess the effectiveness of their practical application in Russian assessment practice. The object of the study is the principle of NEI as an immanent component of the valuation of real estate. The subject of the study is a methodological toolkit of the practical implementation of the NEI principle in assessing the market value of real estate. Field of study. The study was carried out in accordance with clause 5.1 "Theory, Methodology and Conceptual Fundamentals of the Cost of various Property Objects" Passports of the specialty 08.00.10 - Finance, money circulation and credit (Economic Sciences). The theoretical and methodological basis of the study are key provisions of economic theory and system analysis, as well as the conclusions contained in the works of domestic and foreign authors on the theory of value assessment and investment analysis, in particular, according to value estimation real Estate, business, efficiency assessment investment projects, pricing in construction. The fundamentality of the test principle led to the need for 6 application in the work of general scientific theoretical methods of knowledge (historical, analytical, synthetic, methods of deduction and systemic analysis, etc.), as well as modern methods of economic and mathematical analysis: expert assessments, analysis of hierarchies, methods of scenarios, financial Simulation, grouping, tabular presentation of data, etc. Information base of the study was the analytical reviews of real estate markets, scientific reports of conferences and seminars on the subject of the under study, analytical materials of periodicals, and reference and analytical resources of the Internet, legislative and regulatory acts of the Russian Federation, Reports on the assessment of the market value of real estate objects, own research and calculations of the author. The scientific novelty of the study is to improve the theoretical tools for analyzing real estate NEI for valuation purposes. The provisions of the scientific novelty of the dissertation work endowed with the defense are as follows: 1. To prove the need to take into account the principle of NEI in value assessment, as well as determining the content of the analysis, the established views on its role and essence are investigated and justified that it is a key principle of assessment The market value of real estate, which is reflected in the proposed wording. The principle of NEI is the basic position of the theory of assessing the real estate market value, the value of which should be determined on the assumption of its NEI - using a competitive, demanded market and justified to the evaluation date that meets the criteria for legal admissibility, physical feasibility, financial feasibility and maximum realizing value potential for free or Built-up land plot . NEI analysis is a value assessment procedure that ensures the practical implementation of the NEI principle and consisting in a study of the effectiveness of the use of an object that has developed on the evaluation date, and its comparison with alternative development options in order to identify the method of use that maximizing the value of the land plot. 2. The need for the introduction of a new classification feature of real estate objects "The need and degree of standard analysis of NEI" based on the identified key characteristics of real estate: origin, 7 suitability of improvement in operation, divisibility, physical condition of improvements, functional purpose. 3. The need to upgrade and expand the NEA analysis algorithm in the value assessment of real estate, consisting in changing the sequence of analysis, according to which the stages of studying the economic potential of the location and the criterion of legal admissibility should be preceded by the stage of market research and in the introduction of additional stages: classification of the estimated object by degree of detail analysis of NEI; Qualitative analysis of alternative use options. 4. The need for a qualitative comparison of alternative options for using an assessment facility, implemented by the proposed algorithm using a hierarchy analysis method (hereinafter referred to as MAI), based on the use of criteria: a) fullness of the use of the advantages of the location; b) legal reasonable development; c) physical feasibility; d) the potential for the development of the real estate market; e) the effectiveness of attracting financial resources - which allows you to identify the least popular options for the use of real estate and exclude them from the subsequent study. 5. Based on the systematization of existing methods for analyzing NEIs, identifying their advantages and disadvantages, it is reasonable that the method of analyzing the land plot is both conditionally free and with existing improvements, which involves direct capitalization of the income generated by a single object of real estate, followed by subtraction of the cost of creating improvements (or costs To their reconstruction) and bringing the value to the value to the date of assessment, ensures maximum correctness of the results in modern conditions of Russian appraisal activities. 6. As a result of the study of the Russian real estate market, the need to take into account the interim use of facilities in the analysis of NEI, for which the concept of "intermediate type of real estate use" is specified, and the method of its analysis is also developed and tested. The theoretical value of the research results is to develop a deployed algorithm for analyzing the real estate NEI analysis, which allows to implement the fundamental principle of the theory of value assessment in practice, therefore, the elements of scientific novelty are submitted by 8 on protection, it is possible to interpret how its further development in the improvement of the methodological tool for determining the market value of real estate. The main results of the study can be used in the formation of training courses related to real estate assessment. The practical significance of the thesis is that the elements of the scientific novelty obtained by the author are focused on widespread use in the practice of valuable real estate, contribute to improving the quality of assessment and growth services investment attractiveness estimated objects. Independent practical significance: the system of characteristics of real estate objects, which provides them with a grouping according to the proposed classification sign "The need and degree of detail of NEI analysis"; developed methodology for analyzing the physical feasibility criterion based on the systematization of legal documentation and classification of real estate objects, to relievant determining the potentially possible parameters of the construction of the land plot and forecasting the volume-planning characteristics of various options for its use; proposed algorithm for the qualitative comparison of alternative use options using MAI, which makes it possible to exclude inefficient options from the subsequent analysis of the criteria for financial feasibility and maximum efficiency; Developed NEA Analysis Methodology Taking into account the intermediate use option, ensuring the change in the change town planning plans On the development of territories and promising plans for developers with short-term preservation of the current use of real estate. Approbation and implementation of the results of work: the main results of the dissertation study were reported, discussed and received approval at scientific and practical conferences and round table: the annual international scientific and practical conference "Prospects for the development of national economies of the EEA member countries in international integration processes" (Karaganda , Karaganda Economic University Kazdotallia, April 12-13, 2012); Fifth International Scientific Methodological Conference "Cost of Property: Assessment and Management" (Moscow, Moscow Furniture Mural University "Synergy", November 22, 2013); Round table "Property Management: Global Practice and Russian Realies" (Moscow, Congress "Mergers and Acquisitions", Financial University, September 19, 2014). The dissertation was made in the framework of research work carried out in the financial university within the framework of the state task in 2013 on the topic "Increase financial Sustainability russian enterprises based on their cost management. " The results of scientific research are used in the practical activity of the Department of Evaluation of the Complex CJSC Algorithm "Knight Analysis Frank" by applying NEI. Application of the author's developed methodology for the definition of volume-planning decisions of improvements, the method of analysis of the hierarchy, analysis methodology, taking into account intermediate use, comply with the requirements of the evaluation standards, ensure high level Work, objectivity and correctness of the results of the assessment in the context of a limited information space, contribute to the efficiency and competitiveness of the department thanks to a more structured approach to real estate assessment and optimization of the costs of the company. The author's algorithm modernized by the algorithm of NEI analysis, which complements the assessment of the market value of real estate by a methodically substantiated tools, is used in the practical activity of the Russian Estimation Service LLC. In particular, the use of a determined author as the most appropriate method of analyzing the financial feasibility, which also intends to implement risks analysis, allows you to more deeply explore the NEI, contributing to the improvement of the methodological foundations of the work and improving the quality of the services provided. The results of the study are used in educational process In the FGOBULPO "Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation" Department "Evaluation and Management of Property" in teaching academic disciplines "Real estate value assessment" and "real estate market and trends of its development". The introduction of the dissertation research results of organizations is confirmed by relevant references. In the specified 10 publications. On the topic of the dissertation study published 6 works with a total volume of 4.43 pp. (Author's volume of 3.92 pp), including 4 works with a total of 3.55 pp. (Author's volume of 3.2 pp) in peer-reviewed scientific publications identified by the Ministry of Education and Science of Russia. Structure and scope of the dissertation. The thesis consists of an introduction, three chapters, conclusion, a list of references from 119 sources, 3 applications. The text of the thesis is set forth on 204 pages. The work is illustrated by 19 tables and 7 drawings. II. The main content of the thesis in the introduction of work is the relevance of the topic of the dissertation study, presents the degree of its scientific desire and the methodology of work: the purpose and objectives of the study are determined, the elements of the scientific novelty of work and its practical significance are reflected. The first group of issues is related to the study of the historical development of the NEI concept, determining the content of the concept of NEI, the role and place of the principle in the modern system of valuation of real estate objects. The valuation of property objects is based on the fundamental prerequisites for the neoclassical theory that dominates in modern economic thought. The basis of this theory is the concept of a rational consumer, whose behavior is driven by the goal of maximizing utility, predetermined the formation of key principles for assessing market value. The principles of value assessment are combined into four groups depending on the source of the formation and degree of influence on the cost: principles based on the submission of the owner of the object's utility; Principles based on the operational characteristics of the estimated object; Principles due to the influence of the market environment; The principle of NEI. The essence of the NEI principle is that the market value of real estate is formed on the basis of the unique characteristics of the object, which determine the option of its optimal use under the influence of the demand forces and suggestions that have developed at the date of the assessment when all market participants are interested in maximizing their own benefits. The principle of NEI is maximally implemented in estimating 11 real estate, which is due to its "two-component": the constant component is a land plot with a constant reference to a certain place and stability of properties, and the component variable is the improvement. The location and properties of the site predetermine the option of its use that meets the current market needs. The income of the site is provided by the introduced improvements that can be changed in accordance with the in-demand market functions. Therefore, the assessment of the market value of real estate is based on the embodiment of the land plot, the maximum realizing cost potential. The analysis of foreign and Russian scientific literature on the topic of dissertation research, as well as evaluation standards, showed that they contain a large number of different interpretations of the concept of NEI real estate objects that meets four key criteria: legal admissibility, physical feasibility, financial feasibility and maximum efficiency. Unsatisfactory urban planning, changing the conjuncture of the Russian market requires clarification of the concept of NEI from the standpoint of compliance with the market conditions that established on the evaluation date, and the current trends in the development of valuation require an emphasis on its theoretical value. To this end, the author's interpretation of the "NEI principle", which is shown on page 6. The practical implementation of the NEI principle is to analyze the effectiveness of the use of the real estate that has developed at the evaluation date (hereinafter referred to as NEI analysis). According to existing regulatory documents In the field of valuation activities in the Russian Federation this procedure Must be allocated to an independent and mandatory stage, preceding the calculation of the market value of real estate by methods of income, comparative and cost approaches. This requires the introduction of a refined definition of NEA analysis, also presented on page 6. Based on the study and comparison of international (hereinafter MSO), European and American standards with Russian evaluation standards, there was a significant difference in approaches to NEI analysis. In the current edition of MSO, in contrast to their previous editions, it is not written that the market value of the object should be determined on the basis of the identified version of NEI, but it is indicated that it reflects it, since the current practice of zoning 12 suggests effective use Any territory. In this regard, the NEI object of the assessment will be taken into account when analyzing prices of purchase and sale transactions and lease on facilities - analogues in assessing its market value by methods of comparative and profitable approaches. The Russian unstable real estate market and the peculiarities of legislative regulation of urban planning and zoning standards do not guarantee that the exemplary embodiment of the assessment facility is effective, and the prices of analog facilities reflect its NEI. Therefore B. russian standards Currently, it is advisable to allocate NEA analysis to an independent procedure. The complexity of the analysis of real estate NEI, due to the degree of development of its market, differing in limited information infrastructure and poor development of urban planning, requires the introduction of an additional classification feature of real estate objects that takes into account the need for NEI analysis when determining their market value. The proposed system of key characteristics of real estate: origin; suitability of improvement in operation; divisibility; physical condition of improvements; The type of real estate object built in the hierarchical sequence allows you to determine the need for NEI analysis and attribute an object in accordance with a new classification sign - "the need and degree of detail of NEI analysis" to a specific group. The schematic interpretation of the developed system of characteristics for the classification of real estate objects in order to determine the need for NEI analysis and the degree of detail is presented in Figure 1. Thus, the specifics of the Russian real estate market causes the need for the practical implementation of the NEI principle for most objects consisting in the analysis procedure, and The state of the market predetermines the need to improve the methods and directions of this analysis. The second group of issues follows from the need to critical study of the toolkit of the practical implementation of the principle of improving the existing methods of its analysis. NEI Real Estate and 13 The Origin of Existing Improvements Free Upgrades, not suitable for use (wear\u003e 80%) improvements suitable for operation (wear< 80%) Неделимый единый комплекс (здания с участками) Анализ НЭИ для свободного ЗУ Анализ НЭИ для свободного ЗУ и ЗУ с существующими улучшениями Составная часть неделимой вещи (помещения, квартиры) Здания, пригодные к эксплуатации (износ от 20% до 40%) Незавершенное строительство Здания, требующие реконструкции или overhaul (wear from 40 to 80%) New construction or reconstruction (wear<20%) Анализ НЭИ для ЗУ с существующими улучшениями Жилые, коммерческие Обществен ные Анализ НЭИ не проводится Источник: разработка автора Рисунок 1 – Классификация объектов по потребности в проведении анализа НЭИ Изучение существующих подходов к анализу НЭИ недвижимого имущества позволило выявить наличие общепринятого алгоритма его практической реализации. Анализ НЭИ принято проводить в двух направлениях: для земельного участка как условно свободного и с существующими улучшениями. Поскольку функциональное использование любого объекта недвижимости опирается в первую очередь на характеристики местоположения, юридические и физические ограничения использования земельного участка, и направлено на раскрытие его стоимостного потенциала, далее описана процедура анализа для земельного участка как условно свободного. Исследование практики реализации принципа НЭИ недвижимости позволило сформулировать основные пробелы существующего алгоритма: изучение местоположения объекта представляет собой самостоятельный этап, не имеющий отношения к анализу НЭИ; не проводится качественный анализ различных вариантов использования; предлагаемая последовательность этапов анализа НЭИ неэффективна и трудоемка; отсутствуют детализированные рекомендации по отдельным аналитическим процедурам, что осложняет практическую реализацию принципа НЭИ. Для устранения выявленных недостатков автором обоснована необходимость модернизации существующего алгоритма анализа НЭИ, которая включает следующие положения. 14 1. Анализ НЭИ следует начинать с исследования характеристик оцениваемого объекта, позволяющих отнести его к определенной группе в соответствии с предложенным новым классификационным признаком «необходимость и степень детальности анализа НЭИ» в соответствии с рисунком 1. 2. Предлагается в первую очередь включать в процедуру анализа НЭИ этап исследования местоположения объекта с позиции изучения конкурентной среды и выявления основных преимуществ и недостатков его расположения, влияющих на выбор вариантов его потенциального использования. 3. В целях сокращения трудоемкости оценочных работ целесообразно сначала рассмотреть критерий юридической допустимости, и только законодательно разрешенные варианты позиционировать на территориальном рынке недвижимости на предмет их востребованности. 4. Целесообразно ввести этап качественного анализа вариантов с применением метода анализа иерархий, и только по наиболее приемлемым вариантам осуществлять количественные расчеты финансовой целесообразности. Схематичное изображение детализированного алгоритма анализа НЭИ с учетом предложенных преобразований представлено на рисунке 2. Исследование объекта по классификационному признаку «необходимость и степень детальности анализа НЭИ» Формирование полного перечня альтернативных вариантов использования объекта оценки Анализ местоположе ния объекта Анализ юридической допустимости с целью выявления законодательно разрешенных видов использования Анализ рынка и существующих классификаций исследуемых сегментов рынка Составление перечня возможных вариантов использования Анализ осуществимости Анализ физической осуществимости с целью выявления потенциально возможных параметров застройки территории по каждому варианту использования Качественный анализ возможных вариантов использования Количественный анализ возможных вариантов использования по критерию финансовой целесообразности Выбор варианта использования, максимизирующего стоимость объекта оценки Источник: разработка автора Рисунок 2 – Детализированный алгоритм анализа НЭИ недвижимости 15 Исследование юридической допустимости предполагает изучение объекта оценки с целью выявления законодательно разрешенных вариантов использования. Поскольку юридическая верификация заключается в определении соответствия текущего и альтернативных вариантов использования существующим градостроительным нормам, в которых также указывается информация о разрешенных параметрах застройки территории, обоснована логическая взаимосвязь данного этапа анализа с исследованием физической осуществимости. На основании проведенной систематизации существующих нормативно-правовых актов, норм и правил, а также документов на участок, была разработана структурированная схема, содержащая перечень документации с указанием содержащейся в ней информации, необходимой для анализа НЭИ. На основании данной схемы определяются основные сегменты рынка недвижимости, на которых можно специализироваться с учетом законодательной разрешенности, и для которых необходимо изучение классификационных требований. Анализ физической осуществимости опирается на разрешенные параметры застройки территории, полученные на этапе исследования юридической допустимости, и классификационные требования. Существующие рекомендации предполагают ограничение данного этапа анализа исследованием физических характеристик участка, его формы и рельефа, а также возможности размещения на нем новых строений, однако они не учитывают основную цель этапа: определить потенциально возможные параметры застройки участка с учетом ограничений по плотности, высотности, объемам строительства. В литературе по оценке недвижимости существуют краткие рекомендации по определению объемно-планировочных параметров застройки земли в ходе анализа НЭИ недвижимости. К недостаткам данных рекомендаций можно отнести индифферентность к наличию различных исходных данных для выбора способа расчета объемно-планировочных характеристик и отсутствие рекомендаций по учету классификаций объектов недвижимости, содержащих требования к отдельным техническим характеристикам строений. Для устранения указанных недостатков разработана авторская методика определения объемно-планировочных решений строений, схематично представленная на рисунке 3, дополненная вариантами расчетов параметров застройки на основании коэффициента плотности застройки (через общую площадь здания) и на основании данных по этажности и высоте этажа, получаемых в результате анализа рынка и исследования классификаций необходимого сегмента 16 рынка. Предложенный алгоритм может выполняться по одному из трех сценариев в зависимости от наличия доступной исходной информации: коэффициента застройки; коэффициента плотности застройки; информации об этажности и высоте этажа. Результатом данного этапа является формулирование альтернативных вариантов использования объекта оценки с указанием их ключевых физических характеристик. Определение исходного показателя Исходя из нормативноправовых актов, классификаций объектов недвижимости Коэффициент застройки Коэффициент плотности застройки S КЗ З S ЗУ Допустимая площадь застройки S З К З * S ЗУ 1 Допустимая высотность здания К ПЗ SЗ S ЗУ По площади участка, его форме и близости строений ориентировочно определяется SЗ с учетом нормативов по плотности застройки, указанных в СП 42.13330.2011, Приложение Г ввнеш S общ n эт анализ формы участка отступы от границ участка, строений парковка, пожарные проезды корректировка по «строительному модулю» h зд – высотные регламенты, ГПЗУ, внеш S общ hзд hэт * nэт документы, классификации Классификации объектов недвижимости по сегментам Обзоры рынка Отношение допустимой высоты здания к количеству этажей Минимальная высота 1 этажа Целесообразная этажность здания n эт Допустимая общая площадь здания по внешнему обмеру h зд hэт внеш S общ S З * nэт Допустимая общая площадь здания по внутреннему обмеру nэт внеш S общ SЗ внеш S общ К ПЗ * S ЗУ внутр внеш Sобщ Sобщ Толщина наружных стен При наличии данных об этажности или условий 1 и 2 3 2 Для расчета арендопригод ной площади внутр внеш S общ S общ * 0,95 Строительный объем здания (Vстр) внеш Vстр S общ * hзд Источник: разработка автора Рисунок 3 – Схема определения объемно-планировочных характеристик строений Отобранные варианты использования подлежат проверке по критерию финансовой целесообразности, заключающейся в изучении стоимостного потенциала 17 объекта недвижимости и способности генерирования им положительного денежного потока. Для повышения эффективности данного этапа целесообразно предварительно сопоставить данные варианты использования по качественным характеристикам. Выбор варианта НЭИ недвижимости представляет собой процесс принятия решения по совокупности большого числа параметров, поэтому автором рассмотрена возможность применения метода анализа иерархий (далее МАИ). Применение МАИ основывается на качественной интерпретации анализируемых параметров, оцененных на основе экспертных суждений и логики, с учетом их влияния на итоговый результат. Многокритериальный анализ на базе МАИ позволяет представить сложный процесс принятия решения в качестве структурированной иерархической системы и учесть взаимное влияние факторов на каждый из рассматриваемых вариантов использования и сопоставить их на основании отобранных критериев. Исследовательская задача, заключающаяся в определении данных критериев анализа НЭИ недвижимости, формирующих первый и второй уровни иерархии, была решена путем опроса экспертного мнения специалистов-оценщиков в отношении значимости и взаимного влияния отобранных критериев. Результаты анализа представлены в таблице 1. Таблица 1 – Веса критериев анализа НЭИ Критерий 1 порядка Использование потенциала местоположения Юридическая обоснованность Физическая осуществимость Потенциал рынка развития Эффективность привлечения финансовых ресурсов Итог Вес, % 24,8 34,9 26,5 8,4 Критерий 2 порядка Полнота использования преимуществ с точки зрения транспортной доступности Полнота использования преимуществ с точки зрения пассажиропотока Конкуренция в ближайшем окружении Соответствие назначению по градостроительному плану земельного участка Соответствие назначению по кадастровому паспорту или свидетельству Соответствие функции назначению по правилам землепользования и застройки территории Наличие данных о возможности изменения назначения Соответствие функции назначению по генеральному плану поселения Эффективность по критерию плотности застройки Эффективность по критерию максимальной высотности Арендопригодная площадь Наличие свободных ниш рынка Потенциал развития сегмента рынка Средний уровень доходности сегмента Возможность привлечения заемных средств 5,4 Эффективность привлечения заемных средств 100 Вес, % Итого вес, % 33,3 8,3 33,3 8,3 33,3 8,3 44,0 15,4 28,3 9,9 17,1 6,0 7,3 2,6 3,4 1,2 42,9 42,9 14,3 63,7 25,8 10,5 75,0 11,3 11,3 3,8 5,3 2,2 0,9 4,1 25,0 1,4 100 Источник: исследование автора 18 После построения иерархической структуры процесса принятия решения о выборе варианта НЭИ анализ проводится в рамках стандартных процедур МАИ. Альтернативы использования объекта оценки, которые получают наименьшие веса качества, исключаются из последующего анализа. После применения МАИ отобранные варианты использования недвижимости подлежат количественной оценке по критерию финансовой целесообразности с точки зрения способности генерировать положительный денежный поток и раскрывать стоимостной потенциал земельного участка. Количественная оценка отобранных вариантов использования по критериям финансовой целесообразности и максимальной эффективности представляет собой наиболее сложный и трудоемкий этап анализ, опирающийся на классические методы стоимостной оценки, представленные в таблице 2. Таблица 2 – Существующие методы практической реализации принципа НЭИ № п/п Метод анализа НЭИ/Соответствующий метод оценки ЗУ Расчетная формула Трудноопределяемые параметры Вывод о применимости Rb, Rl Область применения ограничена возможностями определения коэффициентов капитализации отдельно для здания и для земельного участка. Не выявлены Применим при наличии информации о стоимости улучшений и сопоставимости анализируемых вариантов по техническим параметрам застройки, срокам реализации и начала операционной деятельности. Анализ ЗУ как условно свободного I O VB * RB RL VL где: V L – рыночная 1 «Земельный участок рассматривается как незастроенный, коэффициенты капитализации для земли и строений различны» / Метод остатка для земли, модификация 1 стоимость земли, ден. ед.; I O – чистый операционный доход, приносимый единым объектом недвижимости, ден. ед.; V B – рыночная стоимость улучшений, ден. ед.; RB – коэффициент капитализации для улучшений; RL – коэффициент капитализации для земли. 2 «Земельный участок рассматривается как незастроенный, коэффициенты капитализации для зданий и земли одинаковы» / Метод остатка для земли, модификация 2 VL где: IO VB , RO Ro – общий коэффициент капитализации. 19 Продолжение таблицы 2 № п/п Метод анализа НЭИ/Соответствующий метод оценки ЗУ Расчетная формула Труднооп ределяе мые параметр ы VL VO VB 3 «Земельный участок рассматривается как незастроенный, и известна рыночная цена продажи недвижимости предполагаемого назначения»/ Метод выделения VB E B * Pr где: VО – рыночная стоимость единого объекта недвижимости, ден. ед.; E B – стоимость Vо воспроизводства улучшений за вычетом физического износа, ден. ед.; Pr – прибыль девелопера. Вывод о применимости Область применения ограничена наличием рыночных данных по сопоставимым со всеми анализируемыми вариантами объектам-аналогам; наличием информации об износе и стоимости улучшений по объектам-аналогам. E1 E2 ... (1 Y) 1 (1 Y) 2 En I1 I2 (1 Y) n (1 Y)1 (1 Y) 2 VL .... In (1 Y) n VOn 1 (1 Y) n где: E1 , E2 , En – сумма 4 Метод предполагаемого использования*/ Метод предполагаемого использования капитальных затрат в n-й период времени, ден. ед.; I1 , I 2 , I n – величина чистого операционного расхода в nй период времени, ден. ед.; E, Y, n Y – ставка дисконтирования, дол. ед.; Применим при условии возможности достоверного определения затрат на создание улучшений, сроков строительства, загрузки объекта, прогноза доходов. VOn1 – стоимость реверсии единого объекта недвижимости в постпрогнозном периоде времени, ден. ед. Анализ ЗУ с существующими улучшениями VO 5 6 «Земельный участок рассматривается как застроенный, строения требуют проведения некоторых улучшений»/Нет где: Применим при наличии возможности достоверного определения затрат на изменение существующих улучшений. IO E Im p RO E Im p - расходы, связанные с проведением работ по реконструкции/модернизаци и/капитальному ремонту, ден. ед. E «Земельный участок Применим при условии рассматривается как анализа земельного участка с Не IO VO застроенный, не требующий не выявле- улучшениями, RO улучшений»/Метод прямой требующими затрат. ны капитализации дохода * Одинаковые условия реализации как для свободного участка, так и для участка с улучшениями
Fedell Education Agency
GOU VPO "Moscow State University of Service"
Faculty: "Institute of Regional Economics and Municipal Administration"
Department: "State and Municipal Management"
Course project.
Topic: Improving real estate assessment methods.
Discipline: management of municipal real estate.
Performed student
PDS Groups 3-2.
Shevchuk M. V.
Accepted teacher
Dubovik M.V.
Introduction .............................................................................. .3.
I Theoretical Part
1.1 Classification of real estate objects .....................................5
1.2 Methods for evaluating residential real estate objects .....................................6
1.3 housing market ..................................................................... 9
1.4 Securities Market for Real Estate ...................................13
1.5 Mortgage ........................................................................ ..15
II analytical part
2.1 Modern principles for analyzing the real estate market ............... 18
2.2 Real estate market research .................................... .... 20
2.3 Methods for estimating the market value of real estate ............... ... 26
2.4 Features of various types of assessment ................................. ... 34
2.5 Effect of environmental factors for the cost ............... ... 36
III Practical part
3.1 Practical application of the method of comparative sales ......... ..39
3.2 Risks of investment and statistics of real estate markets ............... 44
Conclusion ........................................................................ ... 47
List of references ................................................................50
Introduction
The term "real estate" appeared in Russian legislation from the times of Peter I. However, the current legislative acts have not yet been a clear distinction between driven and real estate.
Real estate (real estate, real estate) include land plots, sections of subsoil, isolated water bodies and all that is firmly associated with land, that is, objects, the movement of which without disproportionate damage is impossible, including forests, perennial plantings, buildings , facilities. Real-statements are also subject to state registration of air and sea vessels, internal navigation vessels, space objects. The law to real estate can be attributed to other property. For example, the enterprise as a whole as the property complex is also recognized by real estate.
In accordance with part of the First Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the enterprise is considered not as a subject, but directly as an object of civil rights.
The company as a whole or part of it may be the object of purchase and sale, collateral, lease and other transactions related to establishing, change and termination of real rights. The company may also be inherited.
The company as a property complex includes all types of property intended for its activities, including land, buildings, structures, equipment, equipment, raw materials, products, rights, demand, debts, and the rights to designations, individualizing enterprise, its products, work and services (corporate name, trademarks, service signs), and other exceptional rights, unless otherwise provided by law or contract.
The state body carrying out the state registration of real estate is obliged to provide information on the registration and registered rights of real estate objects to any person. This rule will certainly significantly reduce the risk of improper making transactions with real estate objects for civil turnover participants.
Various forms of ownership: private, property of joint-stock enterprises, local, municipal and finally federal. Determine the effectiveness of one or another form is very difficult - it all depends on the specific situations.
In general, the residential premises market are much more developed than other segments. And this is understandable. There is already a certain legislative base, regulating the privatization processes of housing, obtaining land for the construction of cottages, etc.
The non-residential premises market is mainly once bought or reconstructed premises refurbished under offices. But during privatization, there are more and more objects that are surrendered to the long-term rental or sold from the auctions of the property funds, i.e. local governments. At the second stage of privatization, the real estate market will be replenished with industrial facilities and to an even greater extent of trade and service objects.
After the introduction of the right of private ownership of real estate and privatization in the Russian Federation, the state ceased to be the only owner of the overwhelming number of real estate objects, which served as the beginning of the real estate market.
I Theoretical Part
1.1 Classification of real estate objects.
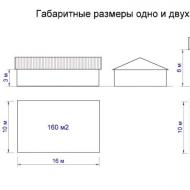
Real estate assessment is of interest, first of all, for categories of objects that are actively accessing the market as an independent product. Currently in Russia it is:
· Apartments and rooms
· Rooms and buildings for offices and shops
· Suburban residential buildings with land plots (cottages and cottages)
· Free land plots designed to build or for other purposes (in the near future)
· Warehouse and production facilities.
In addition, real estate objects, as a rule, are part of the property complex of enterprises and organizations (in particular, privatized) and significantly affects their cost. There are other categories of real estate, the market of which has not yet been formed.
The assessment of the object is influenced by a variety of conditions and their combinations. Give an example of signs of classification.
1. Origin
· Natural (natural) objects.
· Artificial objects (buildings).
2. Purpose
· Free land plots (for building or other goals)
· Natural complexes (deposits) for their operation.
· The buildings
For housing.
For office.
For trading and sphere of paid services.
For industry.
· Others.
3. Scale
· Land arrays.
· Separate land.
· Complexes of buildings and structures.
· Apartment house apartment.
· Apartment house apartment (mansion, cottage)
· Section (entrance).
· Floor in the section.
· Flat.
· Room.
· Summer cottage.
· Complex of administrative buildings.
· Building.
· Room or parts of buildings (sections, floors).
4. Readiness to use
· Ready objects.
· Require reconstruction or overhaul.
· Require completion of construction.
1.2 Methods for assessing residential real estate objects.
Practical experience points out: For a small residential property, it is advisable to conduct estimates on a simplified procedure, which can only be based on the method of comparing market sales. The cost estimate approach from the point of view of sales comparison is based on direct comparison of the estimated object with other real estate objects that were sold or included in the sales registry. Buyers often find out their price conclusions mainly at real estate facilities offered for sale. Appraisers also use this information on a number with information about sold or leased objects. This approach is based on the principle of substitution, which reads: if there are several goods or services of similar suitability, that of them, which has the lowest price, uses the greatest demand and has the widespread distribution. With regard to housing it means: if it can be seen in the market (which is usually happening), then its cost is usually set at the cost of the cost of purchasing housing equal degree of attractiveness, which will not need a lot of time to replace.
The mass assessment of real estate is a special approach to simplified assessment of a large group of homogeneous objects (apartments). This assessment is made according to a specific method: for the estimated object, the corresponding set of values \u200b\u200bof a fixed set of its parameters is determined, and then the value of its evaluation is formed by the rule of all objects.
Mass evaluation has its own special applications. An example of such an assessment is the assessment of the apartment "on a certificate of technical inventory bureaus (BTI) based on the cost approach. It is performed by the state body and is used to determine taxes and fees. However, the assessment of the BTI is not focused on the market value. Therefore, it does not require market information for its construction.
It should be emphasized the difference between the concepts of the actual selling price and market value. Prices are divided into the price of the seller, the price of the buyer and the price of the implementation.
The price of the seller is the amount he is getting as a result of the transaction. The price of the buyer is the total amount of all the cost of buying an apartment. The price of implementation is the amount of money that the buyer gives the seller for the apartment.
They differ on the amount of payment for intermediaries and expenditures on the design of the transaction. The mediator may be, or maybe absent from the buyer of the apartment and the seller. The transaction can insure or not insure. The cost of making a transaction can be divided between its participants in different ways. Therefore, the sale price characterizes the apartment as such, and the prices of the buyer and the seller are strongly dependent on the terms of the transaction. As a rule, if the seller has an intermediary, his payment is deducted from the sale price and reduces the price of the seller, and vice versa payments by the buyer's services of their intermediary increases the price of the buyer in relation to the sale price. Similarly, this prices affect the payment of the transaction. Thus, the price of the seller and the buyer can differ significantly (up to 15% or more). But the price of implementation minimally depends on their specific features of the mechanism for the sale and design of the transaction and is determined by the specifics of the apartment itself. Therefore, it is advisable to simulate precisely the dependence of the pricing price from many apartments.
In accordance with its definition, the market value of the real estate object depends on those factors that determine the average or more probable price of its sale on the market under normal transaction conditions.
At the first level of classification, they can be divided into objective and subjective factors.
When determining the market value, objective factors are considered. As for subjective factors, they are associated with the behavior of a particular buyer, a seller or an intermediary at the conclusion of a transaction, in part of the undefined directly economic conditions (temperament, awareness, honesty, patience, credulity, personal sympathies and antipathy, etc.).
Objective factors are mainly economic defining, ultimately, the average price level of specific transactions.
Economic factors can be divided into macroeconomic and microeconomic. The first is the factors associated with the general conjunction of the market: the initial level of security in real estate objects in the region; the volume and structure of new construction and reconstruction; migration factors; legal and economic conditions of transactions; level and dynamics of inflation; The dollar exchange rate and its dynamics. In our conditions, the following long-term factors may also be indicated as part of a group of economic factors:
· Differences in the dynamics of prices for goods and services, as well as the wage conditions affecting the scale of cash accumulation and the amount of deferred demand;
· The pace and scope of the formation of a new social layer with the possibilities of investing in real estate;
· Development of the mortgage system;
· Development of a system of foreign missions in the region.
Microeconomic factors characterize the objective parameters of specific transactions. These are especially important those that describe the object of the transaction (apartment). The factors associated with the nature of the transaction and terms of payments are essential. The basic procedures for designing transactions and their payment are worked out. Therefore, with a mass assessment of the market value of apartments, it is possible to focus on a typical (medium) nature of the transaction, consider this factor to constant and not take into account it when evaluating the market value of apartments. Then the market value (averaged price) of the apartment is estimated at the fixed date, it is caused by its parameters (characteristics) as a consumer value.
1.3 housing market.
The potential scale of this market is huge. At least 90 percent of housing in any way, as is customary to speak, a civilized country is bought today in installments.
Especially wide scale, the housing market in Russia acquired as a result of the privatization of apartments. Free, as in Moscow, or preferential, as in other cities, the transfer of apartments in private property created new opportunities for owners for operations with this type of real estate.
At the same time, the forms of purchase and sale of apartments and other types of housing have been developed. Among these forms, the acquisition of apartments in installments is becoming increasingly distributed. It should be noted that in the West, almost all the real estate in the population is burdened by debts, the need to pay housing costs in installments. In Russia, as a result of privatization, every citizen became the owner of real estate assets (apartments, garden and country land), not burdened with debts. Therefore, Russian citizens find themselves in this respect in a significantly better position than citizens of other countries.
At the same time, all this will be complemented by newly opened opportunities for the acquisition of housing on credit. Briefly scheme here is such.
The lending is served by the apartment itself. Before paying off the loan, the buyer is legally only its tenant. The buyer immediately posts the first installment - about 30 percent; The remaining 70 pays the bank with which the relevant contract for the real estate company is concluded.
The bank or his subsidiary shall collect documents, deal with the design of the sale of sale, carry out settlements with the seller, etc. Therefore, the amount of commission, for example, in Moscow reaches 13 percent of the market price of the apartment. These costs are justified if the transaction is issued with the participation of reliable organizations, since the housing market has acquired some criminal tint over the past months.
A large number of criminal situations arises due to the presence of almost every transaction of the "left" dollars transmitted from hand to hand after the completion of the official registration procedure.
The "left" dollars are, as a rule, the difference between the market price of the apartment and the amount in which it was estimated by BTI. Therefore, it is not necessary to be a specialist to understand: to eliminate the "left" to choose one of two ways: either a conservative way - closer to the assessment practice of the BTI to the real conditions of the wound; Either the radical path is to abandon this practice and go to other forms of control over the claim price of real estate.
Constantly rising coefficients bring the estimates of the BTI to market prices not by day, but by the hour.
From revenues, which was once bought by a citizen of an apartment (or other property, which can later be sold), all possible taxes have already been deducted. Therefore, at any point of view, the sale of property cannot be considered the fact of obtaining additional income; This is only a change in the shape owned by a citizen of ownership. And the tax charge with the amount of such a change is the secondary charge of the tax on the same income.
The market redistribution of apartments made it possible to improve the use of a housing stock, stimulated the settlement of part of communal apartments, made it possible to partly solve the housing problem.
In general, the housing problem is not only persisted, but also intensifies. This is facilitated by a constant influx of refugees and forced emigrants from neighboring countries.
Use of apartments in non-residential purposes.
After the privatization of a significant share of the residential sector in the cities, the problem of the use of apartments owned, not directly appointed.
Of course, the use of residential premises owned by citizens and legal entities, under non-residential purposes - to accommodate offices, office, workshops, computing centers, etc. - It does not contribute to solving a housing problem, since a significant part of the housing is removed from the city-founding foundation. However, ways to deal with this limit the freedom of owner and are often illegal.
Even if the housing inspection or police body is able to establish the fact of the uncomfortable use of the apartment and, by placing it accordingly, will present the court, then the judges have no legal grounds for meeting such a claim. In accordance with Art. 6 of the law "On the Fundamentals of the Federal Housing Policy" owner of the property in the housing area has the right in the manner prescribed by law, to own, use and dispose of it, including to rent in hiring, lease, deposit, in general and in parts, etc. D., if the existing norms, housing and other rights and freedoms of other citizens are not violated, as well as public interests. Among the responsibilities of the owner when using residential premises established by Art. The same law, there is no such responsibility as the use of residential premises for its intended purpose. True here you can apply Art. 7 Housing Code of the RSFSR, which establishes that residential buildings and residential premises are intended for permanent residence of citizens.
But at best, taking into account this article on the basis of Art. 48 Civil Code of the RSFSR Only the lease agreement of the residential premises can be recognized as invalid, as not corresponding to the requirements of the law. But to terminate, based on this, the transfer agreement to the property is not possible, since neither in one legislative act (and this should be only the law, and not the disposal of the mayor or government decree) does not contain such a legal basis.
The lack of a clear regulatory framework leads to the fact that even the judicial authorities are sometimes not able to figure out who and on what grounds has rights to anyone object. However, the stable demand for offices, trade and storage space, as well as the high cost of such property, guaranteeing considerable commissions, attract a large number of intermediary structures. If in 2000 only 42 percent of respondents were engaged in transactions with non-residential premises, then by now this indicator increased to 70 percent.
1.4 Real Estate Securities Market.
The real estate market segment is the most weakwell. This manifests itself with the lag of the entire stock market, and insufficient involvement in the commercial turnover of the real estate itself. Real estate market participants are still preferred direct investment. Nations and a circle of securities associated with the use and sale of real estate.
First of all, the undoubted advantage of housing bonds is their accumulative essence. They make it possible to gradually accumulate their necessary quantity to buy an apartment, being an identity of the right to point in the denomination of housing.
The fragmentation of the nominal bonds in relation to the study of real apartments allows you to stop at the level of living space and comfort, which will be recognized as sufficient or maximum possible. Although it should be recognized that this positive property of housing bonds is somewhat limited by the fact that they give the right to acquire only newly introduced housing. A fairly limited construction standard and the specifics of the new buildings can significantly narrow the range of those who want to acquire bonds to solve their housing problems, and although there are their basic value. If it was possible to acquire municipal housing using bonds in any area of \u200b\u200bthe city, any level of comfort and "age", their attractiveness would have increased significantly. It could ensure the increase in the competitiveness of housing bonds in relation to other, which are considered sufficiently reliable means of payment (currency).
Another undoubted advantage of housing bonds is their anti-inflational essence: the ability to remove money to one way or another from the depreciation. Therefore, monthly quotes of the cost of housing bonds should assume at least tracking the inflation level. Meanwhile, the mechanism of monthly quotations, provided for by the designed form of emission, is able to absorb only general macroeconomic oscillations, with the time-based, but not current changes in the living market situation.
The ability to change the quotations, depending on the dates of receiving housing, during the repayment of bonds, let's say, in the range from 1 to 6 months, it could significantly increase both the attractiveness of this tool of the stock market and the degree of its liquidity.
Property valuation. Market assessment methods help the most profitably dispose of real estate, this new resource, which enterprises and citizens are at their disposal. This assessment becomes necessary already when the owners of the land and real estate will want to lay them out to obtain a loan. Without adequate assessment, count on attracting additional investments, including foreign ones.
At the first stage of privatization, when creating joint ventures, such assessments or did not do, or were made simply on the eyes. The investor itself determined the price. When it concerned serious objects, Western evaluation firms were attracted, which in most cases were evaluated in favor of foreign investors, understating the real market value of our assets.
The assessment is also necessary in the secondary emission of shares of privatized enterprises, seeking to increase their share capital by the value, supported by real material means. It is the real emission prospectus that will allow investors to avoid errors in the establishment of stock quotes. The assessment is also necessary in the division of property, the definition of the methods of better commercial use of land and real estate and in all other real estate-related operations.
Analysis of the prospects for increasing the cost of real estate and its commercial use should be based on a strict economic calculation, an accurate and professional assessment of the actual market value of the property. Evaluation is reasonable to knowledge, experience, using strictly defined approaches, principles and methods, as well as procedural and ethical standards, the opinion of a specialist or group of experts, as a rule, professional appraisers about the value of the "Real Estate Ekt.
The market value means the most likely price, which will be used when selling the property of the property on the competitive and open market in the presence of all the conditions necessary for the execution of a fair deal.
Such conditions are:
1. The buyer and seller act on the basis of typical, standard motifs. Neither one of the parties is not forced.
2. Both sides have all the full information for decision-making and act, striving for the best satisfaction of their interests.
3. The object is exposed on the open market enough time, and the optimal moment is selected for making a transaction.
4. Payment is made in cash or financial conditions are agreed comparable to cash.
5. The price of the transaction reflects the usual conditions and does not contain discounts, concessions or special lending to any of the parties related to the transaction.
6. The object is in common demand and has the utility recognized on the market.
7. The object is quite deficient, in other words, there is a limited proposal that creates a competitive market.
8. The object is endowed with the properties of alienation and is able to be transmitted from hand to hand.
1.5 Mortgage.
Mortgage means issuing a loan secured by real estate. Classic mortgage object - land. Mortgage opens up the opportunity to provide buildings, buildings, residential buildings, individual apartments as collateral.
Mortgage loans are usually inexpensive, the margin of mortgage banks is small, and the profit is "recruited" due to large amounts of loans placed. Attention attracts these banks also under low interest, but due to the very high reliability of the mortgage bonds, are in sustainable demand.
Four subjects function in the mortgage loan market:
1. The borrower seeking to acquire, possibly better real estate;
2. A bank that seeks to get the highest possible profit by limiting the risk of mortgage;
3. Investor who seeks to get maximum profits by investing in mortgages;
4. The government, which should create legal and economic conditions for the functioning of the mortgage lending system.
Mortgage credit mechanisms should ensure the availability of a loan for the borrower, as well as the profitability of lending.
There are several varieties of credit mechanisms that allow for a greater or lesser extent to bypass a fairly high level of inflation that exists in the country.
The first mechanism is lending to a fixed rate.
The second mechanism is based on loans with a bet, corrected in terms of prices in the country, when periodically (about once a quarter) is revised by a credit rate depending on the change in price level.
The third mechanism is lending to the regulated postponement of payments - developed by one of the US economies in economics specifically for use in Russian conditions. Its essence is that the borrower should pay on the main debt or loan no more than 30 percent of income. The initial amount of payment is relatively low and rises with time. This allows you to transfer the payment of the main part of the debt to a later date. The principle of this mechanism is that two interest rates are calculated, one of which is called "contract" and serves to calculate the amount of debt, and the second - "payment" to calculate monthly payments. These rates are unequivocal.
The Law of the Russian Federation "On Pledge" establishes a general principle regarding mortgage registration. It should be registered in the same state structure that is responsible for the registration of the rights to the proposed property. This principle implies the assumption that mortgages on residential premises should be recorded by the departments of housing privatization.
"Mortgage" agreements regarding buildings and buildings located on earth should be registered in the "land list" of the territory on which the property is located, which is also currently interpreted as registration with local land committees, although at the time of the law enforcement could mean Local tips.
The mechanism for the implementation of the laid property is established by the legislator, both for immovable and movable property.
By virtue of Art. The 350 Civil Code of the Russian Federation implementation (selling) of the laid property, which in accordance with the law is drawn by the penalty, is made by selling from public trading in the manner prescribed by procedural legislation, if the law has not yet been established in other order.
The requirement for the sale of pledged property through public auction is imperative, and if you follow the concept of rules on a pledge, it is impossible to bypass it. But if the pledgee still wants to purchase real estate, which is the subject of a collateral, to the property without a public bidding procedure and is supported by a mortgager, then this can be implemented in accordance with Art. 409 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The article is allowed to conclude between the parties to the accommodation agreement, where the lender states the obligations of the debtor discontinued, and the latter in return provides the extension, that is, in our case, the mortgager conveys the mortgagee real estate.
II analytical part
2.1 Modern principles for analyzing the real estate market.
The success of the business in a market economy is largely predetermined by the quality of information, on the basis of which responsible financial decisions are made. That is why the collection and analytical processing of information, including the market, today are both the subject of a separate study from a scientific and methodological point of view and the subject of independent business.
The most indicative illustration of the foregoing is an example of information management on the stock market. Scientific theories and schools were created and continued to improve the scientific prizes, many works on technical and fundamental analysis were written, which became desktop books of the stock market specialists. The practice of deep testing of knowledge of analysts for their admission to work with information of the securities market is considered to be a normal phenomenon. And this is despite the fact that in the stock market, compared with other markets, the regularities of the perfect market in terms of awareness of the participants should be identified in the most obvious form.
The real estate market, in contrast to the stock, more than far from perfect in many positions, which determines the features of its research. On the one hand, analysts face difficulties, and sometimes the impossibility of correct and unequivocal formalization of economic relations in the real estate market. On the other hand, the unpretentiousness of the transfer of real estate market is obvious in the pure form of analysis technologies used in other markets, since these technologies are adapted for use in another market environment. By virtue of the above, high-quality analytical work in the real estate market seems to be extremely complex subject requiring an analyst, in addition to the deep theoretical knowledge of the real estate economy, constant practice and creative search in studies forming professional intuition.
Studying almost a century of functioning of real estate markets in developed countries of the world, you can come to the conclusion that insufficient attention paid to the quality of analytical work is one of the main reasons for most major crises in the real estate markets. A characteristic example is the crisis in the US real estate market in the late 80s and early 90s. According to experts, excessive and indiscriminate investment in new construction led to the oversaturation of the market and, accordingly, unclaimed by the market of a large number of projects, which loans were issued. The established situation was the unreal market expectations that occurred from the improper structure of incentives when analyzing, a weak analysis methodology and incomplete amount of data characterizing the current conditions. The structure of the incentives that were guided by developers, appraisers and credit organizations were deformed by the interest of alone to receive loans, others - to justify the loan, and third - to place their funds. At the same time, all parties solved their tasks due to unnecessarily optimistic expectations.
The use of a weak analysis methodology expressed in inadequate assumptions and procedures, in collaboration with insufficiently qualitative data of local markets, as a rule, result was the result of unreasonable market research and, accordingly, investment solutions based on them. As a result of the crisis, credit institutions have formed a steady syndrome of distrust in general to any projects and market research in particular. And this, in turn, led to an understanding that real estate market analysts in their work should be guided by some common principles necessary (but not sufficient) to obtain accurate conclusions and results. On the other hand, an urgent need for understandable and easily identifiable criteria, which determine the compliance of the market research categories of the category of reasonableness is formed.
Considering the prospects for the development of the real estate market in Russia, it can be assumed that the lack of potential crises is overly an optimistic scenario. However, the consequences of such crises may be less significant, if today, at the stage of active development of the market, formulate and implement some general principles in everyday practices and
requirements for analytical research, on the basis of which investment solutions will be made.
Not only the threat of crises, but also current daily problems - increasing competition, reducing opportunities for obtaining short-term superfits, the beginning of the implementation of long-term and capital-intensive projects of a commercial real estate development, the coming to the market of foreign investors with high demands for substantiation of decisions, etc. - objectively indicate that the importance of high-quality analysis in the real estate markets of Russia will soon acquire more and more weight.
2.2 Real estate market research for justifying investment solutions.
The ultimate goal of any study of the type under consideration is to measure the ratio of demand and suggestions on a specific type of product in the real estate market in a specific (as a rule, the future) moment of time.
Special properties of real estate, as a product, along with a special place of real estate in a market economy, form a fairly wide range of socio-economic information necessary for the positioning of this market in the market. The current and retrospective macroeconomic characteristics of the national and regional economy, the socio-demographic indicators of regional and local markets, the parameters of the regional and local real estate markets are only common areas in which research needs to be conducted.
Principle 1. For analysis, only the information should be selected that can really determine the future productivity of the investment object.
When this principle is followed by the main difficulty for analytics is the lack of standard rules or unambiguous recommendations for which the initial information should be formed. It is here that the analyst must show all his knowledge, professional intuition, creativity and practical experience. Moreover, it is here that the basis of the viability of the study as a whole is laid.
Principle 2. All current and promising data on the basis of which a study is based, should be used in a quantitative assessment of the performance of the real estate investment project.
However, even carefully selected and directly related to the subject of assessment information is, figuratively speaking, "bugs of bricks", of which the analyst must be addressed in all rules of construction art. Durable foundation for analytical research. And here it is not possible to do without a solid solution connecting individual elements into a single monolith.
Principle 3. All separate blocks of information selected to justify investment solutions should be interconnected by a clear logical scheme that completes the forecasting of future market conditions and the relevant productivity of the project under consideration. The description of the logic scheme should be represented explicitly.
Positive perception by the Customer of the report with the results of a market research in which there is no logical scheme may only be if:
a) analyst enjoys the ignorance of the customer or
b) The customer is initially favorably refers to the results.
On the other hand, building a convincing and obvious logical scheme is a demonstration of higher professional analytics skills.
Continuing reasoning about the need to build a logical research scheme, consider another principle that specifies the content of market analysis.
Principle 4. The maintenance of market analysis should be reduced to the discussion of the factors that make up the main relations to determine the performance of the commercial real estate object.
In accordance with this Principle, the analyst during the study should formulate the main relationships that determine the performance of the commercial object, after which it is to identify the hierarchy of the parameters of the arguments, the functions of which are included in the main expression for productivity.
We illustrate a practical approach to the implementation of this principle on the following simplified example.
Let the performance criterion of the project under consideration are pure operating income (NOI) in a specific period of the future. Then, by definition, the main expression to determine the performance will have the following form:
Noi \u003d pgi-v & l + m-fe-ve, where
PGI - potential gross income,
V & L - losses from underloading and non-payment.
M i - other income.
Fe - permanent operating expenses
VE - variable operating costs.
Consider the procedure for identifying parameters that determine the expected values \u200b\u200bof the main factors.
Potential gross income is determined by the value of the rental rate, which in turn is the function of the current rental rate, as well as the trends in the ratio of the market supply and demand in time.
The predictable loading of the property is a function of the cumulative capacity of the market, the demand parameters, the absorption coefficient by the market and the growth of real estate absorption range. For projects, the projected loading determines the two indicators - the level of loading and time graph of the absorption of the market to this level.
The growth of the absorption range of real estate is determined by either the increase in the number of jobs (level of employment) or population growth. In turn, an increase in the absorption range leads to the need for new real estate.
It should be noted that the growth of employment and the growth of the population in one case may be associated with direct dependence, for example, when opening new jobs and the influx of new able-bodied people. In another case, the growth of the population can grow and without increasing employment, for example, due to an increase in arriving retirees or increase fertility. Qualitative analysis involves the use of several sources of information that give historical trends and the outlook growth forecast, with the subsequent data comparison. It is also obligatory to segmented a range of range, for example, by age groups, sex, family sizes, etc. The lack of listed positions in the study should be attributed to the untenabolic data selection for use in the analysis.
The demand parameters are determined by such specific indicators as the area (office or production) at one workplace, the costs of buying per capita, the number of apartments or houses per capita, etc. Using demand parameters, the amount of real estate required is calculated, which corresponds to the growth of the range of real estate consumption. For example, applying an average cost of purchasing to population growth, an increase in retail sales, and, accordingly, the need for additional trading areas is predicted. When analyzing the housing market, the population, segmented by age, income, size or family composition, is converted into segmented demand. A wealthy analysis of demand parameters involves a study of historical trends, the current state and forecasting their likely value in the future. Moreover, a wealthy analysis measures the change in demand not only at the expense of a new range of range, but also due to the change in the existing structure of the population and employment. For example, in economic lifting, growing companies require large areas, and changes in the demographic situation in the direction of increasing the people of retirement age will require the appropriate type of housing.
The signs of failure to analyze the parameters of demand should be attributed, first of all, the adoption of permanent values \u200b\u200bis usually characteristic for the moment of analysis, as well as ignoring changes in existing population and employment structures.
The absorption coefficient, also called the market penetration rate, is determined by the share of common market demand, which, according to forecasts, will absorb the project under consideration in competition with other projects. After the analyst appreciated the total increase in potential demand, it is necessary to determine the critical parameter for the project - the share of general demand for which the project under consideration may probably claim.
Theoretically, the absorption coefficient is a complex function of many factors. In the first approximation, it can be defined as the ratio of the area of \u200b\u200bthe estimated object to the total area (including the object area) of the competitive proposal at the time of its output to the market. Such an approach, at least, must be present in each market research applying for consistency.
It should be noted that when determining the absorption coefficient, the most important conditions are the detailed segmentation of the demand and competitive supply. It should not be overlooked from the duration of the competing projects launched in the implementation of competing projects, the volume and duration of projects prepared for implementation. The first sign of an insolvent study here is to use any "middle" data.
Losses due to generally accepted discounts and benefits to tenants are also a factor that should not be missed from the prediction of potential gross income.
Other incomes, although they are of themselves, as a rule, a small component of the revenue part must still be predicted, taking into account the likely preferences of potential consumers in the light of their ideas about the style of life, service level and per capita expenditures for receiving this level, and ..
Permanent and variable costs are traditionally considered more specific in forecasting. However, such a statement of the issue for the conditions of Russia is only partially. For example, real estate taxes (today it is taxes on property, land taxes) and land rental in view of the legislative non-marketability can give the potential investor unexpected "surprises" in the future. Therefore, a wealthy market research should include a variant prediction of the specified positions.
A similar situation is observed and mostly variable expenses. Analysis of the communal services market, most of which are provided by natural monopolies, unstable tariff policies require a quantitative justification of the indicators taken into account. At the same time, it is important to use market information on the costs of resources obtained on the basis of testimony of instrumentation. In the absence of market analogues on resource consumption, more preferred is the calculation according to standards, and not the use of accounts exhibited by utility providers.
2.3 Methods for estimating the market value of real estate.
There are three basic methods for assessing the market value of real estate:
1. Comparison method
2. Possible method
3. Method of capitalization of income.
The main assessment method is a method of comparative sales analysis (SAP). This method is applicable in the case when there is a land and real estate market, there are real sales, when it is the market forms prices, and the task of appraisers is to analyze this market, compare similar sales and thus obtain the cost of the estimated object. The method is built on comparison of the object proposed for sale with market counterparts. It finds the greatest use in the West (90 percent of cases). However, this work requires an already formed land and real estate market.
The sales comparison method is used in the presence of a sufficient number of reliable market information on the purchase and sale of facilities similar to the estimated. In this case, the criterion for selecting comparison objects is the same best and most efficient use.
The SAP method can also be called a direct comparative sales analysis approach, a comparative sales method, a market information market information method.
The sequence of application of the SAP method is as follows:
1. The recent sales of comparable objects on the relevant market are allocated. Sources of information are: Own appraiser dossier, Internet, electronic database, real estate firms, real estate brokers dossier, credit institutions archives (mortgage banks), insurance companies, construction and investment companies, territorial insolvency and bankruptcy departments, territorial management of the State Property Committee and DR .
An important point when using the SAP method is the coordination of the results of the comparison of the estimated real estate. The arithmetic averaging of the data obtained is not allowed. The adopted procedure is the study of each result and making judgment as its comparability with the estimated real estate. The smaller the amount and the value of the accuracy of the amendments, the greater weight has this sale in the process of coordination.
As units of comparison, the meters traditionally established in the local market are taken. To evaluate the same object, several comparison units can be applied simultaneously.
Comparison elements include the characteristics of real estate and transactions that cause a change in real estate prices. Elements subject to compulsory accounting include:
· The composition of the transferred property rights;
· Conditions for financing a sale transaction;
· terms of sale;
· Sales time;
· Location;
· physical characteristics;
· Economic characteristics;
· The nature of use;
· Cost components that are not related to real estate.
2. Checking information about transactions: confirmation of the transaction one of the main participants (by the buyer or seller) or agent of the real estate company; Detection of sales conditions.
If there is a sufficient number of reliable market information, to determine the value of the sales comparison method, methods of mathematical statistics are allowed.
3. Adjustment of the cost of comparable objects.
Adjustment can be made in three basic forms: in monetary terms, percentage, general grouping.
Adjustments for the sale of comparable objects are made in the following order:
· First of all, adjustments relating to the conditions of the transaction and the state of the market, which are carried out by applying each subsequent adjustment to the previous result;
· Secondly, adjustments are made directly to the real estate object, which are manufactured by applying the specified adjustments to the result obtained after adjustment to the market conditions, in any order.
To determine the values \u200b\u200bof the adjustments, depending on the availability and accuracy of market information, quantitative and qualitative techniques are applied. The rationale for the calculation of the adjustments is mandatory. The final decision on the value of the result defined by the sales comparison method is made on the basis of an analysis of the adjusted sales prices of comparison objects with the greatest similarity with the assessment object.
The method of assessment on the ground costs is practically not applicable. It can only be used in exceptional cases of land assessment inextricably from improvements produced on it. It is believed that the land is constant and not consumed, and the cost method is used to evaluate artificial objects created by man. When evaluating this method, the cost of land is consistent with the cost of improvements (buildings, structures), and the land is estimated separately by other methods.
The cost estimate of real estate is implemented in the following sequence:
· Determination of the value of the land plot;
· Determination of the restorative or replacement value of buildings and structures;
· Determination of the accumulated wear of buildings and structures;
· Determination of the market value of real estate by the costly method as the amount of the value of the land and replacement or replacement of buildings and structures over the back of the accumulated wear.
The choice of the method adopted to calculate the method of determining the value of the new construction of improvements must be appropriately justified. Applying the value of substitution is advisable in cases where it is difficult to determine the cost of erection of an accurate copy of the building due to obsolete types of building structures and construction methods used when creating an assessment object.
Costs corresponding to the replacement or replacement cost for real estate estimates are calculated as the sum of direct costs, indirect costs and the profit of the entrepreneur.
Direct costs include the following costs directly related to the construction:
· The cost of materials, products and equipment;
· Wages of construction workers;
· The cost of building machines and mechanisms;
· The cost of temporary buildings and structures, safety activities, transport and warehouse expenses and other costs, regulated on the local market;
· Profit and overhead contractor.
Indirect costs include the costs associated with the construction of the building, but not included in the cost of construction and installation work.
· The cost of design, technical supervision, geodesic control;
· Payment of consultations, legal, accounting and auditing services;
· The cost of financing construction;
· Administrative and other expenditures of the developer.
The size of indirect costs is determined taking into account the tariffs for work and services under these positions.
The profit of the entrepreneur is a current market rate that is stimulating an entrepreneur to invest a construction project. The magnitude of the profit is determined by the method of expert assessments based on market information.
The use of the cost method is necessary when analyzing new construction; reconstruction of buildings; evaluation for tax purposes; to detect extension in assessing real estate; when evaluating for insurance purposes; estimate of the effects of natural disasters; Assessment of special buildings and structures.
In the conditions of the same transition to market conditions, the cost method is in assessing the decisive, since the use of other methods requires extensive market information, which is absent due to the undeveloped market. However, it should always be remembered that construction costs are only a market value basis and most often come or more, or less.
For example, the market value of the elite hotel located in an unsuccessful place (on the outskirts of the city) will be less than the cost defined by the cost method. In turn, the market value of the gas stations complex at a certain stage may be more construction costs.
In the conditions of the formation of the market, when the production of production is reorienting on new technologies, it may seem that the object of real estate does not have the cost at all. For example, if an enterprise makes no necessary products and its production areas cannot be reconstructed to new production, the market value of such real estate seeks zero. The use of the same method will lead in this case to the incorrect orientation of potential buyers.
Currently, in Russia, this moment is often taken into account with incorrect assessment of fixed assets of enterprises, since their reassessment is carried out mainly on the costly method and the appraiser should be remembered that the carrying amount of the main funds of enterprises does not correspond to their market value.
The following assessment method, which is applicable to Russia, is the assessment method based on the analysis of the most efficient use of real estate, and this analysis is associated with the definition of the type of use that the owner will bring the maximum income, i.e. Method of capitalization of income.
The method of capitalization of income in the assessment of the market value of real estate is implemented in the following sequence:
· Forecasting future income;
· Capitalization of future income.
Future revenues generated by the object of real estate are divided into two types: income from operating (operational) activities as a result of commercial rental relations and revenues from Reversion.
Revenues from the operating (operational) activity are projected by drawing up a reconstructed (hypothetical) income report. Revenue income is predicted:
· Immediately appointment of the absolute value of reversion;
· Appointment of a relative change in the value of real estate for the period of ownership;
· Using the terminal capitalization coefficient.
Capitalization of future income in this cost can be performed:
· Direct capitalization method;
· Capitalization method according to the rate of return.
The initial prerequisite method of direct capitalization is the constancy and infinity of capitalized income. In the direct capitalization method, the present value of the future income flow is defined as the attitude of the annual income coming to ownership or interest, to the capitalization ratio for this property right or interest.
To calculate the cost of full ownership right, the definition of a general capitalization coefficient is based on market data. Depending on the availability of source information, apply:
· Analysis of comparative sales;
· Calculation using debt coverage coefficient;
· Investment team technology.
The initial prerequisite of the capitalization method is due to the rate of return is the limited period of income receipt. In the capitalization method according to the rate of return, recalculation of the final number of future cash flows in this value is carried out with a specific value of the rate of return, relevant investment risk in this type of real estate.
In the calculations of the present value, without taking into account the conditions of financing, the capitalization method according to the rate of return is formalized either as an analysis of discounted cash flows, or in the form of calculated capitalization models.
The discount rate used in the analysis of discounted cash flows and takes into account both systematic and non-systematic risks is determined:
Method of allocation from market data on sales of similar objects;
Method of alternative investment in the financial market;
Method of monitoring the real estate market.
Recently, the demand for the services of appraisers and their professional training in Russia began to grow intensively. This is also due to the recent events in the financial sector, when attempts to create a lending mechanism through loans insurance suffered fiasco: banks have lost a lot on Lipov Insurance. In the case of real estate, which is taken by the bank in a pledge when issuing a loan, losses are almost impossible. Thus, real estate and capital markets become inseparable components of the economy as a whole.
Naturally, from banks there was a great interest in such operations. And they all need a qualified real estate assessment, conducting insurance for the real value of real estate.
The assessment is also necessary within the framework of regional tax policy. All over the world, the basis of the system of local taxation is a real estate tax, due to this tax, about 70 percent of the local budget is formed. Of course, with the development of the market itself, with the appearance of real costs it is possible to transition to such a taxation system, which would stimulate the development of the real estate market and would provide at the same time replenishment
local budgets. This explains and unconditional interest in the assessment, manifested by local administrations.
The cost of professional assessment services is greatly different depending on the types of estimated objects, the complexity of work and, of course, from which experts are involved in the assessment. Typically, the cost of services is measured either in hours multiplied by the rate of hourly payment, or depends on the value of the object, but never is attached to its value.
2.4 Features of various types of evaluation.
Evaluation for the purposes of purchase or sale and real estate classification.
When implementing real estate assessment, which should be purchased or sold on the open market, the market value or value of the implementation is used as an assessment base for all classes and categories of real estate. At the same time, for specialized real estate, in most cases, the determining method for calculating the cost will be the cost method based on market data.
When implementing real estate assessment for sale for a limited period of time when real estate is set to an open market for sale in terms, significantly less adequate marketing period for this type of real estate, the value of limited implementation is applied as a base for all classes and real estate categories.
To select the appropriate assessment base, the purpose of the evaluation and characteristics of the estimated property is crucial.
In general, the classification of the main objectives for which the real estate is estimated, it is as follows:
1. Evaluation for purchase or sale;
2. Evaluation for sale for a limited period of time;
3. Elimination of land and buildings for their use as secured credit obligations;
4. Evaluation for the preparation of accounting and financial statements;
5. Evaluation for inclusion in stock prospectuses, stock exchanges;
6. Evaluation to address issues in the merger and acquisition of the company;
7. Evaluation for Pension Funds, Insurance Companies, Trust Funds for Real Estate Management.
In practice, other estimates may occur, with their wording and, accordingly, possible databases of estimates should be coordinated by the Client and the appraiser.
After finding out the purpose of the assessment, it should be established, to which class and category applies to the estimated property.
For estimates, two class of ownership are distinguished:
· Specialized
· Non-specialized
Specialized property is such that, due to its special nature, rarely, if at all ever, is sold on the open market to continue its existing use by one owner, except when it is implemented as part of its useful business.
Examples of specialized property are:
1. Museums, libraries and other similar premises, which belong to the public sector;
2. Hospitals, premises of specialized medical care and leisure centers that are missing competitive market demand from other organizations wishing to use these types of property in this area;
3. Schools, colleges, universities and research institutes, which lack market competitive demand from other organizations;
4. Standard property in special geographic areas and in places removed from the main business centers located there for the purpose of production or business.
Non-specialized property is all types of ownership, in addition to the one that falls under the definition of specialized property. In other words, this is the one to which there is universal demand, taking into account possible upgrades or without, and which is usually bought, is sold or rented on the open market in order to use it for existing or similar purposes either as an unoccupied property for one ownership, or (regardless of whether it is occupied or free) as an investment or for development.
When assessing real estate held by the owner for use in the activities of an enterprise (business), as an assessment base applies:
· Market value with existing use - for non-specialized real estate, including real estate estimated on the basis of its commercial potential.
· Residual replacement cost - for specialized real estate.
Non-specialized and specialized property in turn is classified by category depending on the purpose of ownership. Such a classification principle is used both for evaluation purposes and for other purposes.
2.5 The influence of environmental factors for the cost.
Environmental factors, both unfavorable and favorable, are included in the set of factors, usually taken into account when performing estimates. Some factors have an impact on a certain type of real estate and will affect directly on the calculations of the appraiser, where they must be taken into account in relation to market data obtained by comparable and not affected by such real estate factors. In other cases, all properties in any region will be exposed to these factors.
Relevant environmental factors and pollution include in the general case the following categories:
· Natural factors like radon or methane, air pollution or noise;
· Technogenic pollution factors as a result of production activities in the past or present on this land, or as a result of contact with neighboring sites;
· Pollution factors in the form of electromagnetic and other fields;
· Pollution factors when using the materials from the secondary raw materials.
All real estate classes are susceptible to the impact on the cost of environmental factors, but the real estate offered for sale or as providing loans is particularly sensitive to these factors.
The work on the assessment of real estate work on environmental audit of real estate is not included. In cases where the appraiser has reason to believe that environmental factors can significantly affect the cost, it must inform the client about the need to attract a professional environmental expert.
The appraiser must inform the environmental expert regarding the context of its research, including the current and potential future use of the site that will be expressed in value defined on the basis of the best and most efficient use. In general, an environmental expert must answer the following questions:
· Is it possible to successfully and economically eliminate the source of pollution or danger;
· If pollution or danger cannot be completely eliminated, you can isolate them or close to make real estate suitable for this use on a certain, even limited period;
· Is there an opportunity to mitigate the effects of pollution or hazard in any way;
· What is the most effective means of controlling pollution and means of its regulation;
In cases where it is possible to eliminate the source or eliminate the effects of pollution, the assessment can be carried out taking into account the relevant settlement costs for such liquidation or elimination.
III practical part.
3.1 Practical application of the method of comparative sales.
At the end of 2000, cottage construction began in Podolsky district. Low-rise residential complexes are rows of selected cottages that have common walls with the same type of neighboring houses. The word "condominium", denoting property, created and equipped with the works of neighbors-like-minded people, is not too popular. Therefore, to designate the exotic for us, housing, built on the principle of "common walls and a roof - their yard", the English-language word "Town House" took place in Russian everyday life.
Yet, for example, the market value of the cottage using the method of comparative sales.
Total area of \u200b\u200b120 sq.m., cottage has 6 rooms, 3 bedrooms, bathroom, shower, finished basement. The garage is missing for the date of the assessment. Plot area - 1000 sq.m.
For analysis, we will use data on five sales of comparable objects in the same area.
Table number 1.
| Object number 1. | Object number 2. | Object number 3. | Object number 4. | Object number 5. | |||
| Selling price | 65000 | 78000 | 56000 | 70000 | 54000 | ||
| Ownership | full | full | full | full | full | ||
| Conditions nancy | non-market, the price is overestimated by 3000 | non-market, the price is overestimated by 8000 | market | market | market | ||
| Terms of sale | market | market | market | market | market | ||
| Market conditions (time) | 2 weeks | 6 weeks | 1 year | 1 year | 1 year | ||
| Square House | 120 sq.m. | 145 sq.m. | 120 sq.m. | 145 sq.m. | 120 sq.m. | ||
| Land area | 10,000 sq.m. | 12000 sq.m. | 10,000 sq.m. | 12000 sq.m. | 10,000 sq.m. | ||
| Number of rooms | 6 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 6 | ||
| Number of bedrooms | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | ||
| Bath | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Shower | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Basement | not finished | not finished | not finished | not finished | finished | ||
| Garage | there is | there is | there is | there is | not | ||
As can be seen from the source data, comparison objects differ from the terms of financing, sales time and physical characteristics.
The magnitude of the adjustment on the financing conditions is determined by the comparison of the sale price of objects with market and non-market financing. At the same time, credit payments are discounted at market% rate. In our example, the values \u200b\u200bof the adjustments are defined in the amount of 3000 for the object number 1 and 8000 for the object number 2.
Since all comparable facilities are the terms of sale of market, then the adjustment for the terms of the sale is not required.
To adjust to market conditions (time of sale), it is necessary to highlight objects that differ only by this element. In our case, Object No. 1 and No. 3 is different only by the terms of financing and sales time. Adjusting the sale price
object number 1 for financing conditions, you can determine the adjustment for the sale time:
(62000 - 56000) / 156000 \u003d 0.1.t. During the year, the market prices will grow by 10%.
Thus, all comparable objects are given in the same conditions for financing and selling time, which creates a single base for adjustments to the other comparison elements.
In a number of comparison objects, the differences in size are represented by different number of rooms and a different area of \u200b\u200bthe house and the site. Moreover, a plot of 12000kv.m. Corresponds to the house with an area of \u200b\u200b145kv. with 7 rooms, and a plot of 10000kv. Corresponds to the house with an area of \u200b\u200b120kv. With 6 rooms. Hence, adjustment on the size of the comparison of objects No. 1 and No. 2 has the following form:
70000 – 62000 = 8000.
The adjustment for the presence of the garage is derived from the comparison of objects No. 3 and No. 5:
61600 – 59400 = 2200.
The adjustment to the completed basement is determined from the comparison of objects No. 2 and No. 4:
77000 – 70000 = 7000.
The results of the adjusted adjustments are shown in Table No. 2
Table number 2.
| Object number 1. | Object number 2. | Object number 3. | Object number 4. | Object number 5. | |
| Selling price | 65000 | 78000 | 56000 | 70000 | 54000 |
| Transfer of right venalty | full | full | full | full | full |
| Adjusting expense. | 65000 | 78000 | 56000 | 70000 | 54000 |
| Terms of Financiers. | not market | not market | not market | not market | Market |
| Correctrus for financing conditions. | - 3000 | - 8000 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Adjusted price | 62000 | 70000 | 56000 | 70000 | 54000 |
| Terms of a transaction | commercial | commercial | commercial | commercial | commercial |
| Correcting on the terms of the transaction | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Adjusted price in market conditions | 2 weeks | 6 weeks | 1 year | 1 year | 1 year |
| Correction on market conditions | +10 % | +10 % | +10 % | +10 % | +10 % |
| Adjustable price | 62000 | 70000 | 61600 | 77000 | 59400 |
| Location | similar | similar | similar | similar | similar |
| The size | 120kv.m. | 145kv.m. | 120kv.m. | 145kv.m. | 120kv.m. |
| Size Correction | 0 | - 8000 | 0 | - 8000 | 0 |
| Garage | there is | there is | there is | there is | not |
| Correct for garage | - 2200 | - 2200 | - 2200 | - 2200 | 0 |
| Finished basement | not | not | not | yes | not |
| Correction | + 7000 | + 7000 | + 7000 | 0 | + 7000 |
| Adjustable price | 66800 | 66800 | 66400 | 66800 | 66400 |
| Total net correction | 1800 | 11200 | 10400 | 3200 | 12400 |
| The same in% | 3 | 14 | 19 | 5 | 23 |
| From the price of sale Total gross correction | 11200 | 25200 | 14800 | 17200 | 12400 |
| From the price of sale | 19 | 32 | 26 | 25 | 23 |
For each comparison object, the adjusted price is obtained. In accordance with the terms of the task, it is required based on the corrected sales prices to bring the value of the market value.
The rationale for the output of a single market value is to give each member of a number of corrected sales prices of the weight coefficient, given the degree of difference of comparison objects from the assessment objects. It should be taken in
attention range of sales price range, total% adjustments taken in absolute value, total% adjustments defined as the difference between positive and negative adjustments, as well as any other data.
In this example, we have a practically very narrow sale price range - from 66400 to 66800. However, the selling price with smaller adjustments is assigned a greater specific weight - for object No. 5 the number of adjustments \u003d 2. In addition, the total gross adjustment amount for the object number 5 is also Almost the smallest. Therefore, as a market value of the comparison facility, the sale price of the object No. 5 - 66400 was adopted.
3.2 Risks of investment and statistics of real estate markets.
Statistics of real estate markets, as a rule, contains information about rental rates and profitability indicators. For data comparability, information applies only to first-class objects. These facilities are considered to meet the highest requirements for location, equipment, communication, planning solutions, etc., and rental rates are defined in the same standards for measuring and distributing costs between the owner and tenant for maintenance, repair, insurance, etc. .
Information about rental rates is considered accessible. It requires only the verification of the adequacy mentioned. The information about the profitability indicators is more difficult to prepare. Since the purchase and sale transactions are not so much, then the previously perfect transactions are taken into account, integrate data on various objects, take into account breaking breaks, inflation and other processes. The profitability indicators are also involved in regional risks, and the expert began here. Therefore, statistics are one of the specializations in real estate markets.
The activation of business and investment in the region is necessarily accompanied by the activation in the office market, an increase in demand, filling and rental rates. At the same time, new construction and modernization of offices is stimulated, following them - service services, shopping complexes, leisure centers, etc. Such processes are today characteristic of the largest business centers: the traditional financial capitals of America and old light, the rapidly growing capitals of Southeast Asia, China and India. An analysis of the statistics of the rental business indicates a number of interesting phenomena. For example:
Data on lease rates are significantly more dynamic than data on profitability indicators; The dynamics of rental rates is characterized by a certain oscillating, reflecting (albeit with shifts) General rates and recession processes; Changes in the indicators of office and trade real estate may not coincide in time and magnitude; Improving the market situation is reflected in the growth of rental rates and, less likely, in reducing profitability indicators (due to their noticeably lower dynamism); The asymmetric picture takes place and under the deterioration of the market situation;
The values \u200b\u200bof profitability indicators are the better (below), the more reliable and more stable regional economy, and the social situation. The leaders of a stable rental business are London, Paris and Frankfurt, where the area of \u200b\u200bchange of profitability indicators is in the region of 5-6%;
Changes in indicators for Eastern European capitals are less dynamic; This can be explained as smaller volumes of markets, fewer transactions and, apparently, the smaller interest of Western experts and business circles to these markets; Indicators of profitability for Eastern European capitals are stable - 2-3 times higher than similar values \u200b\u200bfor Western capitals. And in the period after the August 1998 crisis, the indicators of profitability in Moscow were worse than 4 or more times. And this happened not only because of the real fall of real estate value, but rather, as a consequence of an expert assessment of the state of instability and increasing business risks in this region;
Additional analytical information is proposed to be obtained using an estimated indicator of the specific capitalized value (UKS) - as estimates of the value of a certain averaged unit of commercial area of \u200b\u200bthe leased object.
A similar assessment simultaneously with an operational response to fluctuations in rental rates carries out expert opinions on the success and risks of the business.
Initial information - rental statistics for European cities - can be found in Western publications (for example, in the monthly "Europroperty"). As objects of representatives, we choose: Frankfurt, London and Paris - the centers of the most stable business, St. Petersburg, Prague and Warsaw - the centers of the transition economy with the most risky (in Europe) rental indicators.
Rental office business.
Observation period 01.99-08.00 For Western capitals, the progress of rental office business overall. We note the absolute stability of the profitability indicator for London (5.00-5.50%) and the improvement of profitability indicators for Frankfurt (from 5.75 to 4.90-5.50%) and Paris (from 6.25-6.75 to 5.50-6.00%). For the Eastern European capitals, the same period is characterized by deterioration of indicators. Analysis of the calculated data VCS allowed, in addition, to comply with the external discrepancy of the logic of rental rates (their excess in St. Petersburg and Warsaw until mid-1999 over the rates in Paris and Frankfurt). As a result, low levels of UKS at high lease rates do not allow optimism to expect investment growth.
Rental shopping business.
Observation period 05.99-08.00 For Western capitals is characterized by a general deterioration of indicators (which is clearly traced with the help of UKS). This suggests that there can be quite long periods of market activity, after which the implementation of purchased retail space will not bring real income at all.
For the Eastern European capitals, the surveillance period of 05.99-08.00 is associated with the passage of a period of long-term stagnation and, possibly, the beginning of the exit of it (an improvement in the dynamics of indicators is noted, although the gap indicators in comparison with Western capitals seems to be gigantic - almost an order of magnitude). Therefore, it should be further limited to the statement that there may be quite long periods in the markets of commercial premises, when investments in the acquisition of trade real estate in Eastern European capitals can bring a noticeable positive effect, including during periods of recession in Western markets. This can serve as a good argument when searching for ways for inter-regional diversification of the real estate portfolio.
Conclusion.
The completion of the real estate market formation period is characterized by the transition from extensive to intensive development. Obviously, in the near future there will be no such rapid growth in the number of transactions, as in the first half of the 90s. Moreover, during a certain period in the housing market, only stabilization of the number of transactions is possible. It is also possible to increase price levels, primarily on the secondary market. But at the same time, the prices for elite housing not only did not decrease, but also increased, which indicates the prospects for the new construction of high quality housing. The managers of firms are also aggravated competition in the market. Most of them are inclined to believe that if for 1995 a moderate extent of competition was characterized, then in 2001 it became high and will continue.
Stabilization of the number of transactions and prices in the secondary housing market is a consequence, primarily macroeconomic factors, the main one is to maintain a low level of income from the majority of the population. The initial rapid increase in demand in the market, as a result, the appearance of a layer of people in the country with high incomes is practically ended. And today, inside this layer there is a new differentiation - the selection of the layer with ultrahigh income. Due to this differentiation, the demand for luxury housing has increased. However, in absolute terms, the potential of this layer is very limited. The greatest expansion of demand is possible either due to increasing the level of income and the formation of a wide average layer capable of becoming the main supplier of buyers, or at the expense of active incentive demand, both the state and the professional participants of the real estate market. At the same time, some increase in demand in the future is quite possible under the influence of the emission of money inevitable in the coming months in the economy for the branch of the non-payment crisis and in connection with the repayment of debts on wages and debt on state orders. Part of this money will come to the real estate market, but they obviously do not change the situation, although the number of applications for the purchase under the influence of this factor will rise several points.
It can also be assumed that in connection with the inevitable and significant increase in tariffs for utilities, it is quite possible to increase the supply in the secondary housing market.
At the same time, if the surge of the supply in the secondary market in 1991-1993. It was caused by the rapid increase in prices, now sellers will proceed not so much of the possibility of a very significant increase in revenues through the sale of housing, how much of the need to reduce the cost of its content, and from here - agree to reduce prices. This, in turn, can also be somewhat lifted demand, which means the revisions of real estate firms.
At the same time, this stabilization will not take a common problem - the residential real estate market in the foreseeable future will experience a deficit of demand, which can significantly reduce income from traditional real estate firms for the provision of services for the sale of real estate.
Under these conditions, it is necessary to substantially expand the range of services provided by the Customer: banking calculations, transport services, services of notaries, the possibility of repair work, providing installments on payments, etc., increased attention to advertising, possibly a decrease in commission. All of these funds can play a significant role in attracting customers, but their possibilities are still limited. If for individual firms these techniques are able to provide the necessary volume of turnover, then, obviously, in general, they will not solve the problem of the development of real estate business. This problem will drastically solve this problem, and in modern conditions it is possible only at the expense of the active participation of the state by creating a mortgage lending system - the creation of federal and regional mortgage lending agencies, supporting the secondary mortgage market, providing state guarantees to banks when issuing mortgage loans.
The consistent development of the real estate market in Russia naturally led to the next stage, characterized by a jump-like increase in the quality of the standard of substantiation of investment solutions. And abroad, and in Russia, the real estate market participants come to understand that the accuracy of business plans, investment projects, etc., which are essentially a standard set of simple formulas, entirely depends on the validity of market research, the results of which are used in the formulas . In other words, the most significant and significant indicator of the impending of the investment project in the real estate market is the consistency of the market research, on the basis of which this decision is made.
Bibliography:
1. Balabanov I.T. "Real Estate Economics", St. Petersburg 2000.
2.Gamekin V.A. Real Estate Economy: Textbook. - 2nd ed., Pererab. And add. - M.: Marketing Publishing and Book Center, 2002
3. Kupchin A.N., Novikov B.D. Real estate market: condition and development trends. - Tutorial. M.: 1995.
4. Maksimov S.N. "Basics of entrepreneurial activity in the real estate market", St. Petersburg. 2000.
5.News B.D. Market and real estate assessment in Russia. - M.: Exam, 2000.
6. Hamin D., Yurkov D. "Real estate market with the eyes of realtors" // Economy and Life, 1997
Other materials
Part of the proposed proposal, it seems not enough argumentary second part of it - on the legal disappearance of the building as an object of civil rights, since the initial immoval thing was not just a thing, but a composite thing with a more complex system level and the type of element-...
Russia until 2005. // http: www.sbrf.ru/concept/2005 C 00.HTM reviews
Fedell Education Agency
| Object number 1. | Object number 2. | Object number 3. | Object number 4. | Object number 5. | |||
| Selling price | 65000 | 78000 | 56000 | 70000 | 54000 | ||
| Ownership | full | full | full | full | full | ||
Conditionsnancy |
non-market, the price is overestimated by 3000 | non-market, the price is overestimated by 8000 | market | market | market | ||
| Terms of sale | market | market | market | market | market | ||
| Market conditions (time) | 2 weeks | 6 weeks | 1 year | 1 year | 1 year | ||
| Square House | 120 sq.m. | 145 sq.m. | 120 sq.m. | 145 sq.m. | 120 sq.m. | ||
| Land area | 10,000 sq.m. | 12000 sq.m. | 10,000 sq.m. | 12000 sq.m. | 10,000 sq.m. | ||
| Number of rooms | 6 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 6 | ||
| Number of bedrooms | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | ||
| Bath | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Shower | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Basement | not finished | not finished | not finished | not finished | finished | ||
| Garage | there is | there is | there is | there is | not | ||
As can be seen from the source data, comparison objects differ from the terms of financing, sales time and physical characteristics.
The magnitude of the adjustment on the financing conditions is determined by the comparison of the sale price of objects with market and non-market financing. At the same time, credit payments are discounted at market% rate. In our example, the values \u200b\u200bof the adjustments are defined in the amount of 3000 for the object number 1 and 8000 for the object number 2.
Since all comparable facilities are the terms of sale of market, then the adjustment for the terms of the sale is not required.
To adjust to market conditions (time of sale), it is necessary to highlight objects that differ only by this element. In our case, Object No. 1 and No. 3 is different only by the terms of financing and sales time. Adjusting the sale price
object number 1 for financing conditions, you can determine the adjustment for the sale time:
(62000 - 56000) / 156000 \u003d 0.1.t. During the year, the market prices will grow by 10%.
Thus, all comparable objects are given in the same conditions for financing and selling time, which creates a single base for adjustments to the other comparison elements.
In a number of comparison objects, the differences in size are represented by different number of rooms and a different area of \u200b\u200bthe house and the site. Moreover, a plot of 12000kv.m. Corresponds to the house with an area of \u200b\u200b145kv. with 7 rooms, and a plot of 10000kv. Corresponds to the house with an area of \u200b\u200b120kv. With 6 rooms. Hence, adjustment on the size of the comparison of objects No. 1 and No. 2 has the following form:
70000 – 62000 = 8000.
The adjustment for the presence of the garage is derived from the comparison of objects No. 3 and No. 5:
61600 – 59400 = 2200.
The adjustment to the completed basement is determined from the comparison of objects No. 2 and No. 4:
77000 – 70000 = 7000.
The results of the adjusted adjustments are given in table # 2.
Table number 2.
| Object number 1. | Object number 2. | Object number 3. | Object number 4. | Object number 5. | |
| Selling price | 65000 | 78000 | 56000 | 70000 | 54000 |
Transfer of right venalty |
full | full | full | full | full |
| Adjusting expense. | 65000 | 78000 | 56000 | 70000 | 54000 |
| Terms of Financiers. | not market | not market | not market | not market | Market |
| Correctrus for financing conditions. | - 3000 | - 8000 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Adjusted price | 62000 | 70000 | 56000 | 70000 | 54000 |
| Terms of a transaction | commercial | commercial | commercial | commercial | commercial |
| Correcting on the terms of the transaction | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Adjusted price in market conditions | 2 weeks | 6 weeks | 1 year | 1 year | 1 year |
| Correction on market conditions | +10 % | +10 % | +10 % | +10 % | +10 % |
| Adjustable price | 62000 | 70000 | 61600 | 77000 | 59400 |
| Location | similar | similar | similar | similar | similar |
| The size | 120kv.m. | 145kv.m. | 120kv.m. | 145kv.m. | 120kv.m. |
| Size Correction | 0 | - 8000 | 0 | - 8000 | 0 |
| Garage | there is | there is | there is | there is | not |
| Correct for garage | - 2200 | - 2200 | - 2200 | - 2200 | 0 |
| Finished basement | not | not | not | yes | not |
| Correction | + 7000 | + 7000 | + 7000 | 0 | + 7000 |
| Adjustable price | 66800 | 66800 | 66400 | 66800 | 66400 |
| Total net correction | 1800 | 11200 | 10400 | 3200 | 12400 |
| The same in% | 3 | 14 | 19 | 5 | 23 |
| From the price of sale Total gross correction | 11200 | 25200 | 14800 | 17200 | 12400 |
| From the price of sale | 19 | 32 | 26 | 25 | 23 |
For each comparison object, the adjusted price is obtained. In accordance with the terms of the task, it is required based on the corrected sales prices to bring the value of the market value.
The rationale for the output of a single market value is to give each member of a number of corrected sales prices of the weight coefficient, given the degree of difference of comparison objects from the assessment objects. It should be taken in
attention range of sales price range, total% adjustments taken in absolute value, total% adjustments defined as the difference between positive and negative adjustments, as well as any other data.
In this example, we have a practically very narrow sale price range - from 66400 to 66800. However, the selling price with smaller adjustments is assigned a greater specific weight - for object No. 5 the number of adjustments \u003d 2. In addition, the total gross adjustment amount for the object number 5 is also Almost the smallest. Therefore, as a market value of the comparison facility, the sale price of the object No. 5 - 66400 was adopted.
3.2 Risks of investment and statistics of real estate markets.
Statistics of real estate markets, as a rule, contains information about rental rates and profitability indicators. For data comparability, information applies only to first-class objects. These facilities are considered to meet the highest requirements for location, equipment, communication, planning solutions, etc., and rental rates are defined in the same standards for measuring and distributing costs between the owner and tenant for maintenance, repair, insurance, etc. .
Information about rental rates is considered accessible. It requires only the verification of the adequacy mentioned. The information about the profitability indicators is more difficult to prepare. Since the purchase and sale transactions are not so much, then the previously perfect transactions are taken into account, integrate data on various objects, take into account breaking breaks, inflation and other processes. The profitability indicators are also involved in regional risks, and the expert began here. Therefore, statistics are one of the specializations in real estate markets.
The activation of business and investment in the region is necessarily accompanied by the activation in the office market, an increase in demand, filling and rental rates. At the same time, new construction and modernization of offices is stimulated, following them - service services, shopping complexes, leisure centers, etc. Such processes are today characteristic of the largest business centers: the traditional financial capitals of America and old light, the rapidly growing capitals of Southeast Asia, China and India. An analysis of the statistics of the rental business indicates a number of interesting phenomena. For example:
Data on lease rates are significantly more dynamic than data on profitability indicators; The dynamics of rental rates is characterized by a certain oscillating, reflecting (albeit with shifts) General rates and recession processes; Changes in the indicators of office and trade real estate may not coincide in time and magnitude; Improving the market situation is reflected in the growth of rental rates and, less likely, in reducing profitability indicators (due to their noticeably lower dynamism); The asymmetric picture takes place and under the deterioration of the market situation;
The values \u200b\u200bof profitability indicators are the better (below), the more reliable and more stable regional economy, and the social situation. The leaders of a stable rental business are London, Paris and Frankfurt, where the area of \u200b\u200bchange of profitability indicators is in the region of 5-6%;
Changes in indicators for Eastern European capitals are less dynamic; This can be explained as smaller volumes of markets, fewer transactions and, apparently, the smaller interest of Western experts and business circles to these markets; Indicators of profitability for Eastern European capitals are stable - 2-3 times higher than similar values \u200b\u200bfor Western capitals. And in the period after the August 1998 crisis, the indicators of profitability in Moscow were worse than 4 or more times. And this happened not only because of the real fall of real estate value, but rather, as a consequence of an expert assessment of the state of instability and increasing business risks in this region;
Additional analytical information is proposed to be obtained using an estimated indicator of the specific capitalized value (UKS) - as estimates of the value of a certain averaged unit of commercial area of \u200b\u200bthe leased object.
A similar assessment simultaneously with an operational response to fluctuations in rental rates carries out expert opinions on the success and risks of the business.
Initial information - rental statistics for European cities - can be found in Western publications (for example, in the monthly "Europroperty"). As objects of representatives, we choose: Frankfurt, London and Paris - the centers of the most stable business, St. Petersburg, Prague and Warsaw - the centers of the transition economy with the most risky (in Europe) rental indicators.
Rental office business.
Observation period 01.99-08.00 For Western capitals, the progress of rental office business overall. We note the absolute stability of the profitability indicator for London (5.00-5.50%) and the improvement of profitability indicators for Frankfurt (from 5.75 to 4.90-5.50%) and Paris (from 6.25-6.75 to 5.50-6.00%). For the Eastern European capitals, the same period is characterized by deterioration of indicators. Analysis of the calculated data VCS allowed, in addition, to comply with the external discrepancy of the logic of rental rates (their excess in St. Petersburg and Warsaw until mid-1999 over the rates in Paris and Frankfurt). As a result, low levels of UKS at high lease rates do not allow optimism to expect investment growth.
Rental shopping business.
Observation period 05.99-08.00 For Western capitals is characterized by a general deterioration of indicators (which is clearly traced with the help of UKS). This suggests that there can be quite long periods of market activity, after which the implementation of purchased retail space will not bring real income at all.
For the Eastern European capitals, the surveillance period of 05.99-08.00 is associated with the passage of a period of long-term stagnation and, possibly, the beginning of the exit of it (an improvement in the dynamics of indicators is noted, although the gap indicators in comparison with Western capitals seems to be gigantic - almost an order of magnitude). Therefore, it should be further limited to the statement that there may be quite long periods in the markets of commercial premises, when investments in the acquisition of trade real estate in Eastern European capitals can bring a noticeable positive effect, including during periods of recession in Western markets. This can serve as a good argument when searching for ways for inter-regional diversification of the real estate portfolio.
Conclusion.
The completion of the real estate market formation period is characterized by the transition from extensive to intensive development. Obviously, in the near future there will be no such rapid growth in the number of transactions, as in the first half of the 90s. Moreover, during a certain period in the housing market, only stabilization of the number of transactions is possible. It is also possible to increase price levels, primarily on the secondary market. But at the same time, the prices for elite housing not only did not decrease, but also increased, which indicates the prospects for the new construction of high quality housing. The managers of firms are also aggravated competition in the market. Most of them are inclined to believe that if for 1995 a moderate extent of competition was characterized, then in 2001 it became high and will continue.
Stabilization of the number of transactions and prices in the secondary housing market is a consequence, primarily macroeconomic factors, the main one is to maintain a low level of income from the majority of the population. The initial rapid increase in demand in the market, as a result, the appearance of a layer of people in the country with high incomes is practically ended. And today, inside this layer there is a new differentiation - the selection of the layer with ultrahigh income. Due to this differentiation, the demand for luxury housing has increased. However, in absolute terms, the potential of this layer is very limited. The greatest expansion of demand is possible either due to increasing the level of income and the formation of a wide average layer capable of becoming the main supplier of buyers, or at the expense of active incentive demand, both the state and the professional participants of the real estate market. At the same time, some increase in demand in the future is quite possible under the influence of the emission of money inevitable in the coming months in the economy for the branch of the non-payment crisis and in connection with the repayment of debts on wages and debt on state orders. Part of this money will come to the real estate market, but they obviously do not change the situation, although the number of applications for the purchase under the influence of this factor will rise several points.
It can also be assumed that in connection with the inevitable and significant increase in tariffs for utilities, it is quite possible to increase the supply in the secondary housing market.
At the same time, if the surge of the supply in the secondary market in 1991-1993. It was caused by the rapid increase in prices, now sellers will proceed not so much of the possibility of a very significant increase in revenues through the sale of housing, how much of the need to reduce the cost of its content, and from here - agree to reduce prices. This, in turn, can also be somewhat lifted demand, which means the revisions of real estate firms.
At the same time, this stabilization will not take a common problem - the residential real estate market in the foreseeable future will experience a deficit of demand, which can significantly reduce income from traditional real estate firms for the provision of services for the sale of real estate.
Under these conditions, it is necessary to substantially expand the range of services provided by the Customer: banking calculations, transport services, services of notaries, the possibility of repair work, providing installments on payments, etc., increased attention to advertising, possibly a decrease in commission. All of these funds can play a significant role in attracting customers, but their possibilities are still limited. If for individual firms these techniques are able to provide the necessary volume of turnover, then, obviously, in general, they will not solve the problem of the development of real estate business. This problem will drastically solve this problem, and in modern conditions it is possible only at the expense of the active participation of the state by creating a mortgage lending system - the creation of federal and regional mortgage lending agencies, supporting the secondary mortgage market, providing state guarantees to banks when issuing mortgage loans.
The consistent development of the real estate market in Russia naturally led to the next stage, characterized by a jump-like increase in the quality of the standard of substantiation of investment solutions. And abroad, and in Russia, the real estate market participants come to understand that the accuracy of business plans, investment projects, etc., which are essentially a standard set of simple formulas, entirely depends on the validity of market research, the results of which are used in the formulas . In other words, the most significant and significant indicator of the impending of the investment project in the real estate market is the consistency of the market research, on the basis of which this decision is made.
Bibliography:
1. Balabanov I.T. "Real Estate Economics", St. Petersburg 2000.
2.Gamekin V.A. Real Estate Economy: Textbook. - 2nd ed., Pererab. And add. - M.: Marketing Publishing and Book Center, 2002 3. Kupchin A.N., Novikov B.D. Real estate market: condition and development trends. - Tutorial. M.: 1995.
4. Maksimov S.N. "Basics of entrepreneurial activity in the real estate market", St. Petersburg. 2000.
Russian Academy of Public Service
Under the President of the Russian Federation
Federal State Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education
North-West Public Service Academy
in Kaluga
finance and credit
THESIS
kaluga
Introduction
Chapter 1. Theoretical basis for estimating the market value of real estate
1.1 Real estate value assessment: Basic concepts and assessment principles
1.2 Approaches and methods for estimating the value of real estate
1.3 PROBLEMS PROBLEMS PROBLEMS
Chapter 2. Determination of the market value of the real estate object
2.1 Description of the Assessment Object
2.2 Determination of the market value of real estate as part of the cost approach
2.3 Determination of the market value of real estate as part of a market approach
2.4 Determination of the market value of real estate as part of an income approach
3.1 Determination of the total value of the market value of the assessment object
Conclusion
Bibliography
Introduction
The transition of our country to a market economy demanded the in-depth development of a number of new areas of science and practice, in particular, estimates of real estate value.
Real estate market - sector of the national market economy, which is a set of real estate objects, economic entities operating in the market, market functioning processes, i.e. Processes of production (creation), consumption (use) and exchange of real estate and market management, and mechanisms that ensure the functioning of the market (market infrastructure and legal environment).
Now in the real estate market, residential apartments and rooms, office buildings and facilities, manufacturing and commercial buildings, cottages, cottages and rural houses with land plots are presented. Regional features of the real estate market should be taken into account.
In the production and economic practice of economic entities, many cases appear when the need to evaluate the market value of the property of enterprises. No cost estimate does not do anything on the purchase and sale of property, lending on bail, insurance, resolution of property disputes, taxation, etc.
The determination of the market value of real estate objects is a complex and unique process, since it is almost impossible to find two absolutely identical objects. Even in the case when the buildings are built on one typical project, but located on different land plots, their cost can vary significantly.
The relevance of the topic of theses is due to the fact that today there is a great need for a competent and objective assessment of the value of real estate, and the institution of property assessment is not yet fully formed, there is no information base of the assessment, the professional training of appraisers in Russia has not yet reached the world.
The purpose of the work is to determine the market value of the property and the rationale for its increase.
To achieve the goal, it is necessary to solve the following tasks:
1. Explore the theoretical basis for estimating the market value of real estate;
2. give the characteristic object of the assessment and its surrounding;
3. justify the market value of the assessment object on the basis of three generally accepted approaches;
The object of the study is the procedure for determining the market value of the property.
The subject of the study is the substantiation of the market value of the property and the development of recommendations for its increase.
Structurally, the work consists of the introduction, three chapters, conclusion and literature of the literature. The first chapter discusses the theoretical foundations of real estate assessment, the second chapter calculates the market value of the real estate object, in the third - the results of the assessment are coordinated and the ways of increasing the market value of real estate are determined.
The theoretical and methodological basis of the study is the dialectical method of cognition, as well as the works of scientists, periodic literature and the materials of the Internet on the problem under study. In addition, the following methods were used: economic-statistical, monographic, calculating-constructive, as well as the comparison method.
Chapter 1. Theoretical basis for estimating the market value of real estate
1.1 Real estate value assessment: Basic concepts and assessment principles
Various benefits (objects, things, property) are created, sold and purchased to meet certain needs of the state, legal entities and individuals, as well as to gain benefits from owning and use. From the possibility of one or another property of the property to satisfy the available needs and advantages that will bring the possession of this object in the future, its value depends, and therefore the cost.
All properties and real estate transactions require the knowledge of the value of the property. In market conditions, the cost of real estate depends on factors, trends and changes in the economy and life of society as a whole. The need for real estate assessment arises in the following cases:
§ Operations of purchase and sale or rental;
§ Property of enterprises and redistribution of property fractions;
§ Attracting new shareholders and additional share emissions;
§ Cadastral assessment for the purpose of taxation of real estate objects: buildings and land;
§ Insurance of real estate objects;
§ lending on the security of real estate objects;
§ introduction of real estate objects as a contribution to the authorized capital of enterprises and organizations;
§ Development of investment projects and attracting investors;
§ elimination of real estate objects;
§ performance of the rights of inheritance, court sentence, resolution of property disputes;
§ Other operations related to the implementation of property rights to real estate.
Real estate (real estate, real estate) include land plots, sections of subsoil, separate water bodies, and all that is firmly connected to the Earth, that is, the objects that are impossible without disproportionate damage to their purpose, including forests, perennial plantings, Buildings, facilities. Real-statements are also subject to state registration of air and sea vessels, internal navigation vessels, space objects. The law to real estate can be attributed to other property.
When assessing real estate it is believed that the Earth has the cost, while improvements is the contribution to the price.
Real estate is located in a free civil circulation and is the object of various transactions, which generates the need for an assessment of its value, i.e. In determining the monetary equivalent of various types of real estate at a specific point in time.
In the modern economy there are many different types of value. They are necessary due to the various needs and functions. This includes such species as borrowed costs, insurance cost, reasonable market value, book value, rental cost, liquidation cost, investment value and many others. However, in general, the cost can be divided into two categories: the cost in exchanging and the cost of use.
Cost in exchange is the price that will prevail on the free, open and competitive market based on equilibrium established by the factors of the proposal and demand. It is sometimes called objective cost, since it is determined by real economic factors.
The cost of use is the cost of ownership for a specific user or user group, i.e. The cost of real estate, which is used as an integral part of the existing enterprise (for example, the real estate used by the plant).
Of all the types of value, the market value was most common - the main type of value in the conditions of market relations. When determining the market value, we proceed from the fact that the market existed in the past (property facilities were already sold), exists in the present (property is created for sale) and will exist in the future, since neither the past nor real market contradicts it.
Based on the foregoing, it can be concluded: not only the market itself, but also formed by the market tools, the most important of which is the cost, have a three-component nature. From these positions we can say that the cost:
Really cost, i.e. the most likely price in the conditions of this market;
Really market, since the space of market values, which includes the cost of a specific object, is formed solely under the influence of factors of the free, open and competitive market;
It is indeed objective, because it reflects the opinions of all major subjects of the manufacturer's market (seller), the buyer and investor, thereby exhausting the market interests of the parties.
The cost can be learned from the past, putting yourself to the buyer's place, from the present, putting yourself to the place of the builder and from the future, if we put ourselves to the place of the investor. From here there are three main approaches to property assessment: market, costly and profitable approaches.
The main task in determining the cost is to predict the quantity, quality and duration of future benefits from the object of assessment and recalculating these benefits to this value. Property is analyzed on the basis of the assessment principles.
The assessment principles are divided into four groups:
1) principles based on user submissions (principles of utility, substitution and expectations);
2) principles arising from the process of operation of the property (principles of deposit, residual productivity, limit performance, balance, economic size and economic separation);
3) principles due to the action of a market environment (the principles of alternativeness, variability, dependence, supply and demand, competition and compliance);
4) The principle of the best and most efficient use is the main principle of evaluation. This principle combines all other principles and is the foundation of any real estate assessment.
A prerequisite for real estate assessment is to account for the specifics of the functioning of the real estate market, as the state of the real estate market has a significant impact on the flows of income, risk levels and on the possible price of real estate object at a certain point in the future, i.e. The basic data used in evaluating the methods of an income approach.
1.2 Approaches and methods for estimating the value of real estate
In assessing real estate, there are three generally accepted approaches to the definition of value: cost, market and profitable. Each approach has its own methods, techniques and procedures. The conceptual similarity of approaches to the assessment of various property facilities is found. At the same time, the type of object of the estimated object determines the features of specific methods arising from specific assessment problems inherent, as a rule, only in this type of ownership.
Cost approach
The cost approach to the assessment of real estate is based on comparison of the cost of creating a real estate facility with the cost of evaluated or comparable objects. The approach is based on the study of the investor's capabilities in the acquisition of real estate and proceeds from the principle of replacement, which the buyer, showing a proper benefit, will not pay a large amount for the object than the one in which the relevant construction site will be obtained and the construction of an object similar to the appointment and quality In a foreseeable period without significant delays.
The main stages of the assessment procedure under this approach:
1. Calculation of the cost of acquisition or long-term lease of free and available land in order to optimally use it;
2. Assessment of the replacement value of the estimated building. The basis of the calculation of the replacement cost is the calculation of the cost of reconstitution of the object under consideration, based on the modern prices and conditions for the manufacture of similar objects for a specific date.
3. Determination of the magnitude of the physical, functional and external wear of the object of real estate;
4. Evaluation of the value of entrepreneurial profits (Investor's profits);
5. Calculation of the total value of the assessment object by adjusting the replacement value for wear with the subsequent increase in the value obtained on the value of the land plot.
The cost approach is most appropriate in assessing objects recently commissioned, it leads to the most convincing results in the case of a sufficiently reasonable value of the land plot and minor accumulated wear of improvements. The cost approach is legitimate when estimating the cost of planned objects, special purpose objects and other property, the transaction on which is rarely held on the market, can be used in assessing for insurance purposes. This approach in assessing objects subject to reconstruction allows you to establish whether construction costs will be compensated by an increase in operational income or revenue from the sale of property. The use of the cost approach in this case allows you to avoid the risk of excess investment.
Also, the cost approach is used for the purpose of taxation of property of legal entities and individuals, during the arrest of real estate, for analyzing the best and most efficient use of the land plot.
Determination of the value of the land
In accordance with Art. 35 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation in the transition of the right to the building, structure, the construction, which are in someone else's land, to another person, it acquires the right to use the appropriate part of the land plot engaged in the building, structure, structure and necessary for their use, under the same conditions and In the same volume as the former owner.
Of all the methods of evaluating the land, the method of comparative sales analysis is determined.
The replacement cost of the construction of an estimated real estate object is calculated at current prices as new (excluding accumulated wear) and correlating to the date of evaluation. The determination of the replacement cost is the calculation of the costs associated with the construction of the facility and the surrender to its customer. Depending on the procedure for taking into account these costs in the cost of construction, it is customary to allocate direct and indirect costs.
Direct costs are directly related to the construction (the cost of materials, the wages of construction workers, the cost of building machines and mechanisms, etc.). Indirect costs - costs that are not directly related to construction (fees in design and estimate organizations, the cost of investment in the land, marketing, insurance and advertising costs, etc.). The profit of the developer reflects the costs of management and organization of construction, overall supervision and development related entrepreneurial risk. The profit of the entrepreneur is defined as part of the profit from the sale of the object. Regardless of the magnitude of the percentage and the relevant foundation (part of the property value), the value of entrepreneurial profits remains constant.
The main source of comparative data on the cost value of real estate objects are building contracts for the construction of structures similar to the estimated. In addition, the design appraisers usually lead their own databases of current prices for ready-made homes, office buildings, apartments, hotels, shopping buildings and industrial facilities. Currently, in Russia there is a system of standards and price levels defined by the relevant price indexes.
The constructed objects under the action of various natural and functional factors lose their operational qualities and are destroyed. In addition, the market value of the object has an influence of an external economic impact on the part of the immediate environment and changes in the market environment. At the same time, physical wear (loss of operational qualities), functional aging (loss of technological conformity and value due to scientific and technical progress), external or economic wear (change in the attractiveness of the object in terms of changes in the external environment and the economic situation in the region) are distinguished. All together, these types of wear are accumulated wear, which will be the difference between the reducing cost of the object and the cost of reproduction (substitution) of the assessment object.
The most complete and reliable source of information on the technical condition of the building or facilities is the materials of a natural survey. The first condition for conducting such surveys should be the exact definition of the functional purpose of the object of the assessment: the use of direct purpose or with a change in technological and functional parameters. At the same time, it is necessary to present the limits of changes in loads and impacts on the supporting structures of buildings.
The second condition for conducting research is to obtain full information on the natural and climatic parameters and specific factors of the impact of the area of \u200b\u200bthe object and their changes in the process of man-made activities.
Market approach
The necessary prerequisite for the application of the methods of a market approach is the availability of information on transactions with similar real estate objects (which are comparable for intended, size and location) in comparable conditions (the time of making a transaction and the terms of financing the transaction).
A comparative approach is based on the three basic principles of real estate assessment: supply and demand, substitution and contribution. Based on these principles of real estate assessment in a market approach, a number of quantitative and qualitative methods for selecting comparison elements and measurement of market data adjustments of comparable objects are used to model the cost of the estimated object.
The main principle in the market approach assessment of real estate is the principle of substitution, which states that the potential buyer will not pay the price of the price that exceeds the cost of acquiring similar, from its point of view, property.
The main difficulties in the application of the methods of a market approach are associated with the opacity of the Russian real estate market. In most cases, real estate prices with real estate objects are unknown. In this regard, it is often used to assess the prices of proposals on the facilities on sale.
The sales comparison method determines the market value of the object based on the analysis of recent sales of comparable real estate objects that are similar to the estimated object in size and use. This method of determining the cost assumes that the market will set the price for an estimated object in the same way as for comparable, competitive objects. In order to apply sales comparison method, specialists use a number of assessment principles, including the principle of substitution.
The application of the sales comparison method consists in a consistent implementation of the following actions:
1. Detailed market research in order to obtain reliable information about all factors related to comparable utility objects;
2. Determination of suitable comparison units and comparative analysis on each unit;
3. Comparison of the estimated object with selected comparison objects in order to adjust their sales prices or exceptions from the list of compared;
4. bringing a number of adjusted indicators of the value of comparable objects to the market value of the assessment object.
Real estate office, government sources, own databases, publications, etc. can be used as sources of information on market transactions with real estate.
After selecting the comparison unit, it is necessary to determine the main indicators or elements of the comparison, using which you can simulate the cost of the object by means of the necessary adjustments to the purchase and sale prices of comparable real estate objects.
In the appraisal practice, in determining the value of the property, such basic elements of comparison are allocated as the transferred rights to real estate, the terms of financial settlements in the acquisition of real estate, the terms of sale (cleanliness of the transaction), the sale time, the functionality of the object, the location, convenience of access roads, the object, technical The condition and level of finishing of the premises.
This method is most effective for regularly sold objects.
To highlight the elements of measuring adjustments, quantitative and high-quality techniques are used.
The quantitative methods include:
· Analysis of paired sales (two different sales are compared to determine the adjustment for one comparison element);
· Statistical analysis (the method is based on the use of the apparatus of mathematical statistics for conducting correlation and regression analysis);
· Analysis of the secondary market (this method determines the magnitude of the adjustments, based on the data that is not directly related to the object of the assessment or the object of comparison) and others.
Qualitative methods include:
· Classification (comparative) analysis (the method is similar to the analysis of paired sales, except that adjustments are not expressed in percent or money amounts, but in the categories of fuzzy logic);
· Distributional analysis (comparative sales are distributed in descending order of adequacy, then the place of assessment object is determined in a number of comparative sales).
Profitable approach
The determination of the market value of real estate objects through an income approach is based on the principle of expectation. In accordance with this principle, a typical investor, that is, the buyer of the real estate object, acquires it in anticipation of receiving income in the future. Considering that there is a direct link between the size of investments and benefits from the commercial use of the investment facility, the cost of real estate is defined as the cost of obtaining income from it, in other words, the cost of the real estate object is defined as the current cost of future income generated by the assessment object.
The advantage of the revenue approach compared to the cost and market approaches is that it reflects the presentation of the investor on real estate as a source of income, that is, this property quality is taken into account as the main pricing factor. The main disadvantage of the income approach is that, unlike two other approaches, it is based on the forecast data.
The main stages of the assessment procedure under this approach:
1. Compiling the forecast of future revenues from the delivery of the estimated areas for rent over the spent period and on the basis of the data obtained, the determination of potential gross income (PVD), which is calculated by Formula 1.1:
PVD \u003d S * CA, (1.1)
S - area, rental, sq.m;
Sa - rental rate for 1 sq.m.
2. Definition based on the analysis of the market for under-use areas and when collecting rent, calculate valid gross income (DVD). As a rule, the owner in the long term does not have the ability to continue to lease 100% of the building area. Rental loss takes place due to the incomplete employment of the object of real estate and non-payment of rental fee by unscrupulous tenants. The degree of unemployment of the object of revenue real estate is characterized by the coefficient of under-use, determined by the ratio of the value of the area not leased to the value of the total area to be leased.
Calculation of valid gross income (DVD) is carried out according to Formula 1.2:
DVD \u003d PVD * kz * ks, (1.2)
Dvd valid gross income;
PVD potential gross income;
Kz coefficient loading of space;
COP Payment Collection ratio.
It should be noted that the DVD, calculated by the foregoing, it is necessary to add other revenues obtained from the functioning of the object over lease payments (for example, for using additional services - automotive parking, etc.).
3. Calculation of the costs of operational estimates, which is based on an analysis of actual costs of its content and / or typical costs in this market. Expenses are conditionally constant (property tax, insurance premiums, payments for land), conditionally variables (utility, current repair work, employee salary, etc.), replacement costs (costs for periodic replacement for spending constructive design Building elements).
Thus, the calculated value of operating costs is deducted from DVD, and the final indicator is a net operating income (chod).
4. Recalculation of net operational income to the current value of the object.
Direct Capitalization Method - Method for determining the market value of an income-based object, based on the direct transformation of the most typical income of the first year in the price by dividing it to the capitalization ratio, obtained on the basis of analyzing market data on the ratios of net income and value of assets similar to the estimated object obtained by the market Extraction. Such a western classic version of the direct capitalization method, in which the capitalization ratio is extracted from market transactions, to apply in Russian conditions is almost impossible due to emerging difficulties in collecting information (most often the conditions and prices of transactions are confidential information). Based on this, in practice you have to use algebraic methods for constructing a capitalization coefficient, providing for a separate assessment of the rate of return on capital and the norms of its return.
It should be noted that the direct capitalization method is applicable to evaluate existing assets that do not require the date of the assessment of large in the duration of capital investments in repair or reconstruction.
1.3 PROBLEMS PROBLEMS PROBLEMS
Difficulties are associated with a number of problems arising in property assessment (approaches and methods), incorrectness or inconsistency of laws and decisions in this area. Consider these questions a little more.
The first problem in the account, and not for the purpose - the choice of capitalization and discount rates.
1. The cost of the loan (capital value) - for enterprises that do not have independent behavior (there is no securities market).
2. The average margin value of own finance - for enterprises whose shares are quoted in the market.
3. Based on the average production profitability of the enterprise or its own industry.
4. Average margin limit costs of projects studied (during investment).
5. Norms of reimbursement on loans.
6. Planned standards.
7. The rate of loan interest (a political economic concept associated with national income (ND) and an internal national product (GNP)).
8. The yield of alternative investment (for example, a deposit account in the bank).
9. Minimum risk-free yield, from the point of view of the investor.
The real short-term interest rate, defined as the difference between the yield of treasury bills and the consumer price index.
A lot of practical techniques for choosing a bet with the same theoretical base indicates the disadvantage of the methods and the criterion of its choice. Determining the rate of the room is beyond the limits of the theory of finance management - in the field of psychology (art sector, not science).
To make an assessment by different specialists, it follows the magnitude of a complex interest rate to adopt legally and reflect in the methodology, as was at one time, according to the regulatory efficiency of capital investments (investments - as it is now considered). Initially, the rate of efficiency was different for each industry, then one norm for all industries was adopted. It should be emphasized that the standard efficiency coefficient performed the same role (carried out the same load) as the capitalization rate (the rate of efficiency, the comparison rate, the investment plant).
The second problem is associated with a point estimate of the property value. The situation is such that ten experts working independently from each other will give ten different estimates of the value of the same property (property). This is due to the procedure for calculating and choosing regulatory coefficients. The situation resembles the manufacture of details. On the same machine with the same working one and the same drawing will be made different details. For this there are plenty of reasons, most of which are in principle cannot be excluded. Therefore, the production system adopted a system of tolerances on the size of parts. If the dimensions of the manufactured part are within the tolerance, it is considered suitable. Deviations and scattering of the source data used to calculate in all approaches and methods, in percentage of the average are more significant than the tolerances on the size of the parts.
The way out of this position (solving this problem) is to replace the point estimate of the property value of the interval - on the one hand, and the numerical calculation should be guided by probabilistic methods. The concept of assessment in mathematics implies an approximate calculation, most often at the level of the number of numbers. For example, when calculating the logarithmic line, it was necessary to determine the number of numbers in the integer part of the number.
Another problem is related to the choice of weight coefficients when coordinating the calculations of the value of the property performed in three approaches. Each author (expert, appraiser) accepts weighting coefficients (the ratio of the significance of the calculation method) at its discretion, and the difference between the estimates is essential. One of the outputs from this situation is the adoption of the weighting coefficient is evenly distributed in a certain range for each method (approach) assessment.
The following problem occurs with a comparative (market) valuation of the property value when it is necessary to introduce correction coefficients to bring to a comparable type of estimated object and market analogues. There is also significant arbitrariness here. This is especially true of correction coefficients in comparison of places of territorial placement of the estimated property objects and a number of others.
One of the most difficult problems is the accuracy of the information. This concerns both market information about the requested and sold price of the estimated cost of property and information on standards when calculating the value by the regulatory method in the cost approach. Previously, this information was from the design and technological institutions of all sectors of the national economy. Such information is either lost or outdated.
To relieve most of the problems arising in the process of valuation of the property, all calculations should be performed on the basis of probabilistic intervals. As a result of the calculation, the cost of ownership will be presented in the form of a truncated distribution. As an offer (OFFER Price OF COST), the cost of the cost should be recommended the median value estimation. In this case, the chances of the seller and the buyer are the same: the likelihood of the buyer to buy cheaper prices of the proposed price is equal to the seller to sell more expensive prices.
In this case, the seller, and the buyer have full information about the possible prices of purchase and sale and their probability. Depending on the urgency of the alleged transaction, the counterparties can make weighted solutions: to wait for the buyer and look for another object of acquisition, if the time is tolerate; For the seller - a decrease in the requested price if urgency arises in the implementation of the transaction.
There are many of these options that occur in the market. For the seller and buyer, urgency in buying-selling can be different.
In 2001, a decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 6 No. 519 was adopted, in which the Ministry of Property Relations of the Russian Federation is charged with the duty "Development and approval of methodological recommendations on appraisal activities." This must be fulfilled in relation to various assessment objects, types of value of the object of assessment, assessment, as well as an assessment report examination. The work is carried out in coordination with the federal executive authorities that regulate in the relevant field of activity.
However, the Ministry is not able to develop a methodology for all property objects (for all occasions) and even more so to develop regulatory materials.
Therefore, at the level of the region, depending on the existing ownership market on the basis of the general-industry methodology, develop regional techniques for groups of homogeneous objects with the creation of the necessary regulatory framework. Then the task of coordination and approval of local techniques at the level of the edge, city or region is arising.
The coordination and approval procedure of regional methodological materials in relation to various property facilities should be regulated by the Ministry of Property Relations of the Russian Federation.
This will help more reasonably evaluate all types of value of various types of ownership, which will remove various misunderstandings, will result in comparability of the results of the calculation by various appraisers and evaluating firms and reduce the semicriminal shade in the scope of evaluating activities.
Chapter 2. Determination of the market value of the real estate object
2.1 Description of the Assessment Object
Currently, there is a sufficiently steady demand for new real estate in the form of separate buildings, in price range $ 330- $ 3250 sq.m. In general, the proposal ranges from $ 400 sq. M to $ 4500 sq.m. At the same time, a tendency to some increase in the upper limit of the price of the offer is noticeable.
This is explained by the fact that even recently insolvent demand becomes financially reasonable.
On the other hand, especially prestigious office premises and retail space to date "found" their relatively permanent owners. Accordingly, the prices of premises are growing although less prestigious, but still alleged for sale. In addition, the price fluctuations are not always justified from the point of view of economic logic.
The property is owned by Aris LLC and is located in the Leninsky district of Kaluga.
The object includes a three-story brick administrative building with a restaurant with a total area of \u200b\u200b1.375.8 sq.m.
The object is located on one of the most extended highways of the city, relatively not far from the business and administrative center of Kaluga. Transport accessibility is good.
Description of the land plot
Plot shape rectangular;
Land area 556.0 m2.
State of soil The base of the foundations of the building is sandy soils.
Topography of terrain: Relief plot calm.
Security infrastructure:
The following communications are connected to the residential building for:
· Water supply;
· Sewage;
· Power supply;
· Heat supply;
· Telephoneization
Possible restrictions on the use and servitude
Permitted use.The practice of working in the real estate market shows that the change in the functional purpose of real estate is possible only when agreeing with the local administration authorities, which confirms the owner of the assessment object.
Services.It is assumed that typical commotes are applied to the site, such as the right to travel and conduct communications, but the assumption is made that none of the existing commotes should be an obstacle to the best and most efficient use of the site. The plot does not include monuments, unique natural objects, LEP supports, remedy signs, etc., therefore there are no special restrictions for the construction of office and residential premises.
Building Description
The building has 3 floors, subject to modern construction standards.
Table 1
Constructive elements of the building
| Constructive element | Characteristic | Technical condition |
| Foundations | Concrete belt | Excellent |
|
and their outdoor decoration |
Silicate brick red finishing brick, t \u003d 0.5 |
Excellent |
| Partitions | Brick | Excellent |
|
Overlap: Attic; Internet; Advance |
W / concrete W / concrete W / concrete |
Excellent |
| Roof | Combined | Excellent |
| Floors | Parquet, tile, linoleum | Excellent |
|
Wooden |
Wooden modernized | Excellent |
| Interior decoration | Euroclass | Excellent |
|
Sanitary and E / Technical devices: · Heating · water pipes · Sewer · E / Lighting · telephone · ventilation |
Central, from boiler room Stock in city collector Hidden wiring Natural |
Excellent |
| Other works | soleshe | Excellent |
2.2 Determination of the market value of real estate as part of the cost approach
As an analog object in this case, an administrative brick three-storey building is selected according to Sat. OPVS number 33, Table. 4 (enlarged indicators of the replacement cost of construction of residential, public, utilities and household service buildings. M: 1972) Table 52 as the most appropriate assessment facility.
table 2
Comparative analysis of the object of evaluation and analog facility
(Definition of the likeness ratio)
| Constructive elements | Object analog | Evaluation object | The degree of similarity (coeff. Like) | Specific weight, elements% | |||
| object analog | evaluation object | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| 1. Foundations | r / B blocks | r / B blocks | 1,00 | 5,0 | 5,0 | ||
| 2. Walls and partitions | brick | brick | 1,00 | 24,0 | 24,0 | ||
| 3. Overlapping | w / concrete | w / concrete | 1,00 | 9,0 | 9,0 | ||
| 4. Floors | concrete | concrete | 1,00 | 10,0 | 10,0 | ||
| 5. Operactions | simple wooden | simple wooden | 1,00 | 11,0 | 11,0 | ||
| 6. Interior decoration | simple | - | 0,00 | 8,0 | 0,0 | ||
| 7. Sanitary and electrical devices |
· Center. Top. · water pipes · Sewer · ventilation · EL / lighting |
· Center. Top. · water pipes · Sewer · ventilation · EL / lighting |
1,00 | 12,7 | 12,7 | ||
| 8. Roof | roll by railway plates | ─ | 0,00 | 6,0 | 0,0 | ||
| 9. Stairs and inputs | – | – | 1,00 | 5,0 | 5,0 | ||
| 10. Simple work | – | – | 1,00 | 9,3 | 9,3 | ||
| TOTAL: | 0,8 | 100 | 86 | ||||
| Correction factor | 0,86 | ||||||
Determination of the total reducing value of the assessment object.
Basic source data:
· Capitalization group - I.;
· Construction volume: vstro. \u003d 4 444 m3;
· Total area: S \u003d 1.375.8 m2;
· Sources of regulatory data: SB OPPS No. 4, Table 52
Basic settlement formula:
PVS \u003d US1969 x vstro. x and69-84 x and84-20.12.2007 x Kn, (3.1)
where PVS is the full reducing cost of the object, rub.
US1969 The cost of construction of a unit of construction volume in prices 1969; Us1969 \u003d 24,9 p / m3
Vc. Building volume, cube. m;
And69-84 index of cost recalculation from 1969 prices in prices 1984; For residential and commercial buildings on average - 2.21;
And84-20.12.2007 - the index of recalculation of the cost from the prices of 1984 in prices for the date of the assessment (20.12.2007) for inf. Sat By pricing and calculations for the work done in construction, Kaluga: December 2007;
K84-20.12.2007 \u003d 61.07
NN correction coefficient by contrast to the assessment facility. Kn \u003d 0.86
Calculation of the full reducing value of the object:
PVS \u003d 24.9 x 4 444 x 2.21 x 61.07 x 0.86 \u003d 12.843.755,88 руб.
Estimation of wear (impairment) of the object
Based on the alleged effective life term of the object (I, the capital capacity group), physical wear (impairment) on the date of the assessment will be 5%, i.e. 642.187.80 rub.
Since the building is new, functional (moral) wear.
Economic (external) wear is not set: the buildings of this type and state are currently in demand by the market, and there is no reason to assume that the specified position will notice anything significantly change in the near future.
Determining the profit of the entrepreneur
The profit of the entrepreneur is the market established by the market, which the entrepreneur expects to receive in the form of a premium for the use of its capital investing in construction.
The profit of the entrepreneur (PPR) can be determined from the relationship between the entrepreneurial income of the DPR and the cost of construction (C / B p.), Taking into account the construction period (TST.) By the formula:
According to the Kaluga Construction Organizations, the cost of construction of 1 square meters. M of individual office buildings of the usual building averages 10500 rubles. Taking into account the finishes. The usual decoration of the premises increases the cost of construction by 9-12%. The trim of the Lux class increases the cost of individual works by 1.38 times (the Marshall & SWIFT directory). The construction period is currently usually not exceeding 2 years. The cost of investing in Kaluga in retail space, located within the central part of the city lies in the range $$ 1200 ÷ 3500 square meters. M. We accept the amount for our calculations - 1,200 dollars, or 30936 rubles. Under these conditions, the profit of the entrepreneur:
 \u003d 0.937, or 97.3%.
\u003d 0.937, or 97.3%.
Table 3.
Calculation of the total value of the value of the assessment object
Thus, the market value of the property obtained by the cost approach is 25.982.918.15 rubles, or rounded 25.982.918 rubles. (Twenty-five million nine hundred eighty-two thousand nine hundred eighteen rubles) without VAT.
2.3 Determination of the market value of real estate as part of a market approach
Table 4.
Characteristics of objects of comparison
| Characteries Tick Comparison Objects | Evaluation object | Object number 1. | Object number 2. | Object number 3. | Object number 4. | ||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||||
| Address of the object | kaluga, ul. Suvorova, D.29 |
g. Kaluga, street-Visionnaya St., D.2A |
g. Kaluga, ul. Moscow, d.237 |
g. Kaluga, ul. Azarovskaya, d.26. |
g. Kaluga, Crystal |
||||
| Year of Construction | 2002 | 1995, Reconstruction of 1998. | 2003 | 1971, Reconstruction 2002. | 1988 | ||||
| Total area (sq. M.) | 1375,8 | 1157,1 | 297,3 | 2234,0 | 3806,0 | ||||
| Main appointment in the current state | Office space, cafe, resting | Office rooms | Office premises, resting | Office-exhibition | Office rooms | ||||
| Initial purpose | also | Administrative building | Administrative building | Book base | Admin.-Watering Building | ||||
| External enclosing structures | brick | brick | brick | brick-panel with foam block inserts | railway panels | ||||
| Location | above average | average | average | below the average | below the average | ||||
| Land plot |
122971 m2 (there are other buildings) |
under the building | under the building + Priarama | ||||||
| Finishing quality | class "E" | class "y" | class "luxury" | class "luxury" | class "E" | ||||
| Parking and vehicle quality | Along the street, special. organized, 20 m long; Playground in the courtyard | Parking along the street (20 m); Internal parking | Organized Parking (Spec. Playground) | Along the street, special. organized with a length of 20 m; Internal parking | Limited internal parking | ||||
| Period of sale | –– | december 2007 | august 2007 | february 2007 | october 2006 | ||||
| Floors | 3 floors | 2 floors | 3 floors | 2 floors | 3 floors | ||||
| Price 1 sq. M. m. total area, rub. rub. | – | 33000 | 41500 | 28500 | 15500 | ||||
Definition (rationale) adjustments
1. Correction on market conditions (sale date)
In this case, the most correct is the use of the pair sales method. It implies the allocation of objects that differ only in terms of sales and determine the magnitude of the adjustments. We have not been detected such objects, because the magnitude of the adjustments was determined on the basis of data on the monthly rates of inflation for the periods of interest to us by the formula:
where Mi average monthly pace of inflation, KINFL. \u003d 1,0072.
Estimated formula: KINFL \u003d KSR.M.INFL \u003d const KSR.M.INFL \u003d 1,0072
100 × KTSRMINFL 100
Table 5.
2. Location.
The location of the compared objects was estimated on the basis of an expert assessment on the scale: "beautiful", "excellent", "good", "above average", "mean", "below average", "satisfactory", "bad", "very bad." Thus, the scale consists of 8 gradations. Each gradation was estimated at 10%.
Table 6.
| Evaluation object | Object number 1. | Object number 2. | Object number 3. | Object number 4. | |
| Location | above average | average | average | below the average | below the average |
| The magnitude of the adjustments,% | - | +10 | +10 | +20 | +20 |
3. Adjustment on a physical difference.
The only significant difference in comparison objects and object object is the material of the enclosing structures in the comparison object No. 3 - railway panel, while in the object of the assessment and in other comparison objects for these purposes a brick is used. This difference is estimated by us in the amount of 6%
4. Adjustment on the state of the object
The state in which the object of purchase and sale has a direct impact on its price. The most simply take into account the difference on the factor "condition", adjusting the sales price for the cost of repair work, which must be carried out so that the comparison object becomes to correspond to the state of the assessment object.
In this case, the state of the object was estimated by the expert in the range of the following gradations: "excellent", "good", "above average", "average", "below average", "satisfactory", "bad", very bad "with the price of one graduation - 6%.
Table 7.
5. Adjustment on the quality of the finish
When evaluating the quality of the finish, six levels of quality were considered:
· Higher quality - class "Lux";
· Increased quality - class "U";
· Average quality - class "C";
· Satisfactory quality - class "E" (economical)
· Low level quality - "H";
· Very bad - "Oh".
Graduation price 5%
Table 8.
6. Adjustment on the object area.
In our case, we have space interval from 297.3 m2 to 3806.0 m2. According to our studies, an increase in 1 m2 area gives a decrease in the price of 1 m2 by magnitude:
(Sob. Sob.Oz) x K, (3.3)
where: Sob.SR Object area of \u200b\u200bcomparison;
Sob.Oz area of \u200b\u200bthe object of assessment;
To empirical coefficient, k \u003d 0.00533
Estimated formula:
Table 9.
7. Adjustment for the presence of a land plot.
The presence of a land plot is regarded as an advantage, since it is one of the potentials of the object. Studies show that in most cases, the presence or absence of a land plot in office buildings is estimated by the market within 5% of the value of the object (in addition to the transport area).
8. Adjustment to floors.
In our case, objects are considered with the number of floors from 2 to 5. Studies show that the number of floors of more than 3rd are not considered an advantage. The present conjuncture of the office office market is such that investors and tenants prefer to use buildings as office space with 2 ÷ 3 floors. From the point of view of market value (value in exchange), not investment (in use), the cost of 1 sq. M. Buildings with a floor of more than 3 years lower than the cost of 1 sq.m. 2 ÷ 3 storey buildings. Up to 5 ÷ 6 floors such a decrease in cost lies within 3 ÷ 5%. For 9, 11-storey buildings, this value is 12 ÷ 15%.
9. Adjustment for the presence and quality of parking.
The presence of parking from the property is regarded as an increase in value factor. In this case, the availability and quality of parking were estimated. Parking quality was viewed in three versions:
· outdoor parking - along the street before the facade of the building highlighted a parking lot of cars within 50m; Such parking was expected to be 5% (secondary quality);
· organized parking -off the road highlighted a special asphalt car parking platform - 10%, (good quality);
· interior parking -parking for cars behind the gates of the enterprise (in the internal territory) - 0%, (bad).
Table 10.
Final adjustments
| Comparison elements | Comparable sales | ||||
| Evaluation object | Object number 1. | Object number 2. | Object number 3. | Object number 4. | |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Price sale, rub. / Sq. M. | –– | 33000 | 41500 | 28500 | 15500 |
| Transferred rights | Full property right | Full property right | Full property right | Full property right | Full property right |
| The magnitude of the adjustment | ― | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Adjusted price | ― | 33000 | 41500 | 28500 | 15500 |
| Financing conditions | Market | Market | Market | Market | Market |
| The magnitude of the adjustment | ― | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Price after adjustment | ― | 33000 | 41500 | 28500 | 15500 |
| Terms of sale | Commercial | Commercial | Commercial | Commercial | Commercial |
| Correction on Sale Conditions | ― | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Price after adjustment | ― | 33000 | 41500 | 28500 | 15500 |
| Market conditions (date of sale) | ― | december 2007 | february 2007 | october 2006 | |
| Correction on market conditions | ― | 0,0 | +9,0 | +13,0 | +17,1 |
| Price after adjustment | ― | 33000 | 45235 | 32205 | 18151 |
Conclusion: The smallest number of adjustments is made according to the object of comparison No. 3, so the price of the assessment object is taken equal to the adjusted price of the comparison object number 3, i.e. 32205 rub. / Sq.m. The value found is in price range from 18151 rubles / sq. M to 45235 rubles / sq.m. The cost of the object of the assessment obtained by the method of direct sales comparison will be: 32205 × 1375.8 \u003d 44.307.639 rub.
Thus, the cost of the assessment object is 44.307.639 rubles. (Forty-four million three hundred seven thousand six hundred thirty nine rubles) without VAT.
2.4 Determination of the market value of real estate as part of an income approach
A direct capitalization method was used to assess the value of the real estate object as ready for operation. This method gives a fairly accurate estimate of the current value of future income in the case when the expected revenue flow is stable or has a permanent growth rate (fall).
Analysis of income
All incomes for the estimated object are predicted based on rental fees for rooms of various functional purposes. We have conducted a market research, the purpose of which is to establish rental rates for residential premises that would be comparable to the object of assessment. This study included an interview with several owners, rental agents and developers, the study of suggestions and conditions of the existing lease.
During the preparatory work, it was found that taking into account the location of the object and its profile to calculate the following monthly rental cost: 1175 rubles / sq.m
Analysis of expenses
Operational costs are current costs associated with the ownership and operation of the property. They are divided into permanent - the value of which does not depend on the degree of production of the building by users (property taxes, insurance premiums, land fees), and variables - depending on the degree of loading of the building (payment of electricity, water, etc.).
Real estate taxes include: land tax, building tax. Since the value of the land under this assessment was not made, the level of its taxation should not be determined.
The property tax is 2% of the balance value of the property (the book value \u003d initial value - wear).
For the newly purchased object, the initial cost is equal to the purchase price. For just built or under construction, the initial value is equal to the cost of construction, wear is equal to 0. The book value of the building on the evaluation date is made up of the price of the acquisition (or book value at the time of purchase) of the building and the costs of reconstruction, excluding VAT. We consider the value of the property tax constant, because For the building of 1 of the Group of Capitalities, the depreciation coefficient is 1% per year, and the change in the value of property tax can be safely neglected.
Insurance payments are 0.3% of the restorative cost of the finished object, excluding VAT.
In this case, the magnitude of communal payments is adopted in the amount of 7% of the valid gross income (DVD).
The inclusion of the cost management costs in operating costs is associated with a feature of the property as an income source. Property ownership, in contrast to ownership of a cash deposit in a bank, requires certain efforts to manage the object. Regardless of whether the owner does this is a management or a third-party company, including the costs of managing general costs, we thus recognize that part of the gross revenue from the lease is not directly directly as a real estate object, but the efforts of the manager.
For this type of objects, the control costs are 2.2% of the actual gross income.
Since the building of the construction of 2002 and overhaul is not required, the costs of current repairs are determined in the amount of 4% of the EU.
On the basis of available reliable data on the cost of replacement of short-lived elements of buildings that have similar characteristics with an assessment object, a value of 3.6% of the EU is taken to calculate.
Other expenses usually make up 2% of the amount of operating expenses.
Determination of the total capitalization coefficient
Capitalization coefficient reflects the dependence of the value of the object from the expected income from its operation. Due to the lack of sufficient data on sales of similar objects, the capitalization rate can be defined only by the method of summation, according to which the value of the capitalization rate is equal to the amount:
SC \u003d NPB / P + P + L ± SV.K., where
SC - capitalization rate;
NPB / R risk-free profit rate;
P is a surcharge for the risk corresponding to the investment in this asset;
L - allowance for the low liquidity of the object;
SV.K. Return rate of capital.
The risk-free rate on urgent currency deposits in the banks of the highest category is 5-9% (we accept 7%).
Risk surcharge (P). The probability of the death of the property was estimated on the basis of information on the number of cases of the death of property in Kaluga, taking into account the collected data p \u003d 4%.
Supplement for extra risk - 4%.
The coefficient of liquidity is determined by the approximate time for the sale of real estate of this type, which is estimated by us, taking into account the current economic situation in 0.4 years.
KN / LIKV. \u003d Kbezezrisk. × Sales time \u003d 0.07 × 0.4 \u003d 0.028 or 2.8%
The premium for the risk of investment management is made in the amount of 4.8%.
The second component of the general coefficient of capitalization is the rate of capitalization or an increase / decline in the cost of the Fund - is calculated as the relationship of a unit by the number of years required to return invested capital.
The time required to return capital on the calculations of a typical investor is 20 years, based on the rate of capital reimbursement will be 5% (1/20).
Currently, the concept of non-residential premises market in Kaluga is such that for relatively new facilities with minor natural wear (impairment) there is no reason to assume a decline in their value in the foreseeable future. In addition, a favorable location of the object near the center of the city and the main transport highways has a great influence on the increase in value. In this case, the investment attractiveness of the assessment object is obvious, therefore the return rate is taken with a sign (-).
The total capitalization coefficient is:
R0 \u003d 0.07 + 0.04 + 0.028 + 0.048 - 0.05 \u003d 0.186
Calculation of the value of the object of assessment by direct capitalization of rental income from
To calculate the potential gross income (PVD) uses available monthly rental rates per year: 14100 rubles / sq.m
Thus, the PVD from the delivery of the area of \u200b\u200bthe object of the assessment will be: 14100 × 1375.8 \u003d 19.398.780 rubles;
Calculation of effective gross income (EU) is made taking into account possible losses from incomprepancies of donated payments and losses when collecting rent. For calculations, an 8% value determined on the basis of available data from external sources and own observations is taken.
The calculations have shown that the EU of the assessment object is:
19.398.780 × 0.92 \u003d 17.846.877.6 rub.
Table 11.
Determination of the market value of the object of assessment by direct capitalization of income
| Effective gross income (EU) | 17846877.60 rub. |
| Operating expenses, | 3045391.19 rub. |
| including | |
| · Building tax | 291494,44 rub. |
| · Insurance plates | 53897,45 rub. |
| · communal payments | 1249281,43 rub. |
| · Object management | 392631,31 rub. |
| · Current repairs (4% of the EU) | 713875.10 rub. |
| · Other expenses (2% of OR) | 47115.76 rub. |
| · Reservation reserve (3.6% of the EU) | 642487,59 rub. |
| Clean operating income (chod) before tax | 14801486,41 rub. |
| Pure operating income (chod), taking into account the income tax | 11249129,67 rubles. |
|
Common capitalization coefficient (R0) |
0,19 |
| The cost of the estimated building is | 60479191,77 rub. |
Thus, the market value of the object of real estate obtained using an income approach is 60.479.191.77 rubles, or rounded 60.479.192 rubles. (Sixty million four hundred seventy-nine thousand one hundred ninety-two ruble) without VAT.
Chapter 3. Recommendations for Management Cost Management
3.1 Determination of the total value of the market value of the assessment object
Applying various approaches to assessing property, we have come to the following results:
Table 12.
| Approaches (methods) | Weight coefficient | Cost, rub. |
| Cost approach (comparative unit method) | 0,35 | 25982918 |
| Market Approach (Direct Sales Comparison Method) | 0,25 | 44307639 |
| Profitable approach (direct capitalization method of income) | 0,4 | 60479192 |
| The final value of the cost | 1,00 | 44362607,85 |
The cost approach weighing mainly to evaluate objects, unique in its kind and appointment, or objects with minor wear. The estimated building belongs to the category of real estate objects with low wear level, therefore the proportion of the value of the market value obtained under the cost approach will have a sufficiently high coefficient - 0.35.
The data based on a market approach cannot be considered absolutely reliable in connection with which the results of the market approach to the estimation of the value of this object must be carefully. Based on this, the result of a market approach is given by the weight ratio of 0.25.
The income value reflects the market behavior of a typical investor, therefore the result of this approach is assigned the maximum weight coefficient - 0.40.
Thus, in our opinion, the most objectively the following distribution of coefficients:
· The cost approach is 0.35;
· Market approach - 0.25;
· Profitable approach - 0.40.
Taking into account the weight coefficients, the market value of the assessment object as of December 20, 2007. It is rounded 44.362.608 rubles. (Forty-four million three hundred sixty-two thousand six hundred eight rubles) excluding VAT.
The cost of the company's real estate is determined by its discounted future cash flows, and the new cost is created only when companies receive such a return on investment capital, which exceeds the cost of attracting capital. Cost management still deepens these concepts, as in such a control system, it is for them that they are built the entire mechanism for making major strategic and operational solutions. Properly established cost management means that all the aspirations of the company, analytical methods and techniques of management are aimed at one common goal: to help the company maximize its real estate value, building a process of making management decisions on key value factors.
The cost management is fundamentally different from the planning systems adopted in the 60s. It ceased to be a function of an exclusively guideline and is intended to improve decision-making at all levels of the organization. It initially laid the premise that the command-administrative style of decision-making on top does not bring proper results, especially in large multidisciplinary corporations. So, the low-level managers need to learn to use the cost indicators for making more sensible solutions. Cost management requires to regulate the balance on a par with a profits and loss report and maintain a reasonable equilibrium between long-term and short-term activities. If the cost is implemented and organized properly, the Corporation receives huge benefits. Such management is essentially continuous reorganization aimed at achieving maximum cost.
For the estimated object, the cost management is reduced to more efficient use of available areas.
The estimated building has a attic with a total area of \u200b\u200b328.2 m2, which is currently partly used as stationery warehouse. On the one hand, the implementation of the appropriate reconstruction will make it possible to make this room by residential. On the other hand, recently, in connection with the expansion of cooperation of Kaluga enterprises with non-resident and foreign companies, the demand for hotel services has increased significantly. In this regard, it is proposed to carry out a comprehensive reconstruction of the attic room to translate it into the category of residential attic, where it is planned to organize a hotel from 14 luxury double rooms.
The cost of measures for the reconstruction of the attic is presented in Table. 13.
Table 13.
Estimation of expenses for the reconstruction of the attic
| № | Name of works | Cost, rub. |
| 1 | Headworking Works (Dismantling) | 406.211 |
| 2 | Headworking Works (New) | 2.448.728 |
| 3 | Cold and hot water supply | 49.818 |
| 4 | Heating | 90.144 |
| 5 | Sewerage and plumbing equipment | 31.738 |
| 6 | Supply exhaust ventilation and air conditioning | 67.534 |
| 7 | Electric equipment and electric lighting | 422.402 |
| 8 | Communication device | 37.010 |
| 9 | Security and fire alarm | 114.531 |
| 10 | Automation of heating, ventilation | 7.638 |
| 11 | Improvement of numbers | 872.640 |
| TOTAL | 4.548.394 | |
To finance these works, it is supposed to use a loan on the following conditions:
· Credit amount - 5.250.000 rub.
· Interest rate - 14% per year;
· Launch period - 1 year;
· Ensuring an estimated object of real estate;
· Credit repayment conditions - quarterly interest payments and the principal amount of debt equal shares, i.e. at 1.866.506 rubles. At the end of each quarter.
As already noted, the hotel will consist of 14 luxury double rooms. The cost of accommodation in such a room in Kaluga hotels ranges from 1400 rubles. up to 2500 rubles. per day. For calculations, the value is 1600 rubles, since the estimated object is close to the city center, but initially this building is not intended for the hotel business, which creates certain inconveniences for customers.
The investment horizon is set for 1 year, since there are no objective grounds to believe that the estimated property will not be sold after this period.
Cash movement is presented in Table. fourteen.
Table 14.
Cash flow in rubles.
| Article expenditure | 1st square. | 2rd square | 3rd square | 4 sq. M. | Total for the year |
| Reconstruction | 4548394 | – | – | – | 4548394 |
| Credit service | 1866506 | 1866506 | 1866506 | 1866506 | 7466025 |
| Operating expenses | 124539 | 127030 | 129571 | 132162 | 513302 |
| Profit Tax | - | 292073 | 291463 | 290841 | 874377 |
| TOTAL | 6539439 | 2285609 | 2287540 | 2289509 | 13402098 |
| Article income | 1st square. | 2rd square | 3rd square | 4 sq. M. | Total for the year |
| Hotel business | – | 1344000 | 1344000 | 1344000 | 4032000 |
| Depreciation | 1299145 | 1302393 | 1305649 | 1308913 | 5216100 |
| Credit | 5250000 | – | – | – | 5250000 |
| TOTAL | 6549145 | 2646393 | 2649649 | 2652913 | 14498100 |
| Balance | 9706 | 360784 | 362109 | 363404 | 1096002 |
The main income is a hotel business. It is important to emphasize that with excessive demand for this type of services of objective reasons for low filling numbers has not been detected.
To determine how much the current market value of the estimated object will increase as a result of the recommended events, it is advisable to use the capitalization coefficient used as part of an increasing approach. This is due to the fact that this project is investment, i.e. Oriented, above all, to receive income.
Consequently, the increase in the current market value of the assessment object will be:
1.096.002 / 0.19 \u003d 5.768.432 (rub.)
(Five million seven hundred sixty-eight thousand four hundred thirty-two rubles) excluding VAT.
Conclusion
As follows from the standards, "all methods, procedures and techniques for measuring market value, if they are based on market indicators, and at the same time are properly applied, lead to the same expression of market value." At the same time, "any method based on market information is at its essence comparative." Thus, according to existing standards, only the quality of information and the correctness of the application can serve as a limitation on the use of one or another method.
The first chapter of the work discusses the concept of real estate, types of real estate value, main approaches, real estate assessment methods, as well as problems associated with the rationale for real estate value.
Real estate is physical objects with a fixed location in space and everything that is inseparable with them is connected both under the surface and above the ground surface or everything that is the mainstream, as well as the rights, interests and benefits caused by the ownership of objects.
Under the property is understood as the property as a whole as a property complex, and secondly, a land plot, an integral part of which can be: building (construction) or a group of buildings; separate water objects, perennial plantings; Engineering facilities and networks; stationary structures improvement of the territory of the site; elements of economic, transport and engineering support; Other objects.
Real estate assessment is carried out from the standpoint of three approaches: an income, expense and comparative. Each approach allows to emphasize certain characteristics of the object.
Each of the three approaches discussed implies use when evaluating methods inherent in it:
Direct capitalization method of income;
Sales comparison method;
Method of a comparative unit.
Thus, real estate objects in the event of a reduction in the efficiency of their use can change their purpose. This happens both as a result of the wear of buildings and other improvements and under the influence of trends in the real estate market.
The second chapter has been an assessment of the property with the use of three assessment approaches.
Each of the methods used has advantages and disadvantages.
A comparative approach provides a direct assessment of market value, based on statistics on the real market for commercial real estate. When processing data, special measures have been taken to protect the creditor from the overestimation of the assessment. In this regard, the comparative approach is assigned the greatest weight.
The cost approach allows you to best take into account the design features and the physical condition of the assessment object. At the same time, the information base is not perfect. The main problems are associated with the estimation of the value of the Earth. In addition, when calculating the replacement cost, it is necessary to rely on the averaged recalculation indexes to the current prices, which can lead to errors.
The income approach is built on market data and deprived of some drawbacks of the cost approach. The main source of the error of the method is the uncertainty associated with the use of forecast data on income, growth rates.
In the third chapter of the work, the results of the estimation of the market value of the real estate object was carried out, its final cost is substantiated, and recommendations are given to increase it.
Calculations have shown that the market value of the assessment object as of December 20, 2007. It is rounded 44.362.608 rubles. (Forty-four million three hundred sixty-two thousand six hundred eight rubles) excluding VAT.
However, the proposed cost management activities allow you to increase the current market value by 5.768.432 rubles. (Five million seven hundred sixty-eight thousand four hundred thirty-two ruble) without VAT.
Bibliography
1. Civil Code of the Russian Federation (part of the first) of 30.11.1994 No. 51-FZ (ed. From 02.07.2005 No. 83-FZ)
2. Federal Law of July 29, 1998 No. 135-FZ "On Assessment Activities in the Russian Federation" (as amended by federal laws of 21.12.2001 N 178-ФЗ, from 21.03.2002 N 31-FZ, dated November 14, 2002 N 143 -FZ, from 10.01.2003 N 15-FZ, from 27.02.2003 N 29-ФЗ, from 08.22.2004 N 122-FZ, from 05.01.2006 No. 7-FZ, from July 27, 2006 No. 157-ФЗ)
3. Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation of 07.06.2002 395 (Ed. 03.10.2002) "On licensing of appraisal activities"
4. Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation of 20.08.1999 932 "On the authorized body for monitoring the implementation of appraisal activities in the Russian Federation"
5. Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation of 06.07.2001 519 "On Approval of Evaluation Standards"
6. Collections of enlarged indicators of the replacement value of buildings and structures
7. International evaluation standards. - M.: ROO, 1995
9. Analysis and assessment of real estate income / D. Friedman, N. Orday. - M.: Case, 1997
10. Valdaytsev S. V. Business evaluation. - M.: Prospekt, 2006. - 355 p.
11. Granova I.V. Real estate assessment. - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2001. - 208 C.: Il. - (Series "Tutorial")
12. Mribovsky S. V., Medvedeva O. E., Kasyanov P. V. Lectures on the assessment of the market value of land. - M.: Armo, 2002. - 95 p.
13. Grigorieva V. V. et al. Assessment of real estate objects. - M.: Infra, 2000. - 78 p.
14. Gryaznova N. A. Estimation of the cost of existing enterprises (business). - M.: Infra-M, 2005
15. Esipov V. E., Makhovikova G. A., Terekhova V. V. Business evaluation. - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2006. - 457 p.
16. Korokkin Yu. I. Real estate assessment. - Kaluga branch of SBAS, Kaluga, 2005
17. Korostylev S. P. Fundamentals of the theory and practice of real estate assessment: Tutorial. - M.: Russian Business Literature, 1998
18. Business Evaluation / Ed. A. G. Mudovna and M. A. Fedotova. - M.: Finance and Statistics, 2004
19. Business Evaluation: Tasks and Solutions / Lights G. I. - RDL, 2006. - 192 p.
20. Real estate assessment: textbook / ed. A.G. M. M.A. Fedotova. - M.: Finance and Statistics, 2005. - 496 p.: Il.
21. Real estate assessment: studies. Handbook for universities / ed. prof. V. A. Schwardar. - M.: Uniti-Dana, 2002. - 303 p.
22. Evaluation of real estate objects: Theoretical and practical aspects / ed. V. V. Grigorieva. - M.: Infra-M, 1997
23. Assessment of the market value of real estate: educational and practical allowance / Ed. V. M. Rutgizer. - M.: Case, 1998
24. Evaluation activities in the economy. Tutorial / under the general ed. Dzhuhi V. M., Kireeva V.D. - M.: ICC Mart, 2003. 101 p.
25. Solovyov M. M. Evaluation activities (real estate assessment): Tutorial. - M.: GU HSE, 2002
26. Simionova N., Simion R. Estimation of the value of the enterprise (business). - M.: March, 2004. - 464 p.
27. Tarasevich E. I. Methods of real estate assessment. St. Petersburg, 1998. - 247 p.
28. Tepman L. N. Real estate assessment. - M.: Uniti, 2006. - 463 p.
29. Land management. Educational and practical manual / Ed. e. n., prof. L. I. Koshkin. - M.: VSPP, 2004. - 520 s.
30. Fedotova M. A. How much is the business? Methods of evaluation. - M., Publishing House "Perspective", 2004
31. Friedman J., Orday Nick. Analysis and assessment of real estate income. Per. from English - M.: Case, 1997. - 480 p.
32. Tzakkin Yu. A., Tsukanov I. L. Legislative acts, regulatory documents and standards on appraisal activities: educational and methodological manual. - M.: Finance and Statistics, 2003. 164 p.
33. Shcherbakov V. A., Shcherbakova N. A. Estimation of the value of the enterprise (business). - M.: Omega-L, 2006. - 286 p.
34. Real estate economics / ed. A. B. Crochik, M. A. Gorengburg. - M.: Lan, 2001. - 297 p.
35. Real estate economics: Tutorial. - M.: Case, 2000
36. Avdeev A. P. Problems of assessing real estate objects // Questions of evaluation. # 1. - 2001. - p. 28-30
37. Akimova I., Biktimirova N. New approaches to standardization of real estate assessment in the system of existing legislation and real law enforcement practice // Right and economics. - 2005. - №12. - from. 18-21
38. Gribovsky S. Mass property assessment // Financial business. 2000. - №4. - from. 43-45
39. Gribovsky S. Assessment of real estate objects using an income approach // Property problems. 2000. 2.
40. Mribovsky S. Economic and Mathematical Models of Real Estate Estimation // Finance and Credit. 2005. - №3. - from. 24-43
41. Grigorieva I. L. Problems of property assessment // Financial business. - 2004. - №1. - from. 48-49
42. Zelensky Yu. V. On comparability of the results of approaches in assessing real estate - the principle of coherence of models // Questions of evaluation. 2005. - №4.
43. Loginov M. P. On the issue of real estate assessment in Russia // Eco. - 2002. - №9. - from. 103-107
44. Ozers E.S. The phenomenon of equilibrium price as the base of axioms of assessment theory // Property problems. 2000. 1. C 32-54.
45. Ozers E.S. Economics and real estate management. SPB: ISS, 2003.
46. \u200b\u200bOzers E.S. On the issue of the substantiation and use of an axiom of the theory of evaluation // Problems of real estate. 2004. Vol. 1. C 3-5.
47. Patzkalev A. F. Assessment of land plots // Evaluation issues. - 2006. - № 1.
48. Official Web site SBFF HTPP: /www.cbr.ru
49. HTPP: /WWW.cfin.ru
P. 1 Article 30 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Real estate economy / ed. A. B. Crochik, M. A. Gorengburg. - M.: Lan, 2001., p. 48-49