PPP facilities. Public-private partnership is a form of mutually beneficial interaction between the state and private business. Examples of
Kryukova Ekaterina Leonidovna
Lemieva Irina Vitalievna, Moscow State University of Design and Technology, Russia
Translation will be available soon.
The first trend : formation of a developed legislative framework in the field of PPP. At the federal level in 2015 was adopted Federal Law of 13.07.2015 No. 224-FZ "On Public-Private Partnership, Municipal-Private Partnership in the Russian Federation and Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation." Other important legal acts in this area are the law on the Development Bank, on the rules for the selection of investment projects, on concession agreements.
Regional legislation is represented by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation on PPP (see. picture 1). At the municipal level, similar regulations are being adopted. Also, the scope of PPP is regulated by model concession agreements and guidelines.
Picture 1.Development of regional legislation on PPP in the Russian Federation as of March 2015
A source:compiled by the authors
The specialists of the PPP Development Center believe that the regional legislation on PPPs needs to be improved in the following directions.
1. Determine the needs of the region in infrastructure facilities, based on their predicted and actual socio-economic and macroeconomic indicators (demographic forecast, growth in transport load).
2. Integrate indicators of infrastructure development into forecast documents of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
3. To fix specific measures for the application and development of PPP mechanisms, as well as indicators for attracting extra-budgetary funds in the planning documents of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
Second trend : differentiation of RF subjects by participation in PPP. According to the calculations of specialists, all subjects of the country can be divided into 5 groups (Table 1)... More than half of the country's subjects have a low or very low level of PPP development. This situation is explained by the weak development of the institutional environment (lack of plans for the use of PPPs in the region, documented models of PPP implementation, authorized bodies for the coordination of PPPs). This affects the lack of experience in implementing PPP projects, which means low investment attractiveness.
The subjects of the first three groups ensured their advantageous position through an effective PPP management system. As a rule, it includes the presence of a single body responsible for choosing a private partner, accounting for PPP in strategic planning documents for the development of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, providing tax and non-tax benefits, an Internet resource that allows you to get all the relevant information about the region's economy. The number of completed projects is also important. One of the latest projects in Moscow was construction"Northern understudy of Kutuzovsky Prospekt", in the Leningrad region - construction of a rehabilitation center in the village of Kommuna, in the Moscow region - two projects in the field of water supply and sanitation with the involvement of the Morton Group of Companies as a concessionaire, as well as summing up the results of the competition for the construction of cancer and radiological centers, where the concessionaire is PET-Technology (a subsidiary of Rusnano).
|
Name of the subject of the Russian Federation |
|
|
Regions are leaders in terms of PPP development (60-75%) |
R. Tatarstan, Novosibirsk region, Nizhny Novgorod region, Leningrad region, St. Petersburg, Moscow. |
|
Regions with a high level of PPP development (45-60%) |
R. Bashkortostan, R. Udmurtia, R. Komi, Perm and Krasnodar Territories, Samara, Sverdlovsk, Moscow, Voronezh, Ulyanovsk, Tula, Rostov, Vladimir, Yaroslavl, Tambov Regions, Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug. |
|
Regions with an average level of PPP development (35–45%) |
R. Sakha, R. Buryatia, R. Chuvashia, Khabarovsk and Primorsky Territories, Kaluga, Orenburg, Pskov, Belgorod, Ryazan, Amur, Sakhalin, Vologda, Lipetsk, Murmansk, Omsk Regions. |
|
Regions with a low level of PPP development (25-35%) |
R. Tyva, R. Khakassia, R. Karelia, R. Mordovia, Altai, Krasnoyarsk, Stavropol, Kamchatka Territories, Kemerovo, Saratov, Tver, Tomsk, Penza, Kirov, Kaliningrad, Bryansk, Astrakhan, Chelyabinsk, Irkutsk, Smolensk, Ivanovskaya , Novgorod, Kostroma, Kurgan, Kursk, Arkhangelsk, Volgograd regions, Jewish Autonomous Region. |
|
Regions with a very low level of PPP development (0-25%) |
R. Chechnya, R. Altai, R. North Ossetia - Alania, R. Kalmykia, R. Crimea, R. Dagestan, R. Kabardino-Balkaria, R. Mari El, R. Karachay-Cherkessia, R. Adygea, R. Ingushetia, Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Trans-Baikal Territory, Tyumen, Oryol, Magadan Regions, Sevastopol. |
A source:compiled by the authors
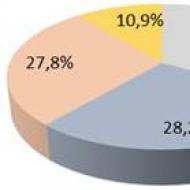
Third trend : allocation of priority areas of PPP depending on the socio-economic needs of society (see. picture 2).

Figure 2.Areas of implementation of PPP projects as of March 2015
A source:compiled by the authors
According to the given data, the leading sphere of the implementation of PPP projects last year was housing and communal services - 194 completed projects. In the social sphere, this figure was 165 projects, in the energy sector - 163 projects, in the transport sector - 64 projects. To date, 1,285 projects are at various stages of implementation. Of these, 505 projects are in the energy sector, 482 projects are in the utilities sector, 203 projects are in the social sector, 95 projects are in the transport sector. A significant increase in PPP projects in the energy sector is explained by the involvement of representatives of domestic and foreign business for the construction of an energy bridge and a transport bridge in the Republic of Crimea.
Fourth trend : highlighting priority forms of PPP. In the current practice, four forms are distinguished:
- concession agreement;
- PPP agreement;
- lease agreement with investment obligations;
- life cycle contract.
The forms of PPP implementation differ in the degree of responsibility that the public and private partners assume for capital and current investments, operation, and risks. For example, the first form of PPP involves two partners: the concessionaire and the grantor. A concessionaire is an individual entrepreneur, Russian or foreign legal entity. He undertakesat their own expense create and (or) reconstruct property and carry out activities using the object of the concession agreement. The grantor is the authorized body of the federal, regional or municipal levels. The concessor has the right of ownership to the property created by the concessionaire and undertakes to provide him with the rights of ownership and use of the object of the concession agreement for the period established by the agreement. At the municipal level, the main branches of concession agreements are nproduction, transmission and distribution of heat and electric energy, as well as water supply, sewerage and heat supply systems and individual objects of such systems.
At the regional level, concessions applyin relation to objects of the social sphere (health care and sports), objects of communal infrastructure (WSS, solid waste) and the energy sector. At the federal level, concessions are practiced for the creation of road infrastructure.
The fourth form of PPP (life cycle contract) isan agreement under which the state, on a competitive basis, concludes an agreement with a private partner for the design, construction and operation of the facility for the life cycle of the facility and pays for the project in equal installments after the facility is put into operation. Currently, only two life cycle contracts are being implemented in Russia, one of which is in the pre-investment phase, the other on an investment basis. Both contracts are being implemented in the Urals Federal District at the municipal level. Their cost is 9 988 971 rubles.Some experts also refer to special economic zones and government procurement as forms of PPP.
Fifth trend: according to the analytical data of Sokolov S.L., the following pattern was found in the field of PPP. The more profitable a PPP project is, the lower the share of public investment. Entrepreneurs are more willing to finance those industries in which there is a guarantee of profit (see. table 2). To a greater extent, the state is forced to invest resources in unattractive industries for business to fulfill its social functions. (Sokolov, 2013).
table 2
Investment structure in PPP projects for the period 1996-2012
|
Branch of the project |
The volume of investments in the PPP project (mean, %) |
|
|
State |
Private |
|
|
1. APK |
10,9 |
89,1 |
|
2. Mining |
15,3 |
84,7 |
|
3. Housing and communal services |
26,1 |
73,9 |
|
4. Healthcare |
24,6 |
75,4 |
|
5. Culture |
17,5 |
82,5 |
|
6. Education |
87,0 |
13,0 |
|
7. Industrial production |
13,0 |
87,0 |
|
8. Development of territories |
19,9 |
80,1 |
|
9. Construction |
15,0 |
85,0 |
|
10. Transport |
40,2 |
59,8 |
Yurieva Tatiana Vladimirovna
Doctor of Economics, Professor, Head of the Department of Project and Program Management
Russia, Russian Academy of National Economy and Public Administration under the President of the Russian Federation
[email protected]
annotation The mechanism of functioning of public-private partnership projects in the modern economy is considered. The world practice of project implementation based on the principles of public-private partnership is analyzed. The main trends in the development of public-private partnership projects at the regional and local levels have been identified. Public-private partnership, municipal-private partnership, regional public-private partnership project. Yurieva Tatiana Vladimirovna Public-private partnership projects in Russia and in foreign countries // Regional Economics and Management: Electronic Scientific Journal... ISSN 1999-2645
Jur "eva Tat" jana Vladimirovna
Doctor of Economics, professor, Head of the Department of project and program management
Russia, The Russian Presidential Academy of National Economy and Public Administration
[email protected]
Abstract The article deals with the mechanism of functioning of public-private partnership in the modern economy. Is analyzed the world practice implementation of projects on the principles of a-public-private partnerships. It's shown the main trends in the development of public-private partnership projects at the regional and local levels. Public-private partnerships, municipal-private partnership, regional project of public-private partnership. Jur "eva Tat" jana Vladimirovna Projects of public-private partnerships at regional level. Regional economy and management: electronic scientific journal. ... Art. # 4833. Date issued: 2016-12-12. Available at: https: // site / article / 4833 /
Introduction
Against the background of the active growth of public needs, limited financial resources of the state, the need for projects implemented on the principles of public-private partnership (PPP) and municipal-private partnership (MPP) is growing. The implementation of such projects is one of the most important factors in the development of industrial and social infrastructure, increasing investment and innovation activity, and increasing the competitiveness of the region and the country as a whole.
The mechanism for implementing PPP and MPP projects is being actively studied in Russia and in foreign countries. Various aspects of this problem are reflected in the works of such Russian authors as A.A. Alpatov, G.A. Borshevsky, V.G. Varnavsky, A.G. Zeldner, N.A. Ignatyuk, V.N. Ivanov, V. A. Kabashkin, V. Yu. Katasonov, V.V. Maksimov and others. Among foreign researchers, one should highlight the works of E. Atkinson, J. Delmon, E. R. Yescomba, V. Kattari, V.V. Knaus, M.K. Lewis, F. Marin, W. Smith, G. Tullock, E. Farquharson, etc.
In scientific publications, the focus is on the economic content of the term "public-private partnership", the prerequisites for the formation and development of this form of interaction between public and private partners in the modern economy. The types, forms and mechanisms of PPP implementation have been identified and investigated in detail. Analyzed the specifics of the implementation of PPP projects in certain industries and sectors of the economy. However, various aspects of the development and implementation of PPP projects at the regional and local levels still remain insufficiently studied. The solution to this problem seems to be relevant due to the fact that a significant part of PPP projects are regional or municipal projects that largely determine the quality of life of the population of a particular region or city.
1. Mechanism of functioning of projects based on PPP principles
A study of the scientific literature on various aspects of PPP allows us to conclude that there are a large number of definitions of PPP. In the most general form, the definition of PPP is given in the documents of the World Bank. In accordance with it, PPP is understood as a contractual relationship formalized in the form of an agreement between the state and a private company for the production of something or the provision of any services. The agreement is concluded in order to attract additional investments for the implementation of the project, as well as to increase the efficiency of state budget financing.
In US regulations, a PPP refers to an agreement, enshrined in a contractual form, between the state and one or more private companies. This agreement gives the right to private companies to take part in the implementation of state public functions and to have ownership of state property. An agreement for the implementation of a PPP project usually provides for a contract, the subject of which is most often a certain type of public goods. Basic property rights, even if private ownership is transferred to a private company, remain with the state.
Much attention is paid to understanding the essence of PPP, its functions in the modern economy in the countries of the European Union (EU). In the UK, which is the leader in the implementation of projects based on PPP principles, this form of interaction between public and private partners is seen as the most important instrument of government strategy.
In the Russian scientific literature, there are various approaches to the definition of PPP. After analyzing and summarizing them, we can conclude that under PPP are considered legally formalized relations between authorities and business entities in relation to objects under the jurisdiction of the state, based on the mandatory sharing of risks, taking into account the interests and coordination of efforts of the parties, carried out in order to most efficiently implement projects of public importance.
Russian federal legislation, based on the accumulated world experience, defines PPP and MPP as a special form of interaction between public and private partners, legalized in the form of a contract or agreement for a certain period of time. The result of such interaction is expressed in attracting additional private investment in the economy, ensuring the availability and growth of the quality of public goods provided to the population.
PPP is an effective means of implementing innovation and investment policies, strengthening the economy, expanding infrastructure, and implementing large-scale social projects. This is an alternative to both state entrepreneurship and the full transfer of the relevant economic activity to the private sector, including through the privatization of the relevant assets.
The priority areas for the implementation of PPP projects are: development of production and transport infrastructure; modernization of housing and communal services; development of innovative infrastructure, stimulation of science-intensive industries; support for higher education and retraining systems; modernization of healthcare; providing consulting support for small and medium-sized businesses, etc.
PPP projects are implemented on the basis of project financing, the mechanism of which in world practice allows attracting funds from various financial and credit structures for the implementation of large investment projects on the basis of complex schemes of long-term cross-financing, guarantees, liability, risk redistribution, etc. Project financing is based on the principle of financing projects from the profit that will be received by a specially created structure (usually a project organization) during the implementation of the project.
In world practice, there is a wide variety of different forms, models, types and options for mutual cooperation between the state and the private sector. In the scientific and practical literature on PPP, classifications of the main PPP schemes are given. The most widespread classification is that includes five basic models of cooperation between the state and the private sector, differing in special forms of ownership, financing and management. These are: operator model; cooperation model; concession model; model is negotiable; leasing model. In practice, these forms are rarely found in their pure form, as a rule, mixed models function, which differ depending on the volume of property rights transferred to the private partner, the investment obligations of the parties, the principles of risk sharing between partners, responsibility for carrying out various types of work, etc.
PPP projects are implemented in various organizational and legal forms. The most common form is a concession (concession agreement). The state (municipality), within the framework of partnership, authorizes private business to perform, for a certain period of time, the functions stipulated in the agreement and endows it for this purpose with the appropriate powers necessary to ensure the normal functioning of the concession object, while remaining the full owner of the property that is the subject of the concession agreement. On the terms reflected in the concession agreement, the concessionaire pays a fee for the use of state or municipal property. The interest of a private partner in such projects arises only if they, with acceptable risks, allow providing the required rate of return on invested capital. The term of concession agreements, as a rule, is long - from 10 to 30 years.
Increasingly, partners in partnerships are using such a form as a "life cycle contract" (from the English "Life Cycle Contract"), which is a type of concession. Its essence lies in the fact that a public partner represented by a state or municipal authority concludes an agreement with a private partner on the design, construction and operation of the object of the agreement during its life cycle. The attraction of financial resources to the project is carried out by a private partner on the basis of project financing through a special project company. The public partner is not an investor in the project, but only pays for goods, works and services created after its commissioning. All this stimulates the performance of work within the object of the agreement at a high quality level, in compliance with time constraints.
Another form of PPP that is often used in practice is a production sharing agreement. Production sharing agreements are mainly applied in the field of prospecting, exploration and production of mineral raw materials and other works related to this type of activity.
2. World practice in the implementation of PPP projects
Currently, PPP projects have a significant impact on the achievement of the strategic goals of the socio-economic development of the country as a whole and its individual regions. The development and implementation of projects based on PPP principles is carried out in many developed and developing countries. The most successful PPP projects are implemented in countries such as Great Britain, USA, Ireland, Israel, France, Italy, Germany, Japan. The recognized leaders in the field of public-private projects are the USA, UK, France and Germany. PPP projects are implemented in many sectors and areas of the economy, but mainly such projects are concentrated in infrastructure, housing and communal services, road construction and reconstruction, education, and healthcare.
A study of statistics published by the European PPP Center shows that in the EU countries over the past decade, the number of projects implemented on the basis of PPP has decreased slightly (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Number of PPP projects reaching completion in EU countries in 2009-2015
At the same time, the cost estimate of projects practically did not change in 2009-2015. The average cost of PPP projects that reached the closing stage in 2015 was 15.6 billion euros, down 17% compared to 2014 (18.7 billion euros). Five major projects were completed in 2015, compared to two in 2014. Their total cost was about 62% of the total cost of PPP projects in the European market. Three large PPP projects are being implemented in Turkey (construction of an airport, two medical centers). One major project is underway in France (port construction) and one project in the Netherlands (sea lock construction). The state took part in paying for more than 85% of PPP projects.
Turkey is the leader in the value of PPP projects (9.2 billion euros) at the end of 2015. This is followed by Great Britain and France. In terms of the number of completed projects, the United Kingdom remains the leader, here in 2015 15 projects were completed against 24 in 2014.
As for the sectoral affiliation of PPP projects implemented in the EU, the transport sector remains the leader, accounting for over 60% of the total market value of all projects. Health care projects are second in value. Education ranks third. According to such a criterion as the number of completed PPP projects in 2015, education (15 projects) leads, followed by transport (12 projects) and healthcare (10 projects).
Of the total number of PPP projects in the EU countries completed in 2015 (49 projects), more than 40% (20 projects) were carried out taking into account the provision of funds by institutional investors (insurance companies, pension funds) through various financial models. Overall, institutional investors provided around € 1.2 billion (€ 2.8 billion in 2014) to participants in the European PPP market. At the same time, the maturity of the debt averaged 25 years (maximum - 31 years). Eight countries are indebted to institutional investors: Great Britain, Belgium, Denmark, France, Ireland, Finland, Turkey and the Netherlands. It should be noted that there remains an important role for EU organizations, national governments and public financial institutions (national or supranational) in financing a number of PPP projects. For example, a project to create an electronic document flow in the courts of Greece was carried out with substantial financial support from the EU. The European Investment Bank financed 11 PPP projects, the total amount of lending amounted to 1.2 billion euros. Other international financial institutions, such as the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, have also participated in financing large PPP projects.
3. Regional and municipal PPP projects in the Russian Federation
A special place is occupied by PPP projects implemented at the regional and municipal level, since through them it is possible to largely satisfy the needs of the population for public goods and services of a qualitatively new level.
As of the end of 2016, about 900 projects are being implemented in the Russian economy based on PPP principles, for which relevant agreements have been concluded. As a result, more than 1,300 projects are at various stages of implementation. The total volume of private investments exceeds 640.0 billion rubles. The main share of PPP projects falls on the municipal level - 86.7% of the total number of projects. The regional and federal levels account for 11.9% and 1.4%, respectively (Figure 2).

Figure 2. Projects of public-private partnership in the Russian Federation and their main characteristics in 2015
The number of PPP projects that passed the stage of commercial closure increased significantly over 2013-2015 from 86 to 875 projects. The average annual growth rate of the number of PPP projects in Russia that have passed the stage of commercial closure is 115%. Mostly PPP projects are implemented in the field of transport, energy and housing and communal services. About 16% of projects implemented on the basis of the PPP mechanism are in the social sector, with the bulk of them concentrated in health care.
As noted earlier, PPP projects in world practice are carried out through project financing. In the Russian Federation, there are PPP projects that are carried out exclusively on the basis of private investment. At the same time, PPP projects can be distinguished, in which the share of state budget funds reaches 90 percent or more.
In Russia, the main form of PPP projects is implemented in the form of a concession. At the regional level, a PPP agreement is often used to implement projects primarily in the social sphere. At the regional and municipal level, projects are also implemented on the basis of contractual commitments, commitments of a private partner for financing at the stage of capital investments, long-term commitments of the parties and the distribution of risks and responsibilities of the parties within the framework of the PPP project. In addition, a life cycle contract is used.
The sectoral characteristics of the regional market for PPP projects shows that the latter are mainly concentrated in the social sphere (healthcare), transport and communal infrastructures. Projects appear in such segments as railway and public transport of general use, in the traffic safety control system, weight and size public order, etc.

Figure 3. Sectoral structure of regional PPP projects in Russia in 2015,
It should be noted that PPP projects are unevenly distributed across Russian regions. The largest number of PPP projects are carried out in such regions as Moscow, St. Petersburg, Samara region, etc. At the same time, there are regions (Republic of North Ossetia - Alania, Karachay-Cherkess Republic, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, etc.) in which such projects are absent or conducted in a minimal amount and often have a low quality of development.
In connection with the recent introduction of legislation on public-private partnerships and municipal-private partnerships in the Russian Federation at the federal level, the authorities of the regions have been tasked with bringing regional legislation in line with the norms of the federal law on PPP. At present, such work has already been carried out in 33 constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
In order to strengthen the place and role of PPP projects in the development of regions, a special comprehensive indicator “The level of development of public-private partnerships in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation” has been introduced. A special methodology for calculating this indicator has been developed and introduced, taking into account the impact of the following factors: development of the institutional environment of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation in the field of PPP; regulatory support of the PPP sphere in the constituent entity of the Russian Federation; experience in implementing PPP projects in the constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
Conclusion
The formation and development of PPP projects is a real prerequisite for the growth of investment and social attractiveness of Russian regions, strengthening their competitiveness, forming a positive image of the country and individual regions. In this regard, great attention should be paid to the availability of the necessary professional competencies in the field of project management among state and municipal employees, the formation and development of regional teams capable of managing projects based on modern standards and technologies. Considerable attention should be paid to the organizational structure of project activities, its effective interaction with the existing management system.
Bibliographic list
- Federal Law N 224-FZ "On Public-Private Partnership, Municipal-Private Partnership in the Russian Federation and Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation" dated July 13, 2015
- PPP in numbers: Unified information system of public-private partnership in the Russian Federation. PPP Development Center with the support of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation. URL .: http://pppi.ru
- Research “Development of public-private partnerships in Russia in 2015–2016. Rating of regions by the level of PPP development "/ Association" PPP Development Center ", Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation. - M .: Association "PPP Development Center", 2016. - 36 p.
- Project management in the structure of modern management // Management of economic systems. Electronic scientific journal. - 2016. - No. 11 (93).
References
- Federal Law N 224-FZ "On public-private partnership, municipal-private partnership in the Russian Federation and the Introduction of Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation" dated July 13, 2015.
- PPP in figures, uniform information system of public-private partnership in the Russian Federation. Center for the development of public-private partnership with the support of Ministry of Economic Development. URL .: http://pppi.ru
- Study “Development of public-private partnership in Russia in 2015-2016. Rating regions by the level of development of PPPs ". Association "PPP Development Center", Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation. Association "Center for PPP development", 2016. 36 p.
- Yurieva T.V. Project management in structure of modern Management. Management of Economic Systems. Electronic scientific journal. No. 11 (93)
- Market Update, Review of the European PPP Market in 2015., March, 2016. URL .: http://www.eib.org/epec/library/epec_market_update_2015_en2
- Market Update, Review of the European PPP Market in 2014., March, 2015. URL .: http://www.eib.org/epec/resources/epec_market_update_2014_h1_en.pd
- Market Update, Review of the European PPP Market in 2013., March, 2014. URL .: http://www.eib.org/epec/resources/publications/epec_market_update_2013_en.pdf
- Market Update, Review of the European PPP Market in 2011., September, 2012. URL .: http://www.eib.org/epec/resources/epec_market_update_2011_en_web.pdf
- Market Update, Review of the European PPP Market in 2010., April, 2011. URL .: http://www.eib.org/epec/resources/epec-market-update-2010-public.pdf
TASS-DOSSIER. On March 2, 2017, the Ministry of Economic Development, which oversees public-private partnership (PPP) infrastructure projects, criticized the claims of the Federal Antimonopoly Service (FAS) to a number of major concession agreements.
In particular, the FAS annulled the results of an open tender for the construction of the Sterlitamak - Kaga - Magnitogorsk highway, citing the fact that this concession implied such a grant from the grantor, in which the investor did not actually bear his own expenses for the project.
What is PPP
Public-private partnership is a scheme for the implementation of investment projects (mainly in the field of infrastructure) on mutually beneficial terms for business and the state. The state receives a functioning facility, saving on financing its construction or reconstruction, entrepreneurs - earn money for the subsequent operation of the facility.
PPP can be implemented in various forms. Usually, a private company builds or reconstructs an object at its own expense, and then receives the right to operate it for a certain period of time at no cost (while the object formally remains in the ownership of the state). This form is called a concession.
However, there are other types of PPPs as well. For example, a constructed object may remain in the ownership of a construction company for some time; or after the commissioning of the facility, the private partner can receive subsidies from the state for the operation of the facility, or vice versa - transfer to the state part of the funds received from its operation. The legal mechanism of concessions and PPPs is not spelled out in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
The basic documents for them are the law "On concession agreements" dated July 21, 2005, as well as "On public-private partnership, municipal-private partnership in the Russian Federation" dated July 13, 2015. However, some of the PPP projects were also implemented in other legal framework, for example, on the basis of the law "On the state company" Russian highways "(July 17, 2009) or on local legislation. One of the first to adopt its own laws on PPP was St. Petersburg (in 2004) ...
Grantor's fee
According to the Russian law "On concession agreements", the grantor (in this case, the contracting state) can pay a certain amount to the partner participating in the concession agreement. This mechanism is required for the implementation of projects with low investment attractiveness, for example, social facilities where the concessionaire will not be able to earn money after their commissioning.
According to the amendments to the law on concessions that entered into force on July 1, 2015, it was allowed to conclude agreements in which the concessionaire simultaneously receives the grantor's payment and collects a fee for the use of the finished object. This was previously prohibited. The law does not stipulate threshold values for the size of the grantor's fee. However, the FAS believes that contracts under which all costs for the construction and operation of the system will be reimbursed by the state are a violation of the public procurement law.
Completed projects
For the first time, a PPP scheme in modern Russia was implemented during the construction of a modern aeration station in Moscow Yuzhny Butovo. It was built in 1998 by the German company SHW Holter Wassertechnik. The company owned the station for 12.5 years and received funds for its operation, and then transferred it to the city.
Among the most famous projects implemented or under construction under a concession or PPP scheme in Russia: toll highways Western High-Speed Diameter in St. Petersburg, the Moscow-St. Petersburg highway, and the Platon truck toll system.
Statistics
In total, according to the Unified PPP Information System (www.pppi.ru), as of March 2017, 1,340 public-private partnership projects were registered in Russia, of which 426 were successfully implemented (put into operation).
Most of the current PPP projects have been created in the communal sector - 901. In the energy sector - 133, transport - 81, the rest of the projects - in the field of social infrastructure.
The total volume of private investments in PPP is 700 billion rubles, of which 440 billion are directed to regional projects.
Criticism
On March 1, 2017, in an interview with reporters, the head of the FAS Igor Artemyev said that a number of PPPs in Russia are "an imitation of a concession", since all expenses of the concessionaire are compensated from the budgets by the payment of the grantor, while the private company does not invest its own funds.
As Rachik Petrosyan, Deputy Head of the Federal Antimonopoly Service, explained to TASS, PPP can be used as a mechanism to bypass public procurement. It is for this reason that the FAS in January 2017 canceled the results of the competition for the construction of the Sterlitamak - Magnitogorsk road. Answering the question whether the concession under the Platon system falls within this definition and whether it will be revised, the head of the FAS said that the department could "look at it too."
Criticizing the glory of Artemyev, Deputy Minister of Economic Development Stanislav Voskresensky said that such statements by the FAS pose a threat to the entire PPP mechanism. Rostavtodor stressed that the approach of the antimonopoly service "blocks the launch of new projects in the transport sector."
In the economies of many countries, a special form of relations between commercial enterprises and authorities has appeared. To denote this interaction, the concept of public-private partnership is used. Let's consider it further in detail.
General information
The state and private business form an alliance for the implementation of projects of public importance in a variety of areas of activity. The interaction between the authorities and commercial structures has now reached a new level. Currently, it is enshrined at the legislative level in 224-FZ. This relationship may well be seen as an essential feature of a mixed economy.
Peculiarities
The development of public-private partnerships contributes to the formation of basic models of financing, management methods, relations related to property. In this process, a set of issues related to the redistribution of powers acquires fundamental importance. They arise as an inevitable consequence of the expansion of interactions between commercial structures and government. A number of experts believe that in many cases public-private partnership is to a certain extent privatization or its absolute alternative. This opinion, for example, is expressed regarding concessions. Meanwhile, it should be noted that public-private partnership is a truly institutional way of transforming the spheres of activity traditionally related to the conduct of power. However, at the same time, the instruments used in cooperation do not completely take them out of the scope of state regulation.
Redistribution of powers
Public-private partnership is a cooperation that involves the provision of not all legal possibilities, into which the sovereign right of the owner in the economic turnover is split, but only a certain part of them. We are talking about the right of management, changes in the capital value of material assets, the assignment of certain powers to other persons. There is a fairly extensive experience in the redistribution of legal opportunities between the government and commercial structures in the spheres of public services, namely, in the infrastructure sectors. They historically formed the tradition of transferring some basic powers to private business by the state. The authorities are responsible to society for the continuous flow of public goods. This is the reason for the desire to keep some industries in state ownership. At the same time, private enterprises are distinguished by high mobility and efficient use of resources. In addition, businesses tend to innovate. Public-private partnerships are a way to harness the benefits of both types of property without profound changes in society.
Government involvement
The state under any conditions remains a participant in public law relations. This circumstance is also key for civil legal relations, in which power as a sovereign is not an ordinary subject of law. In this regard, one cannot talk about the initial equality of the private and public partners. It will come only if, on the basis of the sovereign rights of power in the agreement on interaction, the conditions and specifics of the implementation of civil legal relations are determined. In other words, the state will become a special entity. This is expressed primarily in the fact that the authorities themselves establish the legal framework in which all other participants must act. In addition, it retains its managerial, administrative functions, even if it enters into relations on the principle of equality. This is due to the presence of the authority to issue administrative acts. They, in turn, ignore the specified equality. Initially, it is assumed that the state enters into civilian circulation not to satisfy its own specific interests, but for the most effective implementation of public power.

Role of power
Projects approved under PPPs are not just a pool of resources. They are a very special configuration of the respective powers and interests of the interacting subjects. First of all, the state, acting as one of the parties to the partnership, is the bearer of socially significant goals and needs. At the same time, it also performs a control function. Secondly, being a participant in the economic turnover, the state is interested not only in high results of partnership, but also in ensuring its commercial effect. In addition, like any normal entrepreneur, a participant in such a relationship strives to maximize profits. In this regard, in the sector of commercial interests between the parties it is quite appropriate, and in some cases it is necessary to bargain on the division of probable risks, the nature of the transferred powers, the conditions for their provision and use.
Property relations
As international experience shows, the degree of participation of the authorities and commercial structures, the conditions for their combination may differ, and in some cases, quite significantly. Thus, organizations can act as a party to the agreement. As a rule, this is for the supply of products or the provision of services for state needs, for management, the provision of technical assistance, and so on. In this case, ownership is clearly separated. There are other forms in which such a public-private partnership is manifested. Examples of this are production sharing agreements and leasing agreements. Within the framework of interactions, a partial transfer of a number of ownership rights is possible. Typically, they include the ability to use, manage and own property. Such a partnership takes place at the conclusion. In addition, equity or joint-stock participation of the entrepreneur in state structures is provided. Public-private enterprises are an expression of a higher level of capital integration within the framework of cooperation between commercial organizations and authorities.
Key features
The structure and models of public-private partnerships are very diverse. However, there are a number of characteristic features that make it possible to distinguish this institution into an independent category. First of all, it should be noted that PPP is created as a formalized cooperation of commercial and state structures. Entering into such cooperation is aimed at achieving specific goals and is based on the relevant agreements of the participants. Analyzing foreign experience, the following features of partnership can be noted:
- Defined, often lengthy contract periods. They can be 10-20 years, and in cases of concessions - up to 50. State contracts are formed for a specific object. For example, it can be a road, port, infrastructure. The execution of the order is limited to the exact date.
- Specific types of program financing. The implementation of projects is carried out at the expense of investments of commercial organizations, supplemented by the resources of state funds. There is also a joint investment of capital of several participants.
- Compulsory presence of competition. In such conditions, there is a struggle between potential participants for each contract or concession agreement.
- Responsibility between the parties is distributed in specific forms. The state defines goals from the standpoint of public interest, establishes quality and cost indicators, and monitors the implementation of programs. At the same time, a commercial structure assumes responsibility for operational activities at various stages - development, financing, management, construction, operation, practical provision of services to users.
- The risks between the parties are shared on the basis of agreements.

Contribution of participants
Commercial structures provide professional experience, financial support, effective management, efficiency and flexibility in the decision-making process, and demonstrate the ability to innovate. Within the framework of the partnership, innovative methods of work are being introduced, equipment is being modernized, and technologies are being improved. In the process of cooperation, new forms of production organization appear, companies are formed, including those with foreign capital, effective cooperation with contractors and suppliers is formed. At the same time, the demand for well-paid and highly qualified employees is growing in the labor market.
The state, in turn, provides certain powers of the owner, provides tax breaks, guarantees, financial and material resources. The authorities, within the framework of cooperation with commercial structures, are able to implement their direct functions - control, regulation, observance of the public interest. As the partnership develops, the state can smoothly shift the focus from specific problems of construction and operation of facilities to administrative and control tasks. The emerging ones are redistributed towards commercial structures. The social significance of the partnership is that as a result, society wins as a user of higher quality services.
Local cooperation
Public-private partnership programs are of particular importance in municipalities. Cities and towns bear the main burden on the implementation of socially significant tasks in various spheres of management. These areas, in particular, include transport, housing and communal services, nature protection, housing construction, gas and energy supply. The key problem faced by local authorities is the lack of funding. In this regard, raising capital from commercial structures, in accordance with 224-FZ, is becoming a common practice.

Administrative contracts
In world practice, various forms of cooperation between the government and commercial companies have been adopted. One of them is government contracts. They are administrative contracts that are concluded between a commercial organization and a governing body (federal, regional, local). The most common public-private partnership in the social sphere, in the supply of products for municipal or state needs, management, technical assistance. In administrative contracts, ownership is not granted to a commercial organization. In this case, the risks and costs are entirely borne by the state. The interest of the commercial entity is that, in accordance with the contract, it is entitled to a specified portion of the income or payments collected. As practice shows, such agreements allow not only to increase the prestige of the company, but also to get guaranteed preferences and benefits, sustainable profits and take a position in the market.
Leasing agreements
Within the framework of cooperation, transactions are widespread on the transfer of property that is in municipal or state ownership to a commercial structure for use for a certain fee. It can be a structure, building, premises, land plot. Lease in the traditional form assumes the return of the subject of the agreement. At the same time, the right to dispose of the property remains with the owner, and when the contract is concluded, the commercial structure is not provided. In some cases, an organization can buy out a structure, premises or land. Rent in the form of leasing always presupposes such a condition.

Concession
This form of public-private partnership is now becoming more widespread. The peculiarity of the concession lies in the fact that municipal or state bodies, within the framework of cooperation, remain the full owners of the property, authorize the commercial association to perform the functions stipulated in the contract for a certain period. For this, the firm is transferred the legal capabilities necessary to ensure the operation of the concession object. For the operation of the property, a commercial structure pays a fee in the manner and on the terms established by the agreement. In this case, the ownership of the product is transferred to the user.
Features of the agreement
The concession has the following features:
- The subject is always municipal or state property. It can also be the monopoly activity of the state or the Ministry of Defense.
- An authorized municipal or state agency acts as one of the parties to the agreement.
- The purpose of the concession is to meet public needs.
- The basis of the relationship is the agreement.
- Concession assumes the return of the subject of the contract.
When concluding contracts, leasing agreements, the state or the municipality acts as a subject of civil law. Accordingly, the provisions of the Civil Code are sufficient for their effective work. In concession relations, the state is primarily an institution of public law. In this role, it not only transfers part of the powers to commercial companies, but also delegates a certain share of power functions. Such provision is allowed only in accordance with the regulation. Among the public-law signs of a concession, one should single out the consolidation of public interests in them, the representative of which is the state. According to the agreement, the commercial structure is obliged to obey them, that is, to ensure the continuity of the provision of services, equal tariffs, general availability, and exclude discrimination against consumers.

Areas of distribution of concessions
Such agreements are most popular in world practice in infrastructure industries. These sectors require intensive investment and an influx of highly qualified personnel. Currently, there are three main types of concessions:
- For already operating objects.
- For the construction or modernization of infrastructure.
- Transfer of objects of municipal or state property to management.
Within the framework of these types, forms of concession agreements are possible, based on a different combination of powers, as well as permissible limits of specific investment and business activities.
Situation in Russia
In the Russian Federation, the normative act on concession agreements entered into force in 2005. However, at present, such cooperation has not been developed. According to experts, the main reason for this situation is insufficient protection of user rights. The risk that the commercial organization bears directly related to its activities under the agreement is compounded by the existing obligation to pay a high concession fee. At the same time, the penalty for violation of the terms of the agreement by the user is not established in the normative act. Discussions are ongoing on amendments to the law that could stimulate the emergence of concession relations in Russia.

Product sharing agreement
This form of relations between commercial structures and government agencies has some features of a concession. However, this agreement has a number of peculiarities. The differences are primarily in the configuration of property relations. The rights to the products created by the private partner remain with him. According to the agreement on the division of the results of activity, only a part of them remains for him. The procedure and conditions for the transfer of rights are stipulated by a special agreement.
Additionally
The most popular is public-private partnership in education. So, at present, work is underway to introduce the system. This form of PPP is being distributed in St. Petersburg and Moscow. It involves the involvement of manufacturing companies in the process of training highly qualified employees. At the same time, training is carried out without interrupting production activities.
Another common form of interaction is public-private partnership in health care. We are talking mainly about recreational facilities, the health resort sector. Over the past few years, the forms of public-private partnerships have been developing rapidly. Initially, concession agreements were used in the construction of parking lots, highways, and heat supply. Today, cooperation is becoming more and more widespread in the defense sector, the sector of transport services, and the cultural and educational sphere. When implementing programs, various mechanisms of interaction between the government and commercial organizations are used. They are differentiated in accordance with the scope of property rights, financial obligations of participants, principles of risk distribution, as well as responsibility for the performance of certain types of work.