Plan of houses of the series to 7 16. Will brick five-story buildings and panel Khrushchev be demolished. Features of apartment planners
The first project of mass development of the Soviet period was the housing of the K-7 series. These "Khrushchev" became the first milestone on the way to transition to the construction of typical industrial buildings. Houses on the K-7 project could be erected quickly and at the minimum cost, which made it possible to provide individual housing millions of people.
These houses were erected in three shifts, construction proceeded literally non-stop. Such an innovative approach to the construction allowed to fully mount a 4-section "five-story building" in just 12 working days. After that, it remained only to fulfill finishing work in the building. To ensure uninterrupted supply of construction and concomitant materials (solutions, electrical, sanitary equipment, roofing, joinery, electrodes and nails), special control (OPC) was even formed.
For that time, such a project was a real breakthrough in architecture. However, today the K-7 series at home is hopelessly outdated, in particular, the heat-shielding characteristics of the outer panels due to their wear worsened by about 20%. Low-story and the inability to exploit these buildings in the future without reconstruction (which was inappropriate) became the causes of their mass demolition.





Constructive features of the series and finishing of facades
The designation "K" in the name of the project means "frame", and the components of the houses of the houses were riglels and columns. These elements of houses of houses can be seen inside the apartments - they appear from the walls at the corners of the rooms. Such a design made it possible to reduce the weight of the house and reduce the consumption of concrete through the use of thin-walled LB-panels of the 2-way cross section and a special type of overlap.
A feature of the house design is that the ceiling shields are based on the top ribs of the partitions, and the floor overlap panels are on the lower. Thus, between the shields and panels, the air layer is obtained, which improves the sound insulation of the inter-storey overlap.
In the houses of K-7, the balconies were not envisaged to reduce the maintenance (they were only in one of the early modifications of K-7-3-3, erected in Zelenograd), the ends of the buildings are deaf.
Most of the series of the series were five-storey, but four-storey options have met. The first floor of the K-7 residential, however, in the versions of this project, which were built in Lefortovo and good-poinniki, this floor was sometimes assigned to infrastructure facilities. The elevator nodes of the K-7 houses were not equipped, and the garbage chute was in some buildings of the third modification and in all buildings of the fifth modification of this project.
The facades K-7 were faced with fine tiles of white, light gray or red flowers. Some houses were separated outside the stone crumb to either a mosaic, and part of the buildings of the series did not have facing at all.
The construction volumes of the K-7 project increased annually. Together with them, the K-7 project itself was improved, which was enough "raw" and not worked in the first versions of houses. Thus, at home K-7 of the latest modifications significantly differed from the houses of the same project of the first years of development.
Features of apartment planners
On each floor of the section there were three apartments - 1-, 2-, 3-bedrooms. There was a modification of the project K-7-3-3, in which 4-room apartments made. In the first houses, erected by the K-7 project, the rooms were adjacent, isolated, the project changed and all the rooms became isolated.
The carrier walls of the houses K-7 are internal, which limited redevelopment capabilities.
The positive point was that the bathrooms in K-7 were separate even in the "odnushki", and the kitchens were made sufficiently comfortable in the area - about 7m2.

Specifications
|
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
| Alternative name: |
K-7. |
| Construction regions: |
Moscow: Medvedkovo, Bescordnikovo, North Tushino, Hovrino, Vernadsky Prospect, Degunino, Cheryomushki, Sviblovo, Izmailovo, Zelenograd, Kuzminki, and so on.; Moscow region: Troitsk, Balashikha, Pushchino, Lyubertsy, Railway, Elektrostal, Dubna, Dmitrov, Wedge, Solnechnogorsk, Podolsk et al.; Other cities: Saratov, Tula, Tolyatti |
| Construction technology: |
panel |
| Under the construction period: | Khrushchevka |
| Year of construction: | Moscow - from 1958 to 1966, regions - from 1959 to 1969 |
| Movement Perspective: |
The mass demolition is carried out |
| Number of sections / entrances: | from 2. |
| Number of floors: | 5 (less often - 4) |
| Ceiling height: |
2.5 M. |
| Balconies / Loggia: |
Only in one of the earliest versions (K-7-3-3) in Zelenograd |
| Bathrooms: |
Separate; Standard baths |
| Stairs: |
Without a common fire balcony |
| Garbage chute: |
There are only in versions K-7-3-3, K-7-3-5 |
| Elevators: |
not |
| Number of apartments on the floor: |
3 |
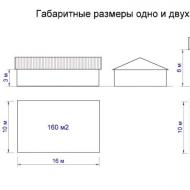
| Apartment Square: |
Total / residential / kitchen 1-room apartment 30/16/6,5-6,7 2-bedroom apartment 44-46/29-32/6,8-7 3-room apartment 61,4/47/6,8 |
| Ventilation: |
Natural exhaust with blocks in the kitchen and in the bathroom. |
| Walls and cladding: |
Exterior walls - Hinged concrete panels with insulation (16 cm) Partitions - ribbed panels (intercardic - 8 cm, interroom - 4 cm) Inter-storey overlap - Of the 2 ribbed zb-panels (5-16 cm) Facades lined with shallow square tiles, sometimes - stone crumbs or mosaic, part of the houses were not faced |
| Roof type: |
Flat, in late modifications - ventilated |
| Manufacturer: |
Zvoropresnensky Zhby Plant (in 1961 entered DSC-1), Dmitrovsky DSC (at home in the Moscow region. Modifications K-7-2-4) |
| Designers: |
Mosproject (workshop №7) |
| Advantages: |
Separate bathrooms even in one-bedroom apartments; Square kitchens are greater than in other "Khrushchev" |
| Disadvantages: |
Bad soundproofing, fragile design of the foundation, the ceilings of the last floors are possible |
Igor Vasilenko
The era of the mass construction of typical housing began at the first secretary of the Central Committee of the CPSU Nikita Khrushchev. In Moscow, the Khrushchev building was built until 1972, and in the Moscow region and in many regions of the country - until the mid-1980s. In the people, these houses were called "Khrushchevki". At first they were built of bricks, and after the 1960s, to speed up and significantly reduce the process, from reinforced concrete panels.
Distinctive features of "Khrushchev" are low ceilings, small kitchens, combined either separate bathroom, weak soundproofing of the inner walls, no elevators, mousing and attic. In the brick series under the window in the kitchen, a niche was made with a thick wall of a half of the brick, which in the winter could serve as a refrigerator.
"Khrushchev" of the defendant series were calculated for 25 years. They were intended to temporarily solve the housing problem, but some of them are used to this day for their intended purpose. "Khrushchevki" of unsigned series had a settlement resource of 50 years, but with timely major repairs, their resource can be extended to 150 years.
Substitable include panel houses series K-7, II-32, II-35, 1605-AM, 1MG-300.In Moscow, they are dismantled according to the urban program of complex reconstruction of areas of five-storey buildings of the first period of industrial home-building. The program included 1722 five-story buildings to be demolished according to the decree of the Moscow Government of July 6, 1999 No. 608.
What series of houses today demolish in Moscow
- 1605-AM
- 1mg-300 (mg-300)
- II-32.
- II-35
- K-7.
1605-AM
The most houses of the 1605-AM / 5 series (1-605a) were built in the Moscow regions of Fili, Davydkovo, Kuntsevo, Ochakovo, Solntsevo, Belyaevo, Zyuzino, Perovo, Zelenograd (MKP. 3, 6, 8). In small volumes, such houses were built in a number of other bedrooms, and in the center of Moscow, the house of the 1605 series is in the Khamovnik area. Outside the capital, such houses were erected in some cities of the Moscow region (Balashikha, Odintsovo, Dolgoprudny, Mytishchi, Pushkino, etc.) in single quantities.
1mg-300 (mg-300)
The 1MG-300 series (MG-300) has been built in the areas of Cheryomushki, Medvedkovo, Hovrino, Coptevo-Mikhalkovo-Likhobor, Bescordnikovo. Inside the garden ring, such houses were not built, there are no them outside of Moscow. The 1MG-300 series was introduced to replace constructively less durable Series K-7 and II-32. Sometimes this series of houses is mistakenly called 1MG-510.
II-32.
The most houses of the II-32 series were built in the Moscow regions of Cheryomushki, Izmailovo, Zyuzino, Vernadsky Avenue, Hovrino. Inside the Garden Ring, the II-32 series has not been built. Outside the city of the house of this series were erected in some cities of the Moscow region in single quantities. The initial name of the series: VK-32 (from the term "viberpical" (panels). The reason for the cessation of construction is a refusal of viberpic panels due to their weak design characteristics.
II-35
The first house of the II-35 series was built on the 2nd Novostankinskaya Street. The construction was also conducted in the areas of Kuzminki and Kuntsevo. Inside the Garden Ring and outside of Moscow, such houses were not built. The II-35 series was experimental, it was on its example that practical methods for calculating the heat shifts of external panels were worked out not only in flat areas, but also in the nodes of the conjugation. As a result, it was decided to refuse from the shell design of the vertical walls, this constructive scheme was further applied only for overlaps
K-7.
| Years of construction | 1958-1966 (Moscow), 1959-1969 (Other Cities) |
| Distinctive features; | lined with shallow light square tiles, without balconies, deaf ends, protruding elements of panels from the inside of the building |
| Material wall | panel |
| Dignity | separate bathrooms, kitchen squares more than in all other Khrushchev |
| Number of entrances | from two |
| Number of floors | 5 (less often 4), first floor most often residential |
| Ceiling height | 2.50 m. |
| Balconies | only in one of the earliest versions (K-7-3-3); in the 1st MKP. Zelenograd |
| Number of apartments on the floor | 3 |
The K-7 series at home can be seen in many frames of films "We live to Monday", "Operation" s "and other adventures of Shurika" (Novella "partner"). Most of the houses of the K-7 series were built in the Moscow regions of the good-mention, Bescordnikovo, Vernadsky Avenue, Medvedkovo. Also, the series Massovo was built in areas of North Tushino, Hovrino, Zelenograd (MKP. 1, 2, 3, 8), Degunino, Butyrsky Farm, Sviblovo, Izmailovo, Kuzminki, Cheryomushki, ul. Innovators, ul. 1905 and others. Inside the Garden Ring, such houses were not erected.
According to the materials of the sites Russianrealty.ru,
AdvanceRealty.ru.
The five-story buildings of the T-7 series became the first project of the mass construction of housing in the Soviet Union and gave impetus to planting "" throughout the country. The series contained a lot of disadvantages (ineffective insulation and sound insulation), therefore, many modifications and differences in layouts appeared.
In Moscow, the frame-panel houses of the K-7 series were built in the main areas of mass construction of the 1950s - in the 1960s. Most of the houses of the K-7 series were built in Moscow areas: good-mnemy, Bescordnikovo, Vernadsky Avenue, Medvedkovo. Also, the series is massively built in areas: Northern Tushino, Hovrino, Zelenograd, Degunino, Butyrsky Khutor, Sviblovo, Izmailovo, Kuzminki, Cheryomushki, ul. Innovators, ul. 1905. According to the prevalence, the series ranked 4th in Moscow among the five-story buildings of all periods with the market share of 19.7%.
In the Moscow region, the K-7 series was built in cities: Lyubertsy, Balashikha, Railway, Elektrostal, Dmitrov, Dubna, Wedge, Solnechnogorsk, Pushchino, Podolsk and Troitsk.
In the regions of Russia, the K-7 series was built in cities: Saratov, Tula and Tolyatti. In Leningrad, a series of analogues were built - OD-4 and OD-6 (Obukhovsky DSC).
 At one time, the K-7 series ("K" means "frame") was a real breakthrough and allowed to move from individual construction to mass industrialization. The cost of construction 1m² of living space was 119 rubles, in prices of 1961 this is the lowest figure (along with) among the Moscow series (and the fourth cheapness in the entire history of industrial home-building). As a result, the K-7 series turned out to be cheap, faster, which made it possible to quickly provide Soviet citizens with housing.
At one time, the K-7 series ("K" means "frame") was a real breakthrough and allowed to move from individual construction to mass industrialization. The cost of construction 1m² of living space was 119 rubles, in prices of 1961 this is the lowest figure (along with) among the Moscow series (and the fourth cheapness in the entire history of industrial home-building). As a result, the K-7 series turned out to be cheap, faster, which made it possible to quickly provide Soviet citizens with housing.
Today, according to the requirements for energy efficiency and housing comfort, K-7 is hopelessly outdated, and therefore is subject to demolition. The mass demolition of the K-7 series houses is carried out in Moscow from the mid-1990s. Absolutely all houses are demolished in Zelenograd, Yuao and Cao, and in the rest of the districts, demolition will be completed in 2015. In St. Petersburg, the relevant decision was made in the early 2000s, but the demolition has not yet begun. In the Moscow region a demolition decision was made in 2007
The K-7 series at home can be seen in many frames of movies "We live to Monday", "Operation" s "and other adventures of Shurik."
Detailed features of the series
| Passages | from 2. |
| Floors | 5 (less often - 4). The first floor is most often residential (versions with a non-residential 1-floor floor were built in good-monsters and in Lefortovo) |
| Ceiling height | 2.50 m. |
| Lifts | not |
| Balconies | Only in one of the earliest versions (K-7-3-3), the place of construction is the first MKP. Zelenograd |
| Apartments on the floor | 3 |
| Years of construction | Moscow: 1958-1966 Regions: 1959-1969 |
| Built houses | 990 |
| Square of apartments | 1-bedroom apartment Total: 30 m², living: 16 m², kitchen: 6.5-6.7 m² 2-room apartment Total: 44-46 m², living: 29-32 m², kitchen: 6.8-7 m² 3-room apartment total: 61.4 m², living: 47 m², kitchen: 6.8 m² 4-room apartments found only in the K-7-3-3 version in the 1st Zelenograd microdistrict |
| Bathrooms | Separate, Baths: Standard |
| Stairs | without a common fire balcony |
| Garbage chute | only in versions K-7-3-3, K-7-3-5 |
| Ventilation | Natural exhaust, in the kitchen and bathroom |
| Walls and overlaps | The outer walls are mounted concrete panels with insulation of a total thickness of 16 cm, the partitions are thin-walled ribbed panels (interspectar - 8 cm, interior - 4 cm), overlap - from 2 ribbed reinforced concrete panels, the maximum thickness of 16 cm, averaged thickness - 5 cm. |
| Bearing walls | Frame (panels are an integral part of it). "K" in the title of the series means "frame" |
| Colors and cladding | Colors: White, light gray, ends in many houses red Facing: shallow square tiles, less often by stone crumb; There are houses with a mosaic in the auction, some of the houses were not faced |
| Type of roof | Flat, combined with a comforter. From the comforter, refused in late modifications in favor of ventilated. |
| Dignity | Separate bathrooms even in one-room apartments, kitchen space is greater than in other Khrushchev |
| disadvantages | Mediocre sound insulation, fragile basement designs, the ceilings of the last floors are possible. |
| Manufacturer | Krasnopresnensky Zhussian plant (in 1961 he entered the structure of Moscow DSC-1), Dmitrovsky DSC (houses in the Moscow region. Modifications K-7-2-4) |
| Designer | Mosproject (Workshop No. 7). Chief Engineer Project: Vitaly Lagutenko |
For several years now, there are rumors about the fact that, according to the plan for the reconstruction of cities, it was decided to demolish the old five-story houses that are in every city and every region. Do there really exist such instructions? And if so, when will it happen?
Unfortunately or fortunately for those people who are not residents of the capital, such houses are true to demolish, but so far only in Moscow. And only the houses of specific "demolished series". Bricks do not belong to them.
Why demolition five-story buildings
In the second half of the last century, panel, block, and then brick five-storey houses are actively built in all cities of the country - and then brick five-storey houses are the so-called Khrushchev. Initially, they were intended to settle people from communal at the time, while the country is built comfortable housing, therefore they did not differ in a convenient layout, nor the quality of the materials used.

For reference. Projects of such houses were created with such a calculation that they would be standing for no more than 25 years, after which they would go under demolition.
However, it is correct that there is nothing more permanent than temporary.
Khrushchev are still to this day, and, according to statistics, lives in them more than eight and a half million people.
Causes of demolition
It is easy to calculate that the estimated service life of these houses has long over, however, experts believe that most of them can stand very long. It is even called a figure of 150 years, but subject to reconstruction using modern repair technologies.
What causes demolition?
- First of all wear. Moreover, the communications are extended faster and exacerbated: heat and power supply, water supply, sewage. Today, each apartment is literally stuffed with modern household appliances, practically incompatible with morally obsolete communications, which are without well coped with their functions. And in recent years, there are increasingly information about the catastrophic wear of carrier structures.

- The irrationality of financing the reconstruction of houses of certain series. Modern technologies that can save Khrushchev - is, of course, great, but what will be the price of such a rework? This money is better to put on the construction of more modern and comfortable housing.
For reference. The method developed by engineers, the method of reconstruction of five-story buildings is to strengthen their columns, an additional heat and sound insulation device, an increase in the storeinities and the union of apartments.
If you add to this replacement of communications and the device of the elevator node, then for each square meter you will have to spend about 20 thousand rubles.
- Improving the appearance of the city. All those years have passed after the mass built of Khrushchev, the city grew and developed, leaving five-story buildings in the historic center. Their design, and rather, its absence, in no way fits into modern architecture.

- The need to expand or build motorways. This is the only reason in addition to the emergency condition, which can be demolished at home unambiguous episodes.
Why they still stand
The decision on the demolition was made a few years ago, but the majority of houses that are subject to him still stand. There are objective reasons for that, among which the economic crisis, as well as the change of the management of Moscow. After all, it is still going only about the metropolitan five-story buildings: no one is going to demolish anything in the regions.
In accordance with the new plans, this should happen until 2015, but how far these plans are fulfilled - a big question. The fact is that not all residents of Khrushchev agreed to leave their homes. Some of them are mostly elderly people - do not want to touch with the usual place.
Others are not satisfied with the proposed exchange options. Many have made high-quality repairs in their apartments, they replaced with their own hands with dilapidation, spending large sums on it. It is clear that they are not pleased with the prospect of moving to a new home.

But the main problem for the city authorities was the high cost of dismantling work. The five-story buildings are located in areas with high construction density and gaskets of engineering communications, which directly affects the rise in price of destruction.
Defended and unsigned series
Residents of houses to be demolished soon, are certainly aware of this. And to those who are going to buy an apartment in the old Fund, it will be interesting to learn which of them should be eliminated to correctly evaluate financial risks.
Houses of demolished series
These include the buildings of a residential foundation created in the late 50s - early 60s of the last century. That is, during the period of mass industrial house-building. These are panel houses of the K-7, II-32, and II-35, 1-MG-300, 1605 am.
First of all, it concerns the first two episodes.
- K-7 - panel multisective five-story buildings of various modifications consisting of ordinary sections with single, two-two-bedroom apartments without balconies. The outer walls are cassette reinforced concrete panels with a thickness of 270 mm with thermal insulation by minvata and foam cell.

- P-32 - houses from viberpic panels, lined with tiles, with balconies on pillars. And the modification of this series is "Malossames" II-32-130 with a living area of \u200b\u200b9-13 m 2 and the kitchen is not more than 3.5 m 2.

For reference. At the moment, most of the houses of this series (about 80%) are demolished.
Erected by one of the first, five-story buildings listed above have thin, having poor thermal insulation properties of the wall. They are not subject to reconstruction, since even the use of modern building technologies is not able to better improve their condition.
Houses of unsigned series
The brick houses of Series 1-447, 1-511 and Maloshemes II-34 are observable primarily. Built on the basis of a fundamentally different design system, they are characterized by higher operational characteristics.
And although the construction used low-quality construction bricks, they are designed for quite a long service life.
- 1-447 and 1-447c - the most common brick five-story buildings in the regions of Russia, which were built from 1958 to the end of the 70s everywhere - in large and small cities. The outer walls with a thickness of 38-40 cm, interior partitions from concrete panels - 8 cm.

- 1-511 - houses of this series were built only in Moscow from the end of the 50s to the mid-60s. The early and late modification of the houses of this series, which differ in the type of roof, the height of the ceilings and the quality of the brick-based brick, which has a double silicate brick M 150, has a thickness of the walls of 38-40 cm, and in the houses of an earlier building - Up to 51 cm. In the regions such houses were not built. (see also an article)

It is interesting. The capital already has a realized project for the reconstruction of the brick five-story building of the series 1-511 with a superstructure of two floors, an extension of the elevator assembly and the construction of erkers that increase the area of \u200b\u200bkitchens.
Reconstruction was carried out without removing tenants.

- II-34. There are only 10 such houses, and only in Moscow - there are no them in the area and regions.
Officially brick five-story buildings are not included in the list of demolition series. Their elimination is possible only if the house is recognized by the domestic emergency housing, not subject to repair and reconstruction.
The perspective of demolition is possible in such a situation when this requires a plan for comprehensive reconstruction of the quarter, the construction of road junctions or expansion of motorways.
To date, only single cases of demolition of brick khrushchev are known. For example, a house of the II-34 series in the Moscow district of Zyuzino came under him.
- 1-335d;
- 1-464a and 1-464d;
- 1-467a and 1-467d;
- 1-468-A, 1-468-b, 1-468-d;
- 1-507;
- 1-510;
- 1-515/9;
- 1-605A and others.
The strength and thermal protection properties of the outer walls of these houses are good, the physical wear of the supporting structures is not critical (as a rule, no more than 20 percent), and the planning of the apartments is more successful than in the homes of the demolished series. Nevertheless, almost all homes require a complete replacement of domestic communications. (Read also an article






A series of houses K-7 (literature "K" means "frame") - a series of multi-speaking five-storey houses, developed by architect Vitaly Lagutenko, a specialist of the institute Mosproject. Such houses were built in 1958-1966 in Moscow, and in 1959-1969 - in other regions.
In the capital of the house K-7 were built in areas of good-mock, Bescordnikovo, Vernadsky Avenue, Medvedkovo, North Tushino, Hovrino, Zelenograd (MKP. 1, 2, 3, 8), Degunino, Butyrsky Farm, Sviblovo, Izmailovo, Kuzminki, Cheryomushki , ul. Innovators, ul. 1905 and others. Inside the Garden Ring, these houses were not built.
IN Moscow region K-7 houses were built in Lyubertsy, Balashikha, Zheleznodorozhny, Elektrostali, Mytishinsky district, Sergiev-Posad district, Dmitrov and Dmitrovsky district, Dubna, Taldomsky district, to Klin and Klinsky district, Solnechnogorsk and Solnechnogorsk district, in Odintsovo district, Pushkin, Podolsk and Podolsk district, Troitsk and in other settlements.



Also at home of the K-7 series were built in Saratov, Tula, Tolyatti and Cellograph (now Astana, Kazakhstan). In Leningrad (now St. Petersburg), the houses of this design were built under the name of OD, and two of them have 9 floors.
Most of the homes of this series were built in 5 floors, less often in 4 floors. The number of sections in the houses of the K-7 series - 2 or more. There is no elevator in the entrance. In the first modifications of the K-7 series houses, there were no balconies. The garbage chute is available only in the later series (K-7-3-3 and K-7-3-5). On the floor there are three apartments (1-bedroom, 2-bedroom and 3-room or three 2-bedroom).
Bathrooms in apartments separate, standard bath. The kitchen is equipped with a gas stove. Ventilation provides a natural extract.
The outer walls are made of mounted reinforced concrete panels, insulated by foamery. Their thickness is 30 cm. Internal bearing walls - reinforced concrete beams-walls are a reinforced concrete dial with a thickness of the vertical wall 40 mm, the width of the upper shelf 240 mm and the width of the lower shelf 170 mm. The living rooms of adjacent apartments are separated by two beams of the waller sections walls installed with a gap of 40 mm. Overlapping - separate part-party concrete panels.
Coarseings are internal.
Part of the houses are not lined, in other outer walls are lined with shallow square tiles of white or beige color. The roof is flat, from ribbed plates with insulation.
Read more reference to Khrushchevok Read by reference.