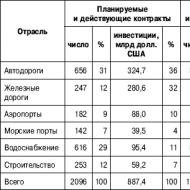
Approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated. Work in progress and deferred expenses. Unfinished capital investments
Issued" (Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts accounting financial- economic activity organizations, approved by the Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia from... received" (Instructions for the application of the Chart of Accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by the Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia from... creditors" (Instructions for the application of the Chart of Accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by the Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated...
Inventories", Instructions for the application of the Chart of Accounts for accounting financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated...
The off-balance sheet account is directly named in the Chart of Accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations. In addition, maintaining this off-balance sheet... follows from the Instructions for using the chart of accounts for accounting of financial and economic activities of organizations (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated... 002). 3. Instructions for the use of the chart of accounts for accounting financial and economic activities of organizations (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated...
The other follows from the analysis of the Chart of Accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations and the Instructions for its application...
Accounts" (Instructions for the application of the Chart of Accounts for accounting of financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated... N 33n, Instructions for the application of the Chart of Accounts for accounting of financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated...
Inventory, Instructions for the use of the Chart of Accounts for accounting of financial and economic activities of organizations). In accounting, such transactions...
In accordance with the Instructions for the application of the Chart of Accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated...
...). Based on the Instructions for the application of the chart of accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated...
Organizations of loans Instructions for the application of the Chart of Accounts for accounting financial and economic activities of organizations (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated...
Russian Federation
"INSTRUCTIONS FOR ACCOUNTING IN BUDGETARY INSTITUTIONS" (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 1999 N 107n) (as amended on June 9, 2001)
Approved
By order of the Ministry of Finance
Russian Federation
dated December 30, 1999 N 107n
The law is simple: ORDER of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 1999 N 107n is included in the database as a separate document.
The cards are stored in file cabinets, in which they are located in subaccounts with divisions within them by financially responsible persons, and in centralized accounting departments - by serviced institutions.
Accounting cards for materials, low-value items, etc. submitted to the archives in a filed form along with the register of cards, accounting registers and others accounting documents annually or once every two years. At the same time, cards for recording fixed assets disposed of during the year are submitted to the archive.
Inventory of inventory cards for accounting of fixed assets f. OS-10. is handed over to the archive when it contains notes on the write-off of inventory according to the last inventory card f. f. OS-6 budget, OS-8, OS-9. The delivery of inventory cards to the archive without an inventory is carried out according to the register of delivery of documents f. 442, which indicates the card number and the name of the written-off inventory, and in centralized accounting departments, in addition, the name of the serviced institution.
IN accounting books All pages (sheets) are numbered before the records begin. On the last page of the sheet, signed by the chief accountant, the following inscription is made: “In this book, a total of ____ pages (sheets) are numbered.”
Each book is inscribed with the name of the institution and the year for which the book was opened. The book must contain a table of contents of the subaccounts opened in it. When transferring entries to another page of the book, a note is made in the table of contents for this subaccount about the transfer of the entry indicating the numbers of the new pages.
Accounting books, if they have blank sheets at the end of the year, can be used to record the transactions of the next year. In these cases, books are handed over to the archive once every two years.
Entries in accounting registers are made in ink, ballpoint pen paste or using typewriters and automation equipment from primary accounting documents no later than the next day after their receipt.
At the end of each month, the total turnover is calculated in the accounting registers and the balances of sub-accounts are displayed.
17. Correction of errors found in accounting records is carried out in the following order:
A) detected error for a given reporting period before the presentation of the balance sheet, which does not require changing the data of the memorial order, is corrected by crossing out the incorrect amounts and text with a thin line so that the crossed out can be read, and writing the corrected text and amount above the crossed out. At the same time, here in the margins, against the corresponding line signed by the chief accountant, the clause “Corrected” is made;
B) an erroneous entry discovered before the presentation of the balance sheet, caused by an error in the memorial order, depending on its nature, is corrected by an additional memorial order or using the “Red Reversal” method; in the same way, errors are corrected in all cases where they are found in the accounting records for the reporting period for which the balance sheet has already been presented. Additional accounting entries for correcting errors, as well as corrections using the “Red Reversal” method, are documented using an accounting certificate f. 433, which makes reference to the number and date of the memorial order or document being corrected, and the rationale for making the correction.
Based accounting certificate f. 433, a memorial order is drawn up f. 274.
18. Accounting registers for synthetic and analytical accounts are opened by recording the amounts of balances at the beginning of the year in accordance with the final balance sheet and accounting registers for the past year.
If a higher organization, when approving the annual report, made corrections to the final balance sheet, then, on the basis of an appropriate written order, these corrections are made both in the accounting registers of the previous year (by means of a corrective accounting entry) and in the accounting registers current year(by changing opening balances).
19. To control the accuracy of accounting records for synthetic and analytical accounting turnover statements are compiled: f. 285 (turnover sheet for account ____), f. M-44 (turnover sheet for inventories) and f. 326 (turnover sheet for fixed assets) for each group of analytical accounts and financially responsible persons united by the corresponding synthetic account. Turnover sheets are compiled monthly, except for fixed assets and low-value items, for which turnover sheets are compiled quarterly. The totals of turnover and balances for each sub-account of the turnover sheets are verified with the totals of turnover and balances of these sub-accounts of the book "Journal - Main" f. 308. Entries in turnover statements can be produced if necessary over several years.
20. Accounting in institutions is carried out on a memorial basis - order form accounting in accordance with these Instructions.
In some cases, the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation may allow federal executive authorities to conduct accounting in institutions under their jurisdiction using the journal-order form of accounting, provided that developed methodological documents are available.
Verified and accepted for accounting primary accounting documents are systematized by the dates of transactions (in chronological order) and are drawn up in separate memorial orders - accumulative statements for transactions at the expense of budget funds and funds received from extra-budgetary sources, which are assigned the following permanent numbers:
memorial order 1 (cumulative statement for cash transactions) f. 381;
memorial order 2 (cumulative statement of the movement of budget funds in subaccounts 090, 091, 097, 100, 101, 102) f. 381;
memorial order 3 (cumulative statement of the movement of funds received from extra-budgetary sources in subaccounts 110, 111, 114, 115, 118) f. 381;
Memorial order 4 (cumulative statement for settlements with checks from limited books) f. 323;
Memorial order 5 (set of pay slips for wages and scholarships) f. 405;
memorial order 6 (cumulative statement of settlements with other debtors and creditors) f. 408;
memorial order 8 (cumulative statement of settlements with accountable persons) f. 386;
memorial order 9 (cumulative statement of disposal and transfer of fixed assets) f. 438;
memorial order 10 (cumulative statement for the disposal and movement of low-value items) f. 438;
Memorial order 11 (set of accumulative statements for the receipt of food products) f. 398;
Memorial order 12 (set of accumulative statements on food consumption) f. 411;
memorial order 13 (cumulative statement of materials consumption) f. 396;
memorial order 14 (cumulative statement of income, profits (losses) f. 409;
memorial order 15 (set of statements on settlements with parents for keeping children in child care institutions) f. 406.
For other transactions and for “reversal” transactions, separate memorial orders are drawn up f. 274, which are numbered starting from number 16 for each month.
Entries to memorial orders are made as transactions are completed, but no later than the next day (upon receipt of the primary accounting document) both on the basis of individual documents and on the basis of a group of similar documents. The correspondence of subaccounts in the memorial order is recorded depending on the nature of the transactions on the debit of one subaccount and the credit of another subaccount or the debit of one subaccount and the credit of several subaccounts (credit of one subaccount and debit of several subaccounts).
To reflect actual expenses by codes economic classification expenditures of the budgets of the Russian Federation, a decoding is applied to the memorial warrant f. 803.
Memorial orders are signed by the chief accountant or his deputy and the executor, and when accounting is centralized, in addition, by the head of the accounting group.
Discrepancies identified during the inventory between actual availability property and accounting data are reflected in the corresponding sub-accounts provided for by these Instructions:
a) surplus property is accounted for market value on the date of the inventory and the corresponding amount is allocated to the increase: targeted funds for the maintenance of the institution and other activities (subaccount 270) - according to budgetary activities, as well as targeted funds and gratuitous receipts; income of the reporting period (subaccount 400) - for business activities.
The current market value is formed on the basis of the price in force on the date of registration of the property for this or a similar type of property. Data on the current price of property must be confirmed by documents or experts;
b) shortage inventories within the limits of natural loss norms refers to book value on the debit of subaccounts 140, 141, 220, 241, 270 and the credit of subaccounts of accounts 04, 05, 06, 08;
C) the shortage of property and its damage in excess of the norms of natural loss are attributed to the guilty persons at market value according to the debit of subaccount 170 and the credit of subaccounts: 040, 041, 043, 044, 050, 060 - 067, 069 (for inventories), 120 (for cash), 173 (for fixed assets, intangible assets and low-value items acquired at the expense of budget funds), 270 (for fixed assets, intangible assets and low-value items acquired at the expense of targeted funds and gratuitous receipts), 401 (for fixed assets , intangible assets and low-value items acquired using funds from business activities).
If the perpetrators are not identified or the court refuses to recover losses from the perpetrators, entries are made to the credit of subaccount 170 and the debit of subaccounts 140, 141, 173, 270, 401.
27. Institutions are required to prepare and submit periodic accounting and annual reporting in the manner established by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
The financial statements of the institution must include performance indicators of branches, representative offices and other separate structural divisions.
Institutions submit monthly, quarterly and annual financial statements to their parent organization within the established deadlines. Institutions funded from federal budget, monthly reporting is submitted only to the federal treasury body of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation. Quarterly and annual reports institutions financed from the federal budget, before submitting to a higher organization, agree with the federal treasury body of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, in which they are opened personal accounts, for compliance of financing volumes, financing balances and cash expenses in the context of codes of economic classification of budget expenditures budget classification Russian Federation.
Institution presentation day financial statements determined by the date of its mailing or the date of actual transfer of ownership.
If the date of submission of financial statements falls on a non-working (weekend) day, then the reporting deadline is considered to be the first working day following it.
Accounting statements containing indicators classified as state secrets current legislation, is presented taking into account the requirements of this legislation.
28. The main managers submit consolidated monthly, quarterly and annual financial statements on the execution of estimates of income and expenses of institutions under their jurisdiction, respectively, to the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and the bodies executing the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local budgets, within the time frames they set.
The consolidated financial statements are signed by the manager and chief accountant of the chief manager.
The responsibility of the persons who signed the consolidated financial statements is determined in accordance with current legislation.
29. Automation of accounting is based on a single interconnected technological process for processing documentation for all sections of accounting with the preparation of a balance sheet in accordance with the chart of accounts provided for in these Instructions and standard design solutions for comprehensive automation of accounting.
In the conditions of complex automation of accounting for the execution of estimates of income and expenses of an institution, synthetic and analytical accounting data are generated in the databases of the software package used and are monthly displayed on paper - output forms of documents (memorial orders, cards, statements, main book, report, etc.). At the same time, the content of indicators in the weekend of non-receipt of material assets during a period sufficient for their transportation must be reported to the customer in order to take measures to search for and deliver them to the addressee.
If the execution of estimates of income and expenses of institutions is kept by a centralized accounting department, the customer must inform it about the sending of material assets to the recipient institutions. Centralized accounting establishes control over the receipt of valuables and informs the customer about their acceptance for accounting.
---The regulations on maintaining accounting records and financial statements in the Russian Federation were approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 29, 1998 N 34n.
The order was registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on August 27, 1998 N 1598.
The document is presented taking into account changes as of the end of 2018.
Pursuant to the Accounting Reform Program in accordance with international standards financial statements, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of March 6, 1998 N 283, and order of the Government of the Russian Federation of March 21, 1998 N 382-r, I order:
1. Approve the attached Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation.
2. To recognize as invalid:
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of December 26, 1994 N 170 “On the Regulations on Accounting and Reporting in the Russian Federation”;
paragraph 3 of Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated February 3, 1997 No. 8 “On the quarterly financial statements of the organization.”
Minister M.M.ZADORNOV
REGULATIONS FOR ACCOUNTING AND ACCOUNTING REPORTING IN THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
I. General provisions
1. These Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Regulations) were developed on the basis of the Federal Law “On Accounting”.
2. The Regulations determine the procedure for organizing and maintaining accounting records, drawing up and presenting financial statements legal entities according to the legislation of the Russian Federation, regardless of their organizational and legal form (with the exception of credit organizations and state (municipal) institutions), as well as the organization’s relationship with external consumers of accounting information.
Branches and representative offices of foreign organizations located on the territory of the Russian Federation can keep accounting records based on the rules established in the country of location foreign organization, if the latter do not contradict the International Financial Reporting Standards developed by the Financial Reporting Committee international standards financial statements.
3. The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, on the basis of the Federal Law "On Accounting", develops and approves regulations (standards) for accounting, other regulatory legal acts and guidelines for accounting that form the system regulatory regulation accounting and mandatory for organizations on the territory of the Russian Federation, including when carrying out activities outside the Russian Federation.
4. In accordance with the Federal Law "On Accounting":
c) the main objectives of accounting are:
generation of complete and reliable information about the organization’s activities and its property status, necessary for internal users of financial statements - managers, founders, participants and owners of the organization’s property, as well as external users - investors, creditors and other users of financial statements;
provision of information necessary for internal and external users of financial statements to monitor compliance with the legislation of the Russian Federation in the implementation of business transactions and their feasibility, the availability and movement of property and liabilities, the use of material, labor and financial resources in accordance with approved norms, standards and estimates;
preventing negative results from the organization’s economic activities and identifying internal reserves to ensure its financial stability.
5. Organization for the implementation of accounting, guided by the legislation of the Russian Federation on accounting, regulations of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and bodies that federal laws granted the right to regulate accounting, independently forms its own accounting policies based on its structure, industry affiliation and other features of its activities.
6. Responsibility for organizing accounting in the organization and compliance with the law when carrying out business operations lies with the head of the organization.
7. The head of the organization can, depending on the volume of accounting work:
a) establish accounting service as a structural unit headed by the chief accountant;
b) add an accountant position to the staff;
c) transfer on a contractual basis the maintenance of accounting to a centralized accounting department, a specialized organization or a specialist accountant;
d) keep accounting records personally.
The cases provided for in subparagraphs "b", "c" and "d" of this paragraph are recommended to be applied in organizations that, according to the legislation of the Russian Federation, are classified as small businesses.
8. The accounting policy adopted by the organization is approved by order or other written order of the head of the organization.
In this case it is affirmed:
working chart of accounts, containing the accounts used in the organization, necessary for maintaining synthetic and analytical accounting;
forms of primary accounting documents used for registration of business transactions for which there are no provisions standard forms primary accounting documents, as well as forms of documents for internal accounting reporting;
assessment methods individual species property and liabilities;
the procedure for conducting an inventory of property and liabilities;
document flow rules and accounting information processing technology;
the procedure for monitoring business transactions, as well as other decisions necessary for organizing accounting.
II. Basic accounting rules
Accounting requirements
9. The organization maintains accounting records of property, liabilities and business transactions (facts of economic activity) by double entry on interrelated accounting accounts included in the working chart of accounts.
The working chart of accounts is approved by the organization on the basis of the Chart of Accounts approved by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
Accounting for property, liabilities and business transactions (facts of business activity) is carried out in the currency of the Russian Federation - in rubles. Documentation of property, liabilities and other facts of economic activity, maintenance of accounting registers and financial statements is carried out in Russian. Primary accounting documents compiled in other languages must have a line-by-line translation into Russian.
10. To maintain accounting records in an organization, an accounting policy is formed that presupposes property isolation and continuity of the organization’s activities, the sequence of application accounting policy, as well as the temporal certainty of the facts of economic activity.
The organization's accounting policies must meet the requirements of completeness, prudence, priority of content over form, consistency and rationality.
11. In the accounting of an organization, current costs for production of products, performance of work and provision of services and costs associated with capital and financial investments are accounted for separately.
Documentation of business transactions
12. The paragraph is no longer valid. - Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 29, 2017 N 47n.
The requirements of the chief accountant (hereinafter referred to as the chief accountant also means persons conducting accounting in the cases provided for in subparagraphs “b”, “c”, “d” of paragraph 7 of these Regulations) for documenting business transactions and submitting documents and information to the accounting service are mandatory for all employees of the organization.
13. Paragraphs one and two are no longer valid. - Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 29, 2017 N 47n.
Depending on the nature of the operation, the requirements of regulations, guidelines for accounting and technology for processing accounting information in source documents Additional details may be included.
14. The list of persons authorized to sign primary accounting documents is approved by the head of the organization in agreement with the chief accountant.
Documents used to formalize business transactions with funds are signed by the head of the organization and the chief accountant or persons authorized by them.
Without the signature of the chief accountant or a person authorized by him, monetary and settlement documents, financial and credit obligations are considered invalid and should not be accepted for execution (with the exception of documents signed by the head of the federal executive body, the design features of which are determined by separate instructions of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation) . Financial and credit obligations are understood as documents formalizing financial investments organizations, loan agreements, loan agreements and contracts concluded on commodity and commercial loan.
In case of disagreements between the head of the organization and the chief accountant regarding the implementation of certain business transactions, the primary accounting documents for them can be accepted for execution with a written order from the head of the organization, who bears full responsibility for the consequences of such transactions and the inclusion of data about them in accounting and accounting reporting.
15. The primary accounting document must be drawn up at the time of the business transaction, and if this is not possible, immediately after the completion of the transaction.
When selling goods, products, works and services using cash registers It is allowed to draw up a primary accounting document at least once a day after its completion on the basis of cash receipts.
The creation of primary accounting documents, the procedure and timing of their transfer for reflection in accounting are carried out in accordance with the document flow schedule approved by the organization. Timely and high-quality execution of primary accounting documents, their transfer within the established time frame for reflection in accounting, as well as the reliability of the data contained in them are ensured by the persons who compiled and signed these documents.
16. Making corrections to cash registers and bank documents not allowed. Corrections can be made to other primary accounting documents only by agreement with the persons who compiled and signed these documents, which must be confirmed by the signatures of the same persons, indicating the date of the corrections.
17. To control and streamline the processing of data on business transactions, consolidated accounting documents can be compiled on the basis of primary accounting documents.
18. Primary and consolidated accounting documents can be compiled on paper and computer media. In the latter case, the organization is obliged to produce, at its own expense, copies of such documents on paper for other participants in business transactions, as well as at the request of the authorities exercising control in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, the court and the prosecutor's office.
Accounting registers
19. Accounting registers are intended to systematize and accumulate information contained in primary accounting documents accepted for accounting, for reflection in accounting accounts and in financial statements.
Accounting registers can be kept in special books (magazines), on separate sheets and cards, in the form of machine diagrams obtained using computer technology, as well as on computer storage media. When maintaining accounting registers on computer media, it must be possible to output them to paper media.
Forms of accounting registers are developed and recommended by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, bodies that are granted the right to regulate accounting by federal laws, or federal executive authorities, organizations, subject to their compliance with the general methodological principles of accounting.
20. Business transactions must be reflected in accounting registers in chronological order and grouped according to the appropriate accounting accounts.
The correct reflection of business transactions in accounting registers is ensured by the persons who compiled and signed them.
21. When storing accounting registers, they must be protected from unauthorized corrections. Correction of an error in the accounting register must be justified and confirmed by the signature of the person who made the correction, indicating the date of the correction.
Persons who have access to information contained in accounting registers and internal accounting reports are required to maintain commercial and state secrets. For its disclosure they bear responsibility established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Valuation of property and liabilities
23. Property, liabilities and other facts of economic activity for reflection in accounting and financial statements are subject to valuation in monetary terms.
The assessment of property acquired for a fee is carried out by summing up the actual costs incurred for its purchase; property received free of charge - at market value on the date of capitalization; property produced in the organization itself - at the cost of its production (actual costs associated with the production of the property).
The actual costs incurred include, in particular, the costs of acquiring the property itself, interest paid on a commercial loan provided upon acquisition, markups (surcharges), commissions (cost of services) paid to supply, foreign economic and other organizations, customs duties and other payments, costs of transportation, storage and delivery carried out by third parties.
The current market value is formed on the basis of the price in effect on the date of recording of property received free of charge for this or a similar type of property. Data on the current price must be confirmed by documents or experts.
The cost of production recognizes the actual costs incurred associated with the use of fixed assets, raw materials, materials, fuel, energy, labor resources and other costs for the production of the property.
The use of other valuation methods, including through reserving, is permitted in cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation, as well as regulations of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and bodies granted by federal laws the right to regulate accounting.
24. Accounting entries for the organization’s foreign currency accounts, as well as for transactions in foreign currency, are made in rubles in amounts determined by converting foreign currency at the exchange rate Central Bank Russian Federation, valid on the date of the transaction. At the same time, these entries are made in the currency of settlements and payments.
25. Accounting for property, liabilities and business transactions may be kept in amounts rounded to whole rubles. The resulting amount differences are included in the financial results of commercial organization or an increase in income (decrease in expenses) for a non-profit organization.
Inventory of property and liabilities
26. To ensure the reliability of accounting data and financial statements, organizations are required to conduct an inventory of property and liabilities, during which their presence, condition and valuation are checked and documented.
The procedure (number of inventories in the reporting year, dates of their conduct, list of property and liabilities checked during each of them, etc.) of the inventory is determined by the head of the organization, except for cases when the inventory is mandatory.
27. Carrying out an inventory is mandatory:
when transferring property for rent, redemption, sale, as well as during the transformation of a state or municipal unitary enterprise;
before drawing up annual financial statements (except for property, the inventory of which was carried out no earlier than October 1 of the reporting year). An inventory of fixed assets can be carried out once every three years, and of library collections - once every five years. In organizations located in the Far North and equivalent areas, inventory of goods, raw materials and materials can be carried out during the period of their smallest balances;
when changing financially responsible persons;
when facts of theft, abuse or damage to property are revealed;
in the event of a natural disaster, fire or other emergency situations caused by extreme conditions;
during reorganization or liquidation of the organization;
in other cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
28. Discrepancies identified during the inventory between the actual availability of property and accounting data are reflected in the accounting accounts in the following order:
a) surplus property is accounted for at market value on the date of the inventory and the corresponding amount is credited to the financial results of a commercial organization or an increase in income of a non-profit organization;
b) shortage of property and its damage within the limits of natural loss norms are attributed to production or distribution costs (expenses), in excess of norms - at the expense of the guilty persons. If the perpetrators are not identified or the court refuses to recover damages from them, then losses from the shortage of property and its damage are written off to the financial results of a commercial organization or an increase in expenses for a non-profit organization.
III. Basic rules for the preparation and presentation of financial statements
Primary requirements
30. Accounting statements of organizations consist of:
a) balance sheet;
b) profit and loss statement;
c) appendices to them, in particular the traffic report Money, applications to balance sheet and other reports provided for by the regulations of the accounting regulatory system;
d) explanatory note;
e) an auditor's report confirming the reliability of the organization's financial statements, if they are subject to mandatory audit in accordance with federal laws.
31. Forms of financial statements of organizations, as well as instructions on the procedure for filling them out, are approved by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
Other bodies, which are granted the right to regulate accounting by federal laws, approve, within their competence, the forms of accounting statements and instructions on the procedure for filling them out, which do not contradict the normative legal acts Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
32. Accounting statements must provide a reliable and complete picture of the property and financial position of the organization, its changes, as well as the financial results of its activities.
When preparing financial statements, the organization is guided by these Regulations, unless otherwise established by other accounting provisions (standards).
33. The organization’s financial statements must include performance indicators of branches, representative offices and other structural units, including those allocated to separate balance sheets.
35. In the financial statements, data on numerical indicators are provided for at least two years - the reporting year and the one preceding the reporting year (except for the report prepared for the first reporting year).
If the data for the period preceding the reporting year are not comparable with the data for the reporting period, then the first of these data are subject to adjustment based on the rules established by regulations. Each material adjustment must be disclosed in explanatory note along with an indication of its reasons.
36. Accounting statements are prepared for the reporting year. The reporting year is considered to be the period from January 1 to December 31 of the calendar year inclusive.
The first reporting year for a newly created or reorganized organization is considered to be the period from the date of its state registration to December 31 inclusive, and for an organization newly created after October 1 (including October 1) - from the date of state registration to December 31 of the following year inclusive.
Data on the facts of economic activities carried out before the state registration of the newly created organization are included in its financial statements for the first reporting year.
37. For the preparation of financial statements, the reporting date is considered to be the last calendar day of the reporting period.
38. Accounting statements are signed by the head and chief accountant of the organization.
In organizations where accounting is carried out on a contractual basis by a specialized organization (centralized accounting department) or a specialist accountant, the financial statements are signed by the head of the organization, the head of a specialized organization (centralized accounting department) or a specialist in charge of accounting.
The responsibility of the persons who signed the financial statements is determined in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
39. Changes in the financial statements relating both to the reporting year and to previous periods (after their approval) are made in the statements prepared for the reporting period in which distortions in its data were discovered.
40. In the financial statements, offsets between items of assets and liabilities, items of profits and losses are not allowed, except in cases where such offset is provided for by the rules established by regulations.
Rules for evaluating financial statements items
Unfinished capital investments
41. Unfinished capital investments include costs for construction and installation work, acquisition of buildings, equipment, vehicles, tools, inventory, other durable material objects not formalized by acceptance certificates and other documents, other capital works and costs (design - survey, geological exploration and drilling work, diversion costs land plots and resettlement in connection with construction, for training of personnel for newly constructed organizations and others).
42. Incomplete capital investments are reflected in the balance sheet at the actual costs incurred by the organization.
Financial investments
43. Financial investments include investments by an organization in government securities, bonds and other securities of other organizations, in the authorized (share) capital of other organizations, as well as loans provided to other organizations.
44. Financial investments are taken into account in the amount of actual costs for the investor. For debt securities, the difference between the amount of actual acquisition costs and the nominal value during their circulation period is allowed to be attributed evenly as the income due on them is accrued to the financial results of a commercial organization or an increase in expenses of a non-profit organization.
Organizations acting as professional participants market valuable papers, can re-evaluate investments in securities purchased for the purpose of generating income from their sale as the quote changes to stock exchange.
Objects of financial investments (except for loans) that have not been paid in full are shown on the asset side of the balance sheet in the full amount of the actual costs of their acquisition under the agreement with the assignment of the outstanding amount to creditors in the liability side of the balance sheet in cases where the rights to the object have been transferred to the investor. In other cases, amounts contributed to the account of financial investment objects subject to acquisition are shown in the asset balance sheet under the item debtors.
45. An organization’s investments in shares of other organizations listed on the stock exchange, the quotation of which is regularly published, are reflected at the end of the reporting year at market value when preparing the balance sheet.
Fixed assets
46. To fixed assets as a set of material assets used as means of labor in the production of products, performance of work or provision of services, or for the management of an organization for a period exceeding 12 months, or the normal operating cycle, if it exceeds 12 months, include buildings, structures, working and power machines and equipment, measuring and control instruments and devices, computer technology, vehicles, tools, production and household equipment and accessories, working and productive livestock, perennial plantings, on-farm roads and other fixed assets.
Fixed assets also include capital investments in radical land improvement (drainage, irrigation and other reclamation works) and in leased fixed assets.
Capital investments in perennial plantings and radical land improvement are included in fixed assets annually in the amount of costs related to the areas accepted for operation in the reporting year, regardless of the completion date of the entire complex of work.
Fixed assets include those owned by the organization land, environmental management objects (water, subsoil and other natural resources).
47. Completed capital investments in leased fixed assets are credited by the tenant organization to its own fixed assets in the amount of actual costs incurred, unless otherwise provided by the lease agreement.
48. The cost of the organization’s fixed assets is repaid by calculating depreciation over their life beneficial use.
Depreciation of fixed assets is calculated regardless of the results of the organization’s economic activities in the reporting period in one of the following ways:
linear method;
method of writing off the cost in proportion to the volume of products (works, services);
reducing balance method;
a method of writing off cost based on the sum of the numbers of years of useful life.
Fixed assets of non-profit organizations are not subject to depreciation.
The cost of land plots and environmental management facilities is not repaid.
49. Fixed assets are reflected in the balance sheet at their residual value, i.e. at the actual costs of their acquisition, construction and manufacture minus the amount of accrued depreciation.
Changes in the initial cost of fixed assets in cases of completion, additional equipment, reconstruction and partial liquidation, revaluation of relevant objects are disclosed in the appendices to the balance sheet. A commercial organization has the right, no more than once a year (at the end of the reporting year), to revaluate fixed assets at replacement cost by indexation or direct recalculation based on documented market prices with the attribution of arising differences to the account of the organization’s additional capital, unless otherwise established by regulatory legal acts on accounting.
54. Material values remaining from the write-off of fixed assets unsuitable for restoration and further use are accounted for at market value on the date of write-off.
Intangible assets
55. Intangible assets used in economic activity for a period exceeding 12 months and generating income include rights arising:
from patents for inventions, industrial designs, selection achievements, from certificates for utility models, trademarks and service marks or licensing agreements for their use;
from rights to “know-how”, etc.
In addition, intangible assets include the business reputation of the organization.
56. The cost of intangible assets is repaid by calculating depreciation over deadline their beneficial use.
For objects for which the cost is repaid, depreciation deductions determined in one of the following ways:
linear method based on standards calculated by the organization based on their useful life;
method of writing off cost in proportion to the volume of products (works, services).
Depreciation is not accrued for intangible assets of non-profit organizations.
Amortization of intangible assets is calculated regardless of the organization's performance in the reporting period.
The acquired business reputation of the organization must be adjusted within twenty years (but not longer than the life of the organization).
Depreciation charges for the positive business reputation of an organization are reflected in accounting by reducing its initial cost. The negative business reputation of the organization is written off in full to the financial results of the organization as other income.
57. Intangible assets are reflected in the balance sheet at their residual value, i.e. at the actual costs of acquisition, production and costs of bringing them to a state in which they are suitable for use for the intended purposes, minus accrued depreciation.
Raw materials, materials, finished products and goods
58. Raw materials, main and auxiliary materials, fuel, purchased semi-finished products and components, spare parts, containers used for packaging and transportation of products (goods), and other material resources are reflected in the balance sheet at their actual cost.
Actual cost material resources determined based on the actual costs incurred for their acquisition and production.
Determining the actual cost of material resources written off for production is permitted using one of the following inventory valuation methods:
at the cost of a unit of inventory;
at average cost;
at the cost of the first acquisitions (FIFO);
59. Finished products is reflected in the balance sheet at the actual or standard (planned) production cost, including costs associated with the use of fixed assets, raw materials, materials, fuel, energy, labor resources, and other costs for production of products or direct cost items in the production process.
60. Goods in organizations engaged in trading activities are reflected in the balance sheet at the cost of their acquisition.
When selling (dispensing) goods, their value may be written off using the valuation methods set out in paragraph 58 of these Regulations.
When accounting for an organization engaged in retail trade, goods at sales prices, the difference between the acquisition cost and the cost at sales prices (discounts, markups) is reflected in the financial statements as a value that adjusts the cost of goods.
61. Shipped goods, delivered work and rendered services, for which revenue is not recognized, are reflected in the balance sheet at the actual (or standard (planned)) full cost, including, along with production cost costs associated with the sale (sale) of products, works, services, reimbursed by the negotiated (contract) price.
62. The values provided for in paragraphs 58 - 60 of these Regulations, for which the price has decreased during the reporting year or which have become obsolete or partially lost their original quality, are reflected in the balance sheet at the end of the reporting year at the price of possible sale, if it is lower than the original cost of procurement (acquisitions), with the difference in prices attributed to the financial results of a commercial organization or an increase in expenses for a non-profit organization.
Work in progress and deferred expenses
63. Products (works) that have not passed all stages (phases, redistributions) provided for by the technological process, as well as incomplete products that have not passed testing and technical acceptance, are classified as work in progress.
64. Work in progress in mass and serial production can be reflected in the balance sheet:
according to actual or standard (planned) production cost;
by direct cost items;
at the cost of raw materials, materials and semi-finished products.
With a single production of products, work in progress is reflected in the balance sheet at the actual costs incurred.
65. Costs incurred by the organization in the reporting period, but relating to the following reporting periods, are reflected in the balance sheet in accordance with the conditions for recognition of assets established by regulatory legal acts on accounting, and are subject to write-off in the manner established for writing off the value of assets of this type.
Capital and reserves
66. In the composition equity organizations take into account the statutory (share), additional and Reserve capital, retained earnings and other reserves.
67. The balance sheet reflects the amount of authorized (share) capital registered in the constituent documents as a set of contributions (shares, shares, shares) of the founders (participants) of the organization.
The authorized (share) capital and the actual debt of the founders (participants) for contributions (contributions) to the authorized (share) capital are reflected in the balance sheet separately.
State and municipal unitary enterprises, instead of authorized (share) capital, take into account authorized capital, formed in the prescribed manner.
68. Revaluation amount non-current assets carried out in accordance with the established procedure, the amount received in excess nominal value outstanding shares ( share premium joint stock company), and other similar amounts are accounted for as Extra capital and are reflected separately in the balance sheet.
69. Created in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation reserve fund to cover the organization's losses, as well as to repay the organization's bonds and repurchase its own shares, is reflected separately in the balance sheet.
70. The organization creates reserves for doubtful debts in the event that accounts receivable are recognized as doubtful, with the amounts of the reserves attributed to the financial results of the organization.
An organization's receivables are considered doubtful if they are not repaid or with a high degree of probability will not be repaid within the time limits established by the agreement and are not secured by appropriate guarantees.
The amount of the reserve is determined separately for each doubtful debt depending on financial condition(solvency) of the debtor and assessing the likelihood of repaying the debt in whole or in part.
If by the end of the reporting year following the year in which the reserve for doubtful debts was created, this reserve is not used in any part, then the unspent amounts are added to the financial results when drawing up the balance sheet at the end of the reporting year.
Settlements with debtors and creditors
73. Settlements with debtors and creditors are reflected by each party in its financial statements in the amounts arising from the accounting records and recognized by it as correct. For loans and credits received, the debt is shown taking into account the interest due at the end of the reporting period.
74. The amounts reflected in the financial statements for settlements with banks and the budget must be agreed upon with the relevant organizations and identical. Leaving unresolved amounts for these settlements on the balance sheet is not permitted.
75. Balances of foreign currency funds in the organization’s foreign currency accounts, other funds (including monetary documents), short-term securities, receivables and accounts payable V foreign currenciesх are reflected in the financial statements in rubles in amounts determined by converting foreign currencies at the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation effective on the reporting date.
76. Fines, penalties and penalties recognized by the debtor or for which court decisions on their collection have been received are attributed to the financial results of a commercial organization or an increase in income (reduction of expenses) of a non-profit organization and, before their receipt or payment, are reflected in the balance sheet of the recipient and the payer according to the items of debtors or creditors.
77. Accounts receivable, according to which the deadline limitation period has expired, other debts that are unrealistic for collection are written off for each obligation on the basis of the inventory data, written justification and order (instruction) of the head of the organization and are assigned, respectively, to the account of the reserve for doubtful debts or to the financial results of a commercial organization, if in the period preceding reporting, the amounts of these debts were not reserved in the manner prescribed by paragraph 70 of these Regulations, or for increasing expenses of a non-profit organization.
Writing off a debt at a loss due to the debtor's insolvency does not constitute cancellation of the debt. This debt must be reflected on the balance sheet for five years from the date of write-off in order to monitor the possibility of its collection in the event of a change in the debtor's property status.
78. Amounts of accounts payable and depositors for which the statute of limitations has expired are written off for each obligation based on the inventory data, written justification and order (instruction) of the head of the organization and are attributed to the financial results of a commercial organization or an increase in income of a non-profit organization.
Profit (loss) of the organization
79. Accounting profit (loss) is the final financial result (profit or loss) identified for the reporting period on the basis of accounting of all business transactions of the organization and assessment of balance sheet items according to the rules adopted by regulatory legal acts on accounting.
80. Profit or loss identified in the reporting year, but relating to operations of previous years, are included in the financial results of the organization for the reporting year.
82. In the case of the sale and other disposal of the organization’s property (fixed assets, inventories, securities, etc.), the loss or income from these transactions is attributed to the financial results of a commercial organization or an increase in expenses (income) of a non-profit organization.
83. In the balance sheet, the financial result of the reporting period is reflected as retained earnings (uncovered loss), i.e. the final financial result identified for the reporting period, minus taxes and other similar mandatory payments due from profits established in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, including sanctions for non-compliance with tax rules.
IV. Procedure for submitting financial statements
84. All organizations submit annual financial statements in accordance with constituent documents founders, participants of the organization or owners of its property, as well as territorial bodies of state statistics at the place of their registration. State and municipal unitary enterprises submit financial statements to the bodies authorized to manage state property.
Financial statements are presented to other executive authorities, banks and other users in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The organization is obliged to submit financial statements to the established addresses, one copy free of charge.
85. Organizations are required to submit annual financial statements in the forms provided for in paragraph 30 of these Regulations.
Small businesses and non-profit organizations are not allowed to submit a cash flow statement. In addition, small businesses have the right not to submit an appendix to the balance sheet, other appendices and an explanatory note.
86. Organizations are required to submit annual financial statements within 90 days after the end of the year, unless otherwise provided by the legislation of the Russian Federation, and quarterly - in cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation - within 30 days after the end of the quarter.
Within the specified time frame, the specific date for the submission of financial statements is established by the founders (participants) of the organization or general meeting.
88. The day an organization submits its financial statements is determined by the date of its mailing or the date of actual transmission according to ownership.
If the date of submission of financial statements falls on a non-working (weekend) day, then the reporting deadline is considered to be the first working day following it.
89. The annual financial statements of an organization are open to interested users: banks, investors, creditors, buyers, suppliers, etc., who can familiarize themselves with the annual financial statements and receive copies of them with reimbursement of copying costs.
The organization must provide an opportunity for interested users to familiarize themselves with the financial statements.
Accounting statements containing indicators classified as state secrets under the legislation of the Russian Federation are presented taking into account the requirements of the said legislation.
90. In cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation, the organization publishes financial statements and audit report.
Publication of financial statements is carried out no later than July 1 of the year following the reporting year, unless otherwise established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The procedure for publishing financial statements is established by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and the bodies that are granted the right to regulate accounting by federal laws.
V. Basic rules of consolidated financial statements
91. If an organization has subsidiaries and dependent companies in addition to its own accounting report consolidated financial statements are also compiled, including indicators of the reports of such companies located on the territory of the Russian Federation and abroad, in the manner established by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
96. Consolidated financial statements are signed by the head and chief accountant of the organization.
97. The responsibility of the persons who signed the consolidated financial statements is determined in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
VI. Storage of accounting documents
98. The organization is obliged to store primary accounting documents, accounting registers and financial statements for periods established in accordance with the rules for organizing state archival affairs, but not less than five years.
99. The working chart of accounts, other accounting policy documents, coding procedures, computer data processing programs (indicating the terms of their use) must be stored by the organization for at least five years after the reporting year in which they were used for the preparation of financial statements for the last time.
100. Primary accounting documents can be seized only by the bodies of inquiry, preliminary investigation and prosecutor’s office, courts, tax inspectorates and the tax police on the basis of their decisions in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Chief accountant or other executive organizations have the right, with the permission and in the presence of representatives of the authorities carrying out the seizure of documents, to make copies of them indicating the reason and date of seizure.
101. Responsibility for organizing the storage of primary accounting documents, accounting registers and financial statements lies with the head of the organization.
MINISTRY OF FINANCE OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
On approval of the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation
Document with changes made:
(Bulletin of normative acts of federal executive authorities, N 7-8, 02/14/2000, 02/21/2000);
(Russian newspaper, N 92-93, 05/16/2000) (came into force starting from the financial statements of 2000);
(Rossiyskaya Gazeta, N 242, October 27, 2006) (came into force starting with the annual financial statements for 2006);
(Rossiyskaya Gazeta, N 99, 05/12/2007) (came into force on January 1, 2008);
(Rossiyskaya Gazeta, N 271, 12/01/2010) (came into force on January 1, 2011);
(Bulletin of regulatory acts of federal executive authorities, N 13, 03/28/2011) (came into force with the financial statements of 2011);
by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 29, 2017 N 47n (Official Internet portal of legal information www.pravo.gov.ru, 04/19/2017, N 0001201704190005);
by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 11, 2018 N 74n (Official Internet portal of legal information www.pravo.gov.ru, 04/26/2018, N 0001201804260017).
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
The document also takes into account:
;
decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of July 8, 2016 N AKPI16-443;
decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated January 29, 2018 N AKPI17-1010 (came into force on March 5, 2018).
____________________________________________________________________
Pursuant to the Program for Reforming Accounting in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated March 6, 1998 N 283, and Order of the Government of the Russian Federation dated March 21, 1998 N 382-r
I order:
1. Approve the attached Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation.
2. To recognize as invalid:
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 1994 N 170 “On the Regulations on Accounting and Reporting in the Russian Federation”;
paragraph 3 of Order No. 8 of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated February 3, 1997 “On the quarterly financial statements of the organization.”
Minister
M.M.Zadornov
Registered
at the Ministry of Justice
Russian Federation
August 27, 1998
registration N 1598
Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation
APPROVED
by order of the Ministry of Finance
Russian Federation
dated July 29, 1998 N 34n
I. General provisions
2. The Regulations determine the procedure for organizing and maintaining accounting records, drawing up and submitting financial statements by legal entities under the legislation of the Russian Federation, regardless of their organizational and legal form (with the exception of credit organizations and state (municipal) institutions), as well as the organization’s relationship with external consumers accounting information (paragraph as amended, put into effect on March 3, 2000, by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n; as amended, put into effect on January 1, 2011 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 25, 2010 N 132n.
Branches and representative offices of foreign organizations located on the territory of the Russian Federation can keep accounting records based on the rules established in the country where the foreign organization is located, if the latter do not contradict the International Financial Reporting Standards developed by the International Financial Reporting Standards Committee.
3. The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, on the basis of the Federal Law "On Accounting", develops and approves provisions (standards) for accounting, other regulatory legal acts and methodological guidelines for accounting, forming a system of regulatory regulation of accounting and mandatory for execution by organizations in the territory of the Russian Federation, including when carrying out activities outside the Russian Federation (clause as amended, put into effect from the financial statements of 2011 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n.
4. In accordance with the Federal Law "On Accounting":
a) the subparagraph has lost force since April 30, 2017 -;
b) the subparagraph has lost force since April 30, 2017 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 29, 2017 N 47n;
c) the main objectives of accounting are:
generation of complete and reliable information about the organization’s activities and its property status, necessary for internal users of financial statements - managers, founders, participants and owners of the organization’s property, as well as external investors, creditors and other users of financial statements;
providing information necessary for internal and external users of financial statements to monitor compliance with the legislation of the Russian Federation when the organization carries out business operations and their feasibility, the availability and movement of property and liabilities, the use of material, labor and financial resources in accordance with approved norms, standards and estimates;
preventing negative results from the organization’s economic activities and identifying internal reserves to ensure its financial stability.
5. To carry out the organization of accounting, the organization, guided by the legislation of the Russian Federation on accounting, regulations of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and bodies granted by federal laws the right to regulate accounting, independently forms its accounting policy, based on its structure, industry affiliation and others features of the activity.
6. Responsibility for organizing accounting in the organization and compliance with the law when carrying out business operations lies with the head of the organization.
7. The head of the organization can, depending on the volume of accounting work:
a) establish an accounting service as a structural unit headed by a chief accountant;
b) add an accountant position to the staff;
c) transfer on a contractual basis the maintenance of accounting to a centralized accounting department, a specialized organization or a specialist accountant;
d) keep accounting records personally.
The cases provided for in subparagraphs "b", "c" and "d" of this paragraph are recommended to be applied in organizations that, according to the legislation of the Russian Federation, are classified as small businesses.
8. The accounting policy adopted by the organization is approved by order or other written order of the head of the organization.
In this case it is affirmed:
working chart of accounts, containing the accounts used in the organization, necessary for maintaining synthetic and analytical accounting;
forms of primary accounting documents used for registration of business transactions, for which standard forms of primary accounting documents are not provided, as well as forms of documents for internal accounting reporting;
methods for assessing certain types of property and liabilities;
the procedure for conducting an inventory of property and liabilities;
document flow rules and accounting information processing technology;
the procedure for monitoring business transactions, as well as other decisions necessary for organizing accounting.
II. Basic accounting rules
Accounting requirements
9. The organization maintains accounting records of property, liabilities and business transactions (facts of economic activity) by double entry on interrelated accounting accounts included in the working chart of accounts.
The working chart of accounts is approved by the organization on the basis of the Chart of Accounts approved by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
Accounting for property, liabilities and business transactions (facts of business activity) is carried out in the currency of the Russian Federation - in rubles. Documentation of property, liabilities and other facts of economic activity, maintenance of accounting registers and financial statements is carried out in Russian. Primary accounting documents compiled in other languages must have a line-by-line translation into Russian.
10. To maintain accounting records in an organization, an accounting policy is formed that presupposes the property isolation and continuity of the organization’s activities, the sequence of application of the accounting policy, as well as the temporal* certainty of the facts of economic activity.
___________________
* In this word the stress is on the penultimate syllable. - Database manufacturer's note.
The organization's accounting policies must meet the requirements of completeness, prudence, priority of content over form, consistency and rationality.
11. In the accounting of an organization, current costs for production of products, performance of work and provision of services and costs associated with capital and financial investments are accounted for separately.
Documentation of business transactions
12. The paragraph has lost force since April 30, 2017 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 29, 2017 N 47n..
The requirements of the chief accountant (hereinafter referred to as the chief accountant also means persons conducting accounting in the cases provided for in subparagraphs “b”, “c”, “d” of paragraph 7 of these Regulations) for documenting business transactions and submitting documents and information to the accounting service are mandatory for all employees of the organization.
13. The paragraph has lost force since April 30, 2017 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 29, 2017 N 47n..
The paragraph has lost force since April 30, 2017 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 29, 2017 N 47n..
Depending on the nature of the transaction, the requirements of regulations, accounting guidelines and technology for processing accounting information, additional details may be included in the primary documents.
14. The list of persons authorized to sign primary accounting documents is approved by the head of the organization in agreement with the chief accountant.
Documents used to formalize business transactions with funds are signed by the head of the organization and the chief accountant or persons authorized by them.
Without the signature of the chief accountant or a person authorized by him, monetary and settlement documents, financial and credit obligations are considered invalid and should not be accepted for execution (with the exception of documents signed by the head of the federal executive body, the design features of which are determined by separate instructions of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation) . Financial and credit obligations are understood as documents documenting the organization’s financial investments, loan agreements, credit agreements and agreements concluded on commodity and commercial loans.
In case of disagreements between the head of the organization and the chief accountant regarding the implementation of certain business transactions, the primary accounting documents for them can be accepted for execution with a written order from the head of the organization, who bears full responsibility for the consequences of such transactions and the inclusion of data about them in accounting and accounting reporting.
15. The primary accounting document must be drawn up at the time of the business transaction, and if this is not possible, immediately after the completion of the transaction.
When selling goods, products, works and services using cash registers, it is allowed to draw up a primary accounting document at least once a day after its completion on the basis of cash receipts.
The creation of primary accounting documents, the procedure and timing of their transfer for reflection in accounting are carried out in accordance with the document flow schedule approved by the organization. Timely and high-quality execution of primary accounting documents, their transfer within the established time frame for reflection in accounting, as well as the reliability of the data contained in them are ensured by the persons who compiled and signed these documents.
16. Corrections to cash and bank documents are not allowed. Corrections can be made to other primary accounting documents only by agreement with the persons who compiled and signed these documents, which must be confirmed by the signatures of the same persons, indicating the date of the corrections.
17. To control and streamline the processing of data on business transactions, consolidated accounting documents can be compiled on the basis of primary accounting documents.
18. Primary and consolidated accounting documents can be compiled on paper and computer media. In the latter case, the organization is obliged to produce, at its own expense, copies of such documents on paper for other participants in business transactions, as well as at the request of the authorities exercising control in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, the court and the prosecutor's office.
Accounting registers
19. Accounting registers are intended to systematize and accumulate information contained in primary accounting documents accepted for accounting, for reflection in accounting accounts and in financial statements.
Accounting registers can be kept in special books (magazines), on separate sheets and cards, in the form of machine diagrams obtained using computer technology, as well as on computer storage media. When maintaining accounting registers on computer media, it must be possible to output them to paper media.
Forms of accounting registers are developed and recommended by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, bodies that are granted the right to regulate accounting by federal laws, or federal executive authorities, organizations, subject to their compliance with the general methodological principles of accounting.
20. Business transactions must be reflected in accounting registers in chronological order and grouped according to the appropriate accounting accounts.
The correct reflection of business transactions in accounting registers is ensured by the persons who compiled and signed them.
21. When storing accounting registers, they must be protected from unauthorized corrections. Correction of an error in the accounting register must be justified and confirmed by the signature of the person who made the correction, indicating the date of the correction.
Persons who have access to information contained in accounting registers and internal accounting reports are required to maintain commercial and state secrets. For its disclosure they bear responsibility established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Valuation of property and liabilities
23. Property, liabilities and other facts of economic activity for reflection in accounting and financial statements are subject to valuation in monetary terms.
The assessment of property acquired for a fee is carried out by summing up the actual costs incurred for its purchase; property received free of charge - at market value on the date of capitalization; property produced in the organization itself - at the cost of its production (actual costs associated with the production of the property).
The actual costs incurred include, in particular, the costs of acquiring the property itself, interest paid on a commercial loan provided upon acquisition, markups (surcharges), commissions (cost of services) paid to supply, foreign economic and other organizations, customs duties and other payments, costs of transportation, storage and delivery carried out by third parties.
The current market value is formed on the basis of the price in effect on the date of recording of property received free of charge for this or a similar type of property. Data on the current price must be confirmed by documents or experts.
The cost of production recognizes the actual costs incurred associated with the use of fixed assets, raw materials, materials, fuel, energy, labor resources and other costs for the production of the property in the process of manufacturing property.
The use of other valuation methods, including through reserving, is permitted in cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation, as well as regulations of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and bodies granted by federal laws the right to regulate accounting.
24. Accounting entries for the organization’s foreign currency accounts, as well as for transactions in foreign currency, are made in rubles in amounts determined by converting foreign currency at the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation effective on the date of the transaction. At the same time, these entries are made in the currency of settlements and payments.
25. Accounting for property, liabilities and business transactions may be kept in amounts rounded to whole rubles. The amount differences arising in this case are attributed to the financial results of a commercial organization or an increase in income (reduction of expenses) for a non-profit organization (clause as amended, put into effect on March 3, 2000 by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n.
Inventory of property and liabilities
26. To ensure the reliability of accounting data and financial statements, organizations are required to conduct an inventory of property and liabilities, during which their presence, condition and valuation are checked and documented.
The procedure (number of inventories in the reporting year, dates of their conduct, list of property and liabilities checked during each of them, etc.) of the inventory is determined by the head of the organization, except for cases when the inventory is mandatory.
27. Carrying out an inventory is mandatory:
when transferring property for rent, redemption, sale, as well as during the transformation of a state or municipal unitary enterprise;
before drawing up annual financial statements (except for property, the inventory of which was carried out no earlier than October 1 of the reporting year). An inventory of fixed assets can be carried out once every three years, and of library collections - once every five years. In organizations located in the Far North and equivalent areas, inventory of goods, raw materials and materials can be carried out during the period of their smallest balances;
when changing financially responsible persons;
when facts of theft, abuse or damage to property are revealed;
in the event of a natural disaster, fire or other emergency situations caused by extreme conditions;
during reorganization or liquidation of the organization;
in other cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
28. Discrepancies identified during the inventory between the actual availability of property and accounting data are reflected in the accounting accounts in the following order:
a) surplus property is accounted for at market value on the date of the inventory and the corresponding amount is credited to the financial results of a commercial organization or an increase in income of a non-profit organization (subparagraph as amended, put into effect on March 3, 2000 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n;
b) shortage of property and its damage within the limits of natural loss norms are attributed to production or distribution costs (expenses), in excess of norms - at the expense of the guilty persons. If the guilty persons are not identified or the court refuses to recover damages from them, then losses from the shortage of property and its damage are written off against the financial results of a commercial organization or an increase in expenses for a non-profit organization (subclause as amended, put into effect on March 3, 2000 by order of the Ministry of Finance Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n.
III. Basic rules for the preparation and presentation of financial statements
Primary requirements
29. The clause has lost force since May 7, 2018 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 11, 2018 N 74n..
30. The financial statements of organizations consist of (paragraph as amended, put into effect on March 3, 2000 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n:
a) balance sheet;
b) profit and loss statement;
c) appendices to them, in particular the cash flow statement, appendices to the balance sheet and other reports provided for by the regulations of the accounting regulatory system;
d) explanatory note;
e) an auditor's report confirming the reliability of the organization's financial statements, if they are subject to mandatory audit in accordance with federal laws.
The paragraph was excluded from March 3, 2000 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n..
31. Forms of financial statements of organizations, as well as instructions on the procedure for filling them out, are approved by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
Other bodies, which are granted the right to regulate accounting by federal laws, approve, within their competence, the forms of accounting statements and instructions on the procedure for filling them out, which do not contradict the regulatory legal acts of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
32. Accounting statements must provide a reliable and complete picture of the property and financial position of the organization, its changes, as well as the financial results of its activities.
When preparing financial statements, the organization is guided by these Regulations, unless otherwise established by other provisions (standards) on accounting (the paragraph was additionally included from the financial statements of 2011 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n).
33. The organization’s financial statements must include performance indicators of branches, representative offices and other structural units, including those allocated to separate balance sheets.
35. In the financial statements, data on numerical indicators are provided for at least two years - the reporting year and the one preceding the reporting year (except for the report prepared for the first reporting year).
If the data for the period preceding the reporting year are not comparable with the data for the reporting period, then the first of these data are subject to adjustment based on the rules established by regulations. Each significant adjustment must be disclosed in an explanatory note along with the reasons for it.
36. Accounting statements are prepared for the reporting year. The reporting year is considered to be the period from January 1 to December 31 of the calendar year inclusive.
The first reporting year for a newly created or reorganized organization is considered to be the period from the date of its state registration to December 31 inclusive, and for an organization newly created after October 1 (including October 1), from the date of state registration to December 31 of the following year inclusive.
Data on the facts of economic activities carried out before the state registration of the newly created organization are included in its financial statements for the first reporting year.
37. For the preparation of financial statements, the reporting date is considered to be the last calendar day of the reporting period.
38. Accounting statements are signed by the head and chief accountant of the organization.
In organizations where accounting is carried out on a contractual basis by a specialized organization (centralized accounting department) or a specialist accountant, the financial statements are signed by the head of the organization, the head of a specialized organization (centralized accounting department) or a specialist in charge of accounting.
The responsibility of the persons who signed the financial statements is determined in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
39. Changes in the financial statements relating both to the reporting year and to previous periods (after their approval) are made in the statements prepared for the reporting period in which distortions in its data were discovered.
40. In the financial statements, offsets between items of assets and liabilities, items of profits and losses are not allowed, except in cases where such offset is provided for by the rules established by regulations.
Rules for evaluating financial statements items
Unfinished capital investments
41. Unfinished capital investments include costs for construction and installation work, acquisition of buildings, equipment, vehicles, tools, inventory, other durable material objects not formalized by acceptance certificates and other documents, other capital works and costs (design - survey, geological exploration and drilling work, costs of land acquisition and resettlement in connection with construction, training of personnel for newly constructed organizations and others) (paragraph supplemented starting from the financial statements of 2000 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 24, 2000 N 31n order Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n.
..
42. Incomplete capital investments are reflected in the balance sheet at the actual costs incurred by the organization (as amended, put into effect from the financial statements of 2011 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n.
Financial investments
43. Financial investments include investments by an organization in government securities, bonds and other securities of other organizations, in the authorized (share) capital of other organizations, as well as loans provided to other organizations.
44. Financial investments are taken into account in the amount of actual costs for the investor. For debt securities, the difference between the amount of actual acquisition costs and the nominal value during their circulation period is allowed to be attributed evenly as the income due on them is accrued to the financial results of a commercial organization or an increase in expenses of a non-profit organization (paragraph as amended from On March 3, 2000, by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n.
Organizations acting as professional participants in the securities market may revaluate investments in securities purchased for the purpose of generating income from their sale as quotes on the stock exchange change.
Objects of financial investments (except for loans) that have not been paid in full are shown on the asset side of the balance sheet in the full amount of the actual costs of their acquisition under the agreement with the assignment of the outstanding amount to creditors in the liability side of the balance sheet in cases where the rights to the object have been transferred to the investor. In other cases, amounts contributed to the account of financial investment objects subject to acquisition are shown in the asset balance sheet under the item debtors.
45. An organization’s investments in shares of other organizations listed on the stock exchange, the quotation of which is regularly published, when drawing up the balance sheet, are reflected at the end of the reporting year at market value (clause as amended, put into effect from the financial statements of 2011 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24 2010 N 186n.
Fixed assets
46. To fixed assets as a set of material assets used as means of labor in the production of products, performance of work or provision of services, or for the management of an organization for a period exceeding 12 months, or the normal operating cycle, if it exceeds 12 months, include buildings, structures, working and power machines and equipment, measuring and control instruments and devices, computer technology, vehicles, tools, production and household equipment and supplies, working and productive livestock, perennial plantings, on-farm roads and other fixed assets.
Fixed assets also include capital investments in radical land improvement (drainage, irrigation and other reclamation works) and in leased fixed assets.
Capital investments in perennial plantings and radical land improvement are included in fixed assets annually in the amount of costs related to the areas accepted for operation in the reporting year, regardless of the completion date of the entire complex of work.
Fixed assets include land plots owned by the organization and environmental management facilities (water, subsoil and other natural resources).
47. Completed capital investments in leased fixed assets are credited by the tenant organization to its own fixed assets in the amount of actual costs incurred, unless otherwise provided by the lease agreement.
48. The cost of the organization's fixed assets is repaid by calculating depreciation over their useful life.
Depreciation of fixed assets is calculated regardless of the results of the organization’s economic activities in the reporting period in one of the following ways:
linear method;
method of writing off the cost in proportion to the volume of products (works, services);
reducing balance method;
a method of writing off cost based on the sum of the numbers of years of useful life.
The paragraph has lost force since the financial statements of 2011 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n..
Fixed assets of non-profit organizations are not subject to depreciation (the paragraph was additionally included starting from the financial statements of 2000 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 24, 2000 N 31n).
____________________________________________________________________
The paragraph, additionally included by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 24, 2000 N 31n, was declared invalid (ineffective), not entailing legal consequences from the moment of publication, - decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of August 23, 2000 N GKPI 00-645.
____________________________________________________________________
The cost of land plots and environmental management facilities is not repaid.
49. Fixed assets are reflected in the balance sheet at their residual value, i.e. at the actual costs of their acquisition, construction and production minus the amount of accrued depreciation (paragraph as amended, put into effect on March 3, 2000 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n.
Changes in the initial cost of fixed assets in cases of completion, additional equipment, reconstruction and partial liquidation, revaluation of relevant objects are disclosed in the appendices to the balance sheet. A commercial organization has the right, no more than once a year (at the end of the reporting year), to revaluate fixed assets at replacement cost by indexation or direct recalculation at documented market prices with attribution of any resulting differences to the organization’s additional capital, unless otherwise established by regulatory legal acts on accounting (paragraph as amended, put into effect from the 2011 financial statements by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n.
50. The paragraph has become invalid since the financial statements of 2011 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n..
51. The point has become invalid since the financial statements of 2011 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n..
52. The paragraph has become invalid since the financial statements of 2011 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n..
53. The paragraph has become invalid since the financial statements of 2011 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n..
54. Material assets remaining from the write-off of fixed assets unsuitable for restoration and further use are accounted for at market value on the date of write-off (clause as amended, put into effect on March 3, 2000 by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n; as amended , put into effect from the financial statements of 2011 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n.
Intangible assets
55. Intangible assets used in economic activity for a period exceeding 12 months and generating income include rights arising:
from patents for inventions, industrial designs, selection achievements, from certificates for utility models, trademarks and service marks or licensing agreements for their use (paragraph as amended by ;
from rights to “know-how”, etc.
In addition, intangible assets include the business reputation of the organization (paragraph as amended, put into effect from the financial statements of 2011 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n.
56. The cost of intangible assets is repaid by calculating depreciation over the established period of their useful life.
For objects for which the cost is repaid, depreciation charges are determined in one of the following ways:
linear method based on standards calculated by the organization based on their useful life;
method of writing off cost in proportion to the volume of products (works, services).
The paragraph has lost force since the financial statements of 2011 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n..
For intangible assets received under a gift agreement and free of charge during the privatization process, acquired using budgetary allocations and other similar funds (in terms of the cost attributable to the amount of these funds), depreciation is not accrued (paragraph as amended, entered into force on March 3, 2000 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n.
____________________________________________________________________
Paragraph four of paragraph 56 was stated in new edition on the basis of order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 24, 2000 N 31n.
The specified change in paragraph four of paragraph 56 was declared invalid (ineffective), not entailing legal consequences from the moment of publication, - decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of August 23, 2000 N GKPI 00-645.
The decision can be appealed to the Cassation Board Supreme Court Russian Federation within ten days from the date of its issuance in final form.
____________________________________________________________________
Amortization of intangible assets is calculated regardless of the organization's performance in the reporting period.
The acquired business reputation of the organization must be adjusted within twenty years (but not more than the life of the organization) (the paragraph was additionally included starting from the financial statements of 2000 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 24, 2000 N 31n).
Depreciation charges for the positive business reputation of an organization are reflected in accounting by reducing its initial cost. The negative business reputation of the organization is written off in full to the financial results of the organization as other income (the paragraph was additionally included starting from the 2000 financial statements by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 24, 2000 N 31n; as amended, effective from the annual financial statements for 2006 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 18, 2006 N 116n; as amended, put into effect from the financial statements of 2011 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n.
57. Intangible assets are reflected in the balance sheet at their residual value, i.e. according to the actual costs of acquisition, production and costs of bringing them to a state in which they are suitable for use for the planned purposes, minus accrued depreciation (clause as amended, put into effect on March 3, 2000 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n.
Raw materials, materials, finished products and goods
58. Raw materials, main and auxiliary materials, fuel, purchased semi-finished products and components, spare parts, containers used for packaging and transportation of products (goods), and other material resources are reflected in the balance sheet at their actual cost.
The actual cost of material resources is determined based on the actual costs incurred for their acquisition and production.
Determining the actual cost of material resources written off for production is permitted using one of the following inventory valuation methods:
at the cost of a unit of inventory;
at average cost;
at the cost of the first acquisitions (FIFO);
the paragraph was excluded from January 1, 2008 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 26, 2007 N 26n - see previous reaction.
59. Finished products are reflected in the balance sheet at actual or standard (planned) production costs, including costs associated with the use of fixed assets, raw materials, materials, fuel, energy, labor resources, and other costs for production of products or direct cost items.
60. Goods in organizations engaged in trading activities are reflected in the balance sheet at the cost of their acquisition.
When selling (dispensing) goods, their value may be written off using the valuation methods set out in paragraph 58 of these Regulations.
When an organization engaged in retail trade accounts for goods at sales prices, the difference between the acquisition cost and the cost at sales prices (discounts, markups) is reflected in the financial statements as a value that adjusts the cost of goods (paragraph as amended, effective from the 2011 financial statements by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n.
61. Goods shipped, works delivered and services rendered, for which revenue is not recognized, are reflected in the balance sheet at the actual (or standard (planned) full cost, which includes, along with production costs, costs associated with the sale (sale) of products, works, services , reimbursed by the negotiated (contract) price (the clause was supplemented from the 2011 financial statements by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n.
62. The values provided for in paragraphs 58-60 of these Regulations, for which the price has decreased during the reporting year or which have become obsolete or partially lost their original quality, are reflected in the balance sheet at the end of the reporting year at the price of possible sale, if it is lower than the original cost of procurement (acquisitions), with the difference in prices attributed to the financial results of a commercial organization or an increase in expenses for a non-profit organization.
Work in progress and deferred expenses
63. Products (works) that have not passed all stages (phases, redistributions) provided for by the technological process, as well as incomplete products that have not passed testing and technical acceptance, are classified as work in progress.
64. Work in progress in mass and serial production can be reflected in the balance sheet:
according to actual or standard (planned) production cost;
by direct cost items;
at the cost of raw materials, materials and semi-finished products.
With a single production of products, work in progress is reflected in the balance sheet at the actual costs incurred.
65. Costs incurred by the organization in the reporting period, but relating to the following reporting periods, are reflected in the balance sheet in accordance with the conditions for recognition of assets established by regulatory legal acts on accounting, and are subject to write-off in the manner established for writing off the value of assets of this type ( clause as amended, put into effect from the financial statements of 2011 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n.
Capital and reserves
66. The organization’s own capital takes into account the authorized (share), additional and reserve capital, retained earnings and other reserves.
67. The balance sheet reflects the amount of authorized (share) capital registered in the constituent documents as a set of contributions (shares, shares, shares) of the founders (participants) of the organization.
The authorized (share) capital and the actual debt of the founders (participants) for contributions (contributions) to the authorized (share) capital are reflected in the balance sheet separately.
State and municipal unitary enterprises, instead of authorized (share) capital, take into account the authorized capital formed in the prescribed manner.
68. The amount of additional valuation of non-current assets carried out in the prescribed manner, the amount received in excess of the par value of issued shares (share premium of a joint stock company), and other similar amounts are taken into account as additional capital and are reflected in the balance sheet separately (clause as amended, entered into force starting from from the financial statements of 2000 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 24, 2000 N 31n; as amended, put into effect from the financial statements of 2011 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n.
69. The reserve fund created in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation to cover the losses of the organization, as well as to repay the organization’s bonds and repurchase its own shares is reflected separately in the balance sheet.
70. The organization creates reserves for doubtful debts in the event that accounts receivable are recognized as doubtful with the amounts of reserves attributed to the financial results of the organization (paragraph as amended, put into effect from the financial statements of 2011 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n.
An organization's receivables are considered doubtful if they have not been repaid or with a high degree of probability will not be repaid within the terms established by the agreement and are not provided with appropriate guarantees (paragraph as amended, put into effect from the financial statements of 2011 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n.
The paragraph has lost force since the financial statements of 2011 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n..
The amount of the reserve is determined separately for each doubtful debt, depending on the financial condition (solvency) of the debtor and the assessment of the likelihood of repaying the debt in whole or in part.
If by the end of the reporting year following the year in which the reserve for doubtful debts was created, this reserve is not used in any part, then the unspent amounts are added to the financial results when drawing up the balance sheet at the end of the reporting year.
71. The item has been excluded since the financial statements of 2000 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 24, 2000 N 31n..
72. The paragraph has become invalid since the financial statements of 2011 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n..
Settlements with debtors and creditors
73. Settlements with debtors and creditors are reflected by each party in its financial statements in the amounts arising from the accounting records and recognized by it as correct. For loans and credits received, the debt is shown taking into account the interest due at the end of the reporting period.
74. The amounts reflected in the financial statements for settlements with banks and the budget must be agreed upon with the relevant organizations and identical. Leaving unresolved amounts for these settlements on the balance sheet is not permitted.
75. Balances of foreign currency funds on the organization’s foreign currency accounts, other funds (including monetary documents), short-term securities, receivables and payables in foreign currencies are reflected in the financial statements in rubles in amounts determined by converting foreign currencies at the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation effective as of the reporting date.
76. Fines, penalties and penalties recognized by the debtor or for which court decisions on their collection have been received are attributed to the financial results of a commercial organization or an increase in income (reduction of expenses) of a non-profit organization and, before their receipt or payment, are reflected in the balance sheet of the recipient and the payer respectively, according to the items of debtors or creditors (clause as amended, put into effect on March 3, 2000 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n.
77. Accounts receivable for which the statute of limitations has expired and other debts that are unrealistic for collection are written off for each obligation based on the inventory data, written justification and order (instruction) of the head of the organization and are charged accordingly to the reserve for doubtful debts or to financial results from a commercial organization, if in the period preceding the reporting period, the amounts of these debts were not reserved in the manner prescribed by paragraph 75* of these Regulations, or to increase expenses from a non-profit organization (paragraph as amended, put into effect on March 3, 2000 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n.
________________
*Probably an error in the original. Should read "point 70".
- Database manufacturer's note.
Writing off a debt at a loss due to the debtor's insolvency does not constitute cancellation of the debt. This debt must be reflected on the balance sheet for five years from the date of write-off in order to monitor the possibility of its collection in the event of a change in the debtor's property status.
78. Amounts of accounts payable and depositors for which the statute of limitations has expired are written off for each obligation based on the inventory data, written justification and order (instruction) of the head of the organization and are attributed to the financial results of a commercial organization or an increase in income of a non-profit organization (clause as amended, put into effect on March 3, 2000 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n.
Profit (loss) of the organization
79. Accounting profit (loss) is the final financial result (profit or loss) identified for the reporting period on the basis of accounting of all business transactions of the organization and assessment of balance sheet items according to the rules adopted by regulatory legal acts on accounting (clause as amended, put into effect from the financial statements of 2011 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n.
80. Profit or loss identified in the reporting year, but relating to operations of previous years, are included in the financial results of the organization for the reporting year.
81. The point has become invalid since the financial statements of 2011 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n..
82. In the event of the sale and other disposal of the organization’s property (fixed assets, inventories, securities, etc.), the loss or income from these transactions is attributed to the financial results of a commercial organization or an increase in expenses (income) of a non-profit organization (clause as amended , put into effect on March 3, 2000 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n.
83. In the balance sheet, the financial result of the reporting period is reflected as retained earnings (uncovered loss), i.e. the final financial result identified for the reporting period, minus taxes and other similar mandatory payments due from profits established in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, including sanctions for non-compliance with tax rules.
IV. Procedure for submitting financial statements
84. All organizations submit annual financial statements in accordance with the constituent documents to the founders, participants of the organization or owners of its property, as well as to the territorial bodies of state statistics at the place of their registration. State and municipal unitary enterprises submit financial statements to bodies authorized to manage state property (paragraph as amended, put into effect on March 3, 2000 by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n.
Financial statements are presented to other executive authorities, banks and other users in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The organization is obliged to submit financial statements to the established addresses, one copy free of charge.
85. Organizations are required to submit annual financial statements in the amount of forms provided for in paragraph 30 of these Regulations (paragraph as amended, put into effect on March 3, 2000 by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n.
Small businesses and non-profit organizations are not allowed to submit a cash flow statement. In addition, small businesses have the right not to submit an appendix to the balance sheet, other appendices and an explanatory note.
86. Organizations are required to submit annual financial statements within 90 days after the end of the year, unless otherwise provided by the legislation of the Russian Federation, and quarterly - in cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation - within 30 days after the end of the quarter (paragraph as amended by effective from March 3, 2000 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n.
Within the specified time frame, the specific date for the submission of financial statements is established by the founders (participants) of the organization or the general meeting (paragraph as amended, put into effect with the financial statements of 2011 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n.
The paragraph has lost force since the financial statements of 2011 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n..
87. The clause has lost force since March 3, 2000 - ..
88. The day an organization submits its financial statements is determined by the date of its mailing or the date of actual transmission according to ownership.
If the date of submission of financial statements falls on a non-working (weekend) day, then the reporting deadline is considered to be the first working day following it.
89. The annual financial statements of an organization are open to interested users: banks, investors, creditors, buyers, suppliers, etc., who can familiarize themselves with the annual financial statements and receive copies of them with reimbursement of copying costs (paragraph as amended On March 3, 2000, by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n.
The organization must provide an opportunity for interested users to familiarize themselves with the financial statements.
Accounting statements containing indicators classified as state secrets under the legislation of the Russian Federation are presented taking into account the requirements of the said legislation.
90. In cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation, the organization publishes its financial statements and auditor’s report (paragraph as amended, put into effect with the financial statements of 2011 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n.
Publication of financial statements is carried out no later than July 1 of the year following the reporting year, unless otherwise established by the legislation of the Russian Federation (paragraph as amended, put into effect with the financial statements of 2011 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n.
The procedure for publishing financial statements is established by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and the bodies that are granted the right to regulate accounting by federal laws.
V. Basic rules of consolidated financial statements
91. If an organization has subsidiaries and dependent companies, in addition to its own financial statements, consolidated financial statements are also compiled, including indicators of the reports of such companies located on the territory of the Russian Federation and abroad, in the manner established by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
92. The paragraph has become invalid since the financial statements of 2011 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n..
93. The paragraph has become invalid since the financial statements of 2011 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n..
94. The point has become invalid since the financial statements of 2011 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 24, 2010 N 186n..
95. The clause has lost force since March 3, 2000 - order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1999 N 107n..
96. Consolidated financial statements are signed by the head and chief accountant of the organization.
97. The responsibility of the persons who signed the consolidated financial statements is determined in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
VI. Storage of accounting documents
98. The organization is obliged to store primary accounting documents, accounting registers and financial statements for periods established in accordance with the rules for organizing state archival affairs, but not less than five years.
99. The working chart of accounts, other accounting policy documents, coding procedures, computer data processing programs (indicating the terms of their use) must be stored by the organization for at least five years after the reporting year in which they were used for the preparation of financial statements for the last time.
100. Primary accounting documents can be seized only by the bodies of inquiry, preliminary investigation and prosecutor's office, courts, tax inspectorates and tax police on the basis of their decisions in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The chief accountant or other official of the organization has the right, with the permission and in the presence of representatives of the authorities conducting the seizure of documents, to make copies of them indicating the reason and date of seizure.
101. Responsibility for organizing the storage of primary accounting documents, accounting registers and financial statements lies with the head of the organization.
Revision of the document taking into account
changes and additions prepared
JSC "Kodeks"
Approve the attached Guidelines for the implementation of the Budget Accounting Instructions.
Minister
A.L. KUDRIN
APPROVED
By order of the Ministry of Finance
Russian Federation
dated February 24, 2005 N 26n
METHODOLOGICAL INSTRUCTIONS
FOR IMPLEMENTATION OF INSTRUCTIONS ON BUDGET ACCOUNTING
1. These Guidelines for the implementation of the Instructions for Budget Accounting (hereinafter referred to as the Guidelines) were developed by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in order to implement the provisions of Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated August 26, 2004 N 70n “On approval of the Instructions for Budget Accounting” (registered in Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation October 5, 2004, registration number 6055) (hereinafter referred to as Instruction No. 70n) in government bodies, government bodies off-budget funds, management bodies of territorial state extra-budgetary funds, bodies local government, budgetary institutions(hereinafter referred to as institutions).
2. In accordance with the effective date of Instruction No. 70n - January 1, 2005, regardless of the timing of the transition to its application in accordance with the organizational and technical readiness of institutions, the outgoing balances of accounting accounts (hereinafter referred to as account balances) approved by the Instructions on accounting in budgetary institutions, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 1999 N 107n (registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on January 28, 2000, registration number 2064) (hereinafter referred to as Instruction N 107n), and the Instructions on accounting accounting for budget execution, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 17, 1999 N 15n (registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on April 22, 1999, registration number 1765) (hereinafter referred to as Instruction N 15n), as of January 1, 2005 are transferred to incoming balances on the accounts of the budget accounting chart of accounts as of January 1, 2005.
The institution transfers account balances after completing operations to close accounting accounts and drawing up financial statements for 2004. The results of the inventory (registration of unlisted objects, write-off of shortages, etc.) must be reflected in the accounting records of the institution before the conclusion of the 2004 accounts.
The transfer of account balances is carried out for each account separately at the cost at which they were listed as of January 1, 2005 in the accounting records of the institution in accordance with the Table of correspondence of accounts of the chart of accounts of accounting in budgetary institutions and the unified chart of accounts for accounting of budget execution to the chart of accounts budget accounting and accounting records for transfer to budget accounting accounts (hereinafter referred to as Table No. 1), given in Appendix No. 1 to these Methodological Recommendations and the Table of correspondence of the budget accounting account code to the code of income classification, departmental, functional classification of budget expenditures, classification of deficit financing sources budgets (hereinafter referred to as Table No. 2), given in Appendix No. 2 to these Methodological Recommendations.
Accounting transactions for the transfer of account balances are reflected in the Certificate (f. 0504833), established by Instruction No. 70n (hereinafter referred to as the Certificate), during the inter-reporting period (the period of reformation of balances on old sub-accounts as of January 1, 2005 to new balances on accounts of the budget accounting chart of accounts as of January 1, 2005).
3. When implementing Instruction No. 70n during 2005, along with incoming account balances as of January 1, 2005, the turnovers established in sub-accounts of accounting are subject to transfer.
Accounting records for the transfer of final turnover on accounts are reflected in the Certificate as of the date of transition to the application of Instruction No. 70n in accordance with Table No. 1 and Table No. 2.
4. Newly introduced objects of budget accounting (property of the state and municipal treasury, financial investments, etc.) are accepted for budget accounting in an assessment that meets the requirements of Instruction No. 70n by making adjustment entries contained in Table No. 1. Accounting operations for acceptance for budget accounting newly introduced budget accounting objects are reflected in the Certificate during the inter-reporting period.
5. When reflecting accounting records in accordance with paragraphs 2-4 of these Guidelines The following features must be taken into account.
5.1. Transfer of account balances for low-value items worth up to RUB 1,000. inclusive (except for dishes and soft equipment) is reflected:
for low-value items in use - accounting entry on the debit of account 040103000 " Financial results past reporting periods" and the credit of subaccount 071 "Low-value items in operation" with the simultaneous reflection of the same amount on the credit of account 040103000 "Financial result of past reporting periods" and the debit of sub-account 260 "Fund for low-value items" in the inter-reporting period;
for low-value items that are not in use - an accounting entry to the debit of the corresponding analytical accounts of account 010100000 "Fixed assets" and the credit of sub-account 070 "Low-value items in warehouse" with the simultaneous reflection of the same amount on the credit of account 040103000 "Financial result of past reporting periods" and debit subaccount 260 “Fund for low-value items” during the inter-reporting period.
5.2. The transfer of account balances for low-value items worth over 1,000 rubles, as well as dishes and soft equipment, regardless of cost, whether in use or not, is reflected in the accounting entry as a debit to the corresponding accounts of account 010100000 “Fixed Assets” and a credit to the corresponding sub-accounts 070 “Low-value items” in the warehouse", 071 "Low value items in use", 072 "Linen, bedding, clothes and shoes in the warehouse", 073 "Linen, bedding, clothes and shoes in use" with the simultaneous reflection of the same amount on the credit of account 040103000 " Financial result of previous reporting periods" and the debit of subaccount 260 "Fund for low-value items" in the inter-reporting period.
At the same time, it is necessary to take into account that the remnants of low-value items worth over 1000 rubles that are transferred to fixed assets are in use. it is necessary to accrue depreciation in the amount of 100% in the manner established by Instruction No. 70n during the inter-reporting period.
5.3. The transfer of balances on inventory accounts from the composition of medicines and dressings before making appropriate changes to Instruction No. 70n is reflected in the accounting entry as a debit to account 010501000 “Medicines and dressings” and a credit to subaccounts 062 “Medicines and dressings”, 063 “Household materials and office supplies accessories" during the inter-reporting period.
5.4. When transferring balances non-financial assets from the composition of low-value items, their value, expressed in rubles and kopecks for one object, is accepted for budget accounting in whole rubles with the assignment of kopecks to the debit of account 040103000 "Financial result of past reporting periods" and the credit of the corresponding subaccounts of account 07 "Low-value items" in the interreporting period.
5.5. The transfer of balances on account 020 “Depreciation of fixed assets” for non-financial asset objects reflected in subaccounts 017 “Working and productive livestock” and 019 “Other fixed assets” is recorded as an accounting entry as the debit of subaccount 020 “Depreciation of fixed assets” and the credit of account 010406000 " Depreciation of production and household equipment" with further provision of separate budgetary accounting of the specified amount until appropriate changes are made to Instruction No. 70n.
Subsequent accrual of depreciation amounts on objects of other fixed assets subject to depreciation is reflected in the debit of account 040101271 “Expenses for depreciation of fixed assets and intangible assets” and the credit of account 010406000 “Depreciation of production and business equipment”, ensuring separate budgetary accounting of the specified amount before making appropriate changes to Instruction No. 70n.
5.6. The transfer of balances on intangible asset accounts reflected as of January 1, 2005 in subaccount 031 “Intangible assets” is carried out in the following order:
if the copyright holder does not have exclusive property rights - on the debit of account 040103000 "Financial result of past reporting periods" and the credit of subaccount 031 "Intangible assets" with the simultaneous reflection of the same amount on the credit of account 040103000 "Financial result of past reporting periods" and the debit of subaccount 251 "Fund in intangible assets" during the inter-reporting period;
if the copyright holder has exclusive property rights, confirmed by properly executed documents - on the debit of account 010301000 "Intangible assets" and the credit of subaccount 031 "Intangible assets" with the simultaneous reflection of the same amount on the credit of account 040103000 "Financial result of past reporting periods" and the debit of subaccount 251 "Fund in intangible assets" during the inter-reporting period;
if the copyright holder has exclusive property rights that are not confirmed by properly executed documents - on the debit of account 010602000 "Capital investments in intangible assets" and the credit of subaccount 031 "Intangible assets" with the simultaneous reflection of the same amount on the credit of account 040103000 "Financial result of past reporting periods" and the debit of subaccount 251 “Fund in intangible assets” during the inter-reporting period. These assets are recorded on account 010602000 “Capital investments in intangible assets” until documents confirming exclusive ownership rights are prepared.
5.7. After reflection accounting transactions in the manner established by paragraphs 2, 3, 4 of these Methodological recommendations, non-financial assets should be subject to depreciation in the manner established by Instruction No. 70n, taking into account the following features:
for intangible assets acquired (created) before January 1, 2005 and reflected in account 010301000 “Intangible assets” as of January 1, 2005, as well as for intangible assets transferred from account 010602000 “Capital investments in intangible assets” after registration documents confirming the exclusive right of the copyright holder to intangible assets, depreciation is calculated at rates calculated in accordance with the useful life calculated taking into account the date of acceptance intangible asset to accounting;
for fixed assets (except for the library collection) worth up to 10,000 rubles. inclusive, acquired before January 1, 2005 and in operation, additional depreciation is calculated up to 100% in the manner established by Instruction No. 70n during the inter-reporting period;
Note. Access to full content of this document limited.
IN in this case Only part of the document is provided for review and to avoid plagiarism of our work.
To gain access to the full and free resources of the portal, you just need to register and log in.
It is convenient to work in extended mode with gaining access to paid portal resources, according to