Economic components of the state program for the development of health care. Federal target programs. Reducing the prevalence of infectious diseases
I approve
Chief physician GBUZ RB GB
G. Kumertau
___________ O. A. Astakhov
REPORT
FOR 2015
Afonina Evgeniya Valerievna
MEDICAL SISTERS
PEDIATRIC DEPARTMENT
State state-financed organization Healthcare of the Republic of Bashkortostan City Hospital of the city of Kumertau
For assignment of the second qualification category in the specialty
"Nursing in Pediatrics"
kumertau
I. Introduction
1. Reforming health care 3
2.Basic federal programs on health
population 7
3.Biography 8
II.The main part
4. City health care 9
5. Characteristics of the pediatric department 11
6. Performance indicators of the pediatric department 13
7. Basic orders regulating the work of a nurse 16
pediatric ward
8.Organization of the work of the ward nurse of pediatric 19
branches
9. Sanitary and anti-epidemic work of the ward nurse of the 27th pediatric department
10. Sanitary and educational work 32
III. Final part.
11. Conclusions 34
12. Sentences 35
13. References 36
Reforming health care.
Health care is a series of socio-economic and medical reforms aimed at preserving and improving the level of health of each individual and the population as a whole. The goal of health care reform is to preserve and develop the state municipal health care system, organize their activities, as well as the activities of the private health care system to maximize the rights of citizens in the field of health care.
Health care reform offers solutions to the following priority tasks:
1. From stationary medical care to outpatient - this is an increase in the volume of medical care in a polyclinic, the introduction of hospital-replacing technologies: day hospitals in a polyclinic, at home;
2. From specialized care to general medical practice, family medicine, when medical care is as close as possible to the place of residence and is a long process;
3. From increasing the amount of resources in the industry to their effective use;
4. From the volume of medical services to their quality;
5. From an increase in the number of beds, to their rational use, re-profiling and phasing of inpatient care;
6. From an increase in the number of doctors and nurses to the quality of their work - improving the quality of professional training of personnel, the system of practical health care, providing primary medical care.
7. From government funding to funding from different sources: paid services.
8.Supplying the population medicines accessible to all segments of the population.
9. From partial - to full provision of the patient's rights and obligations. This is the provision of free, affordable and qualified help from a doctor and a medical institution to the population, the right to receive a medical insurance policy.
10. From the treatment of diseases to their prevention and health promotion of the population. This is ensuring the priority of disease prevention, the creation of centers for psycho-preventive support. Publication of articles promoting a healthy lifestyle. Supply of good quality food, water supply, maternal and child health; immunization against major infectious diseases; prevention of endemic diseases.
In order to strengthen the health of the population of Russia, reduce the level of morbidity, disability, mortality, increase the availability and quality of medical care, strengthen primary health care, develop preventive health care, meet the needs of the population in high-tech types of medical care, a national project "Health" was developed. is being implemented.
National project "Health"
The main objectives of the priority national health project:
1. Strengthening the health of the population of Russia, reducing the level of morbidity, disability, and mortality.
2. Improving the availability and quality of medical care.
3. Strengthening primary health care, creating conditions for the provision of effective medical care at the pre-hospital stage:
Training and retraining of general (family) practice doctors, local general practitioners and pediatricians;
Magnification wages medical workers of primary care, feldsher-obstetric points and ambulance;
Strengthening the material and technical base of the diagnostic service of primary medical care, emergency medical care.
4. Development of preventive health care:
Prevention of HIV infection, hepatitis B and C , identification and treatment of HIV patients;
Additional immunization of the population within the framework of the national immunization schedule;
Introduction of new screening programs for newborns;
Additional medical examination of the working population;
Provision of medical care to women during pregnancy and childbirth in state and municipal health care institutions.
5. Meeting the needs of the population in high-tech medical care:
Increase in the volume of high-tech medical care;
Construction of new centers of high medical technologies;
Training for these centers of highly qualified doctors and nurses.
Measures to solve the main problems of health care imply effective spending of budgetary funds, focused on the end result, a shift in the emphasis of medical care to the primary link (prehospital stage), and a preventive focus of health care.
Federal target programs
for the protection of public health
1. Construction of medical centers for the provision of specialized medical care in the field of obstetrics, gynecology and neonatology (perinatal centers).
2. Republican target program "Formation healthy way life of the population of the Republic of Bashkortostan, including the reduction of alcohol, tobacco consumption and the fight against drug addiction, for 2011-2015. "
3. Republican target program "Prevention and fight against socially significant diseases in the Republic of Bashkortostan (2011-2015)" The program includes the subprograms "Oncology", "Sexually transmitted infections", "Vaccine prophylaxis", "Diabetes mellitus".
4. The program of state guarantees for the provision of free medical care to citizens in the Republic of Belarus for 2014-2016.
5. Departmental target program of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Bashkortostan "Safe blood for 2012-2014"
6. Departmental target program of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Bashkortostan "Treatment of viral hepatitis in the Republic of Bashkortostan for 2013-2015"
7. Departmental target program of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Bashkortostan "Tuberculosis" for 2013-2015 "
Biographical information.
I, Afonina Evgeniya Valerievna, was born in 1988.
In 2008 she graduated from the Sterlitamak Medical School of the Kumertau branch with a degree in Nursing.
I have been working in GBUZ RB GB Kumertau since 2008.
Tatarnikov M.A. Research Institute of Public Health and Healthcare Management, Moscow Medical Academy I.M.Sechenova
The program-targeted method is the most important tool for the implementation of state socio-economic policy, incl. and in the field of health. Federal target programs (FTP) are a complex of research, development, production, socio-economic, organizational and economic and other activities, linked in terms of resources, performers and timing of implementation, that ensure an effective solution of problems in the field of state, economic, environmental, social and cultural development Russian Federation (RF). Them the most important feature is the definition of priority problems and ways to solve them, taking into account the possibilities of financing program activities at the federal, regional or local levels. Thus, program-targeted management allows not only to concentrate resources on priority areas, but also to implement an integrated approach to solving the most pressing health problems based on intersectoral interaction.
FTPs in the field of public health protection stimulate the participation of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in solving health problems in their territories on the basis of co-financing or the adoption and implementation of their own similar programs.
Currently, a regulatory and methodological framework has been created that defines the rules for the consideration, approval and financing of FTPs. In working with target programs, the following stages are distinguished:
- selection of problems for software development;
- making a decision on the development of a target program and its formation;
- examination and evaluation of the target program;
- approval of the target program;
- managing the implementation of the target program and monitoring the progress of its implementation.
According to the current legislation, the initiators of the formulation of problems in the field of health care for the solution of program methods at the federal level can be any legal and individuals... However, as a rule, the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia and its subordinate institutions act in this capacity.
The selection of problems for their software development and solution at the federal level is determined by the following factors:
- significance of the problem;
- the inability to comprehensively solve the problem within an acceptable time frame and the need state support to solve it;
- fundamental novelty and high efficiency of technical, organizational and other measures necessary for the large-scale dissemination of progressive achievements;
- the need to coordinate cross-sectoral relations to solve this problem
When justifying the need to solve problems by program methods at the federal level, the priorities and goals of the socio-economic development of the Russian Federation, the results of the analysis of the economic and social state of the country are taken into account. In accordance with the approved procedure, proposals must contain:
- name of the problem and analysis of the causes of its occurrence;
- possible ways solving the problem;
- the need for financial resources and possible sources of their provision ( federal budget, budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, extra-budgetary funds);
- preliminary assessment of socio-economic efficiency and consequences from the implementation of the program;
- government customers and developers of the target program, the time and cost of preparing the target program.
The Ministry of Economic Development (MED), together with the Ministry of Finance of Russia and other interested federal executive bodies and executive bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, on the basis of forecasts of the socio-economic development of the country, prepares proposals for solving this problem using program methods at the federal level and sends them to the Government of the Russian Federation. The Government of the Russian Federation, on the basis of the submitted proposals, makes a decision on the preparation of an appropriate target program, the timing and cost of its development, and determines the state customer.
The state customer is responsible for the timely and high-quality preparation and implementation of the target program, prepares the initial task for its formation, manages the actions of developers, manages the executors of the program after its approval, ensures efficient use funds allocated for the implementation of the program. The state customer of the FTP in the field of public health protection is, as a rule, the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia.
The target program consists of the following sections:
- content of the problem and justification of the need to solve it by software methods;
- main goals and objectives, terms and stages of program implementation;
- system of program activities;
- resource support of the program (at the expense of the federal budget and extra-budgetary sources, budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and with the distribution of costs by regions of the country);
- program implementation mechanism;
- organizing program management and monitoring the progress of its implementation;
- evaluating the effectiveness of the program;
- passport of the target program.
Attached to the draft target program explanatory note, a business plan with socio-economic and feasibility studies, a preliminary budget application for allocations from the federal budget to finance the program for the next year, an approval sheet with interested federal executive authorities and, if necessary, agreements (contracts) of intent between the state the customer of the program with enterprises, organizations, state authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, confirming the financing of the program from extra-budgetary sources, budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
The Ministry of Economic Development and the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation evaluate the submitted draft target program, paying particular attention to:
- the priority nature of the problem proposed for the software solution;
- the validity and complexity of program activities, the timing of their implementation;
- need to attract extrabudgetary funds, funds from the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation for the implementation of the program in conjunction with the possibilities of its state support at the expense of centralized resources;
- the effectiveness of the program delivery mechanism;
- socio-economic efficiency of the program as a whole, the expected final results of the program.
The MED, with the participation of the Ministry of Finance, prepares an opinion on the draft target program and preliminary budget application. Taking into account the comments and suggestions, the state customer of the target program, together with its developers, finalizes the draft program. The revised draft of the target program is re-sent to the Ministry of Economic Development.
In case of a positive assessment, the Ministry of Economic Development, in agreement with the Ministry of Finance of Russia, submits a draft target program for approval to the Government of the Russian Federation.
Target programs and state customers are approved by the Government of the Russian Federation. Government customers are provided financial resources in the amount established by the federal budget, and are responsible for the implementation of federal target programs. The interaction of several state customers under one program is carried out by the state customer - the coordinator, determined by the Government of the Russian Federation.
The forms and methods of organizing the management of the implementation of the target program are determined by the state customer. The current management of the FTP for the protection of public health is carried out by the directorate formed by the state customer, headed by one of the Deputy Minister of Health of the Russian Federation, who is responsible for the implementation of the target program.
The implementation of the target program is carried out on the basis of state contracts (agreements) concluded by the state customer of the program with all executors of program activities. The selection of objects and projects of program activities and their performers is carried out on a competitive basis.
The MED, with the participation of interested public authorities, organizes expert reviews of the implementation of individual target programs. At the same time, attention is paid to meeting the deadlines for the implementation of program activities, to the targeted and effective use of financial resources and the end results of the program.
Currently, the main active FTP in the field of health care is the program "Prevention and fight against socially significant diseases (2007-2011)", which includes the subprograms "Diabetes mellitus", "Tuberculosis", "HIV infection", "Oncology", "Sexually Transmitted Infections", "Viral Hepatitis", "Mental Disorders", "Arterial Hypertension" and "Vaccine Prophylaxis" approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 05/10/2007 N 280 (as amended by RF Government Decisions of 18.02.2008 N 95 , dated 02.06.2008 N 423, dated 09.04.2009 N 319). The program is an essential component of the national priority project "Health".
Description of the problem to be solved by the program
The federal target program "Prevention and fight against socially significant diseases (2007-2011)" (hereinafter referred to as the Program) was developed in accordance with the order of the Government of the Russian Federation of 11.12.2006 N 1706-r, the list of socially significant diseases approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 12/01/2004 N 715, the procedure for the development and implementation of federal target programs and interstate target programs, in the implementation of which the Russian Federation participates, approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 06/26/1995 N 594.
The need to prepare and implement the Program is caused by a number of factors of a socio-economic nature that affect the decline in the quality of life of the population, including excessive stress loads, a decrease in the level of sanitary and hygienic culture, as well as still high rates of morbidity, disability and mortality, despite the implementation of the federal target program "Prevention and control of social diseases (2002-2006)".
The share of complications in diabetes mellitus is currently 35 percent. Limb amputations were performed in 1 percent of patients. In total, for the first time during the year, 38.6 thousand people were recognized as disabled due to diabetes mellitus.
The incidence of tuberculosis in correctional institutions of the Federal Penitentiary Service is currently 1515 cases per 100 thousand people, mortality - 153.4 cases per 100 thousand people, the proportion of cases of cessation of bacterial excretion - 73.5 percent, mortality from tuberculosis - 22.6 cases per 100 thousand population.
The number of newly registered cases of HIV infection reached 37.7 thousand cases, in correctional facilities of the Federal Penitentiary Service - 2 thousand cases, the share of HIV-infected pregnant women included in the program for preventing HIV infection in newborns was 75 percent.
The proportion of patients with visual localizations of malignant neoplasms detected at I and II stages of the disease in the total number of patients with visual localizations of the tumor is 67.6 percent, the proportion of patients who died from malignant neoplasms within a year from the date of diagnosis among patients who were first registered in the previous year - 31.6 percent, mortality from malignant neoplasms per 100 thousand of the population was 186.8 cases for men, 93.5 cases for women.
The incidence of syphilis is 72 cases per 100 thousand of the population, in correctional institutions of the Federal Penitentiary Service - 176.6 cases per 100 thousand people, the incidence of syphilis in children - 21.2 cases, gonorrhea - 23.4 cases per 100 thousand of the child population ... At the same time, the share of specialized medical institutions monitoring the variability of sexually transmitted infections in the total number of dermatovenerological institutions is 15 percent. Total number of adolescents specialized centers prevention and treatment of sexually transmitted infections does not exceed 12 in the whole country.
The incidence of acute viral hepatitis B and C is currently 8.6 and 4.5 cases per 100 thousand population, respectively, chronic viral hepatitis B and C - 51.4 cases per 100 thousand population.
The proportion of patients covered by brigade mental health services in the total number of observed patients is 5 percent, the proportion of patients requiring inpatient psychiatric care in the total number of observed patients is 16 percent. At the same time, the average duration of a patient's treatment in a psychiatric hospital is 75.6 days, and the proportion of repeated hospitalizations in a psychiatric hospital during the year is 20 percent.
The incidence of cerebrovascular disorders (cerebrovascular diseases, including stroke) due to arterial hypertension is 5776 cases per 100 thousand of the population, and the mortality from vascular disorders of the brain (cerebrovascular diseases, including stroke) due to arterial hypertension is 325 cases per 100 thousand of the population.
The 95% coverage of children with preventive vaccinations is maintained. The incidence of diphtheria and measles is currently 0.25 and 1.6 cases per 100 thousand population, respectively.
The main goals and objectives of the program, the period of its implementation, as well as target indicators and indicators
The objectives of the Program are to reduce morbidity, disability and mortality of the population with socially significant diseases, increase the duration and improve the quality of life of patients suffering from these diseases.
The objectives of the Program are:
- improvement of methods of prevention, diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation for socially significant diseases;
- development and implementation of modern methods of prevention, diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation for socially significant diseases based on advanced technologies;
- construction and reconstruction of specialized medical institutions.
Within the framework of the Program, it is envisaged to carry out a set of interrelated measures for the prevention, diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation of socially significant diseases throughout the entire duration of the Program.
Program implementation mechanism
The state customer - the coordinator of the Program is the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia, the state customers of the Program are the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia, the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare, the Federal Service for the Execution of Punishments and the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences.
The implementation of the Program is carried out on the basis of government contracts concluded by government customers with the executors of the Program activities in accordance with Federal law "On the placement of orders for the supply of goods, performance of work, provision of services for state and municipal needs", as well as co-financing of expenditure obligations of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation under the relevant regional (municipal) programs (plans).
Interaction of state customers with executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation is carried out on the basis of agreements.
The implementation of the Program in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation is carried out through a set of measures aimed at reducing the incidence of socially significant diseases, improving methods of their prevention and early diagnosis, ensuring the quality of treatment and rehabilitation.
To manage the implementation of the Program activities, a coordination council (hereinafter referred to as the council) is created, formed from officials the state customer - the coordinator of the Program, state customers of the Program and interested federal executive bodies.
The Council performs the following functions:
- develops proposals on the topics and volumes of financing orders for the supply of goods, performance of work and provision of services under the Program;
- considers materials on the implementation of the Program activities;
- organizes checks on the implementation of the Program activities, targeted and effective use of funds allocated for their implementation;
- prepares recommendations for the effective implementation of the Program activities, taking into account the progress of the Program implementation and trends in the social and economic development of the Russian Federation
- identifies scientific, technical and organizational problems during the implementation of the Program;
- considers the results of the examination of projects and activities proposed for implementation in the next financial year, in terms of their content and cost.
The Council approves the following developed by state customers:
Detailed organizational and financial plans for the implementation of the Program activities;
Indicators for monitoring the implementation of the Program activities.
The Council is headed by the Deputy Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia. The regulation on the council and its composition are approved by the Minister of Health and social development Russian Federation.
Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia:
- monitors the activities of state customers of the Program;
- prepares drafts of regulatory legal acts of the Government of the Russian Federation necessary for the implementation of the Program;
- annually, if necessary, clarifies the mechanism for implementing the Program, target indicators and indicators, expenses for the implementation of the Program's activities;
- prepares, taking into account the progress of the Program implementation in this year and submits, in accordance with the established procedure, to the Ministry of Economic Development a consolidated budget application for financing the Program activities in the next financial year;
- quarterly submits to the Ministry of Economic Development statistical, reference and analytical information on the progress of the Program implementation as a whole, monitoring data on the implementation of the Program activities;
- submits annually, by February 1, to the Ministry of Economic Development and the Ministry of Finance of Russia, in the prescribed form, a report on the progress of work under the Program, the results achieved and the effectiveness of the use of financial resources;
- initiates, if necessary, expert reviews of the implementation of certain activities of the Program;
- submits to the Ministry of Economic Development and the Ministry of Finance of Russia proposals on adjusting measures for the implementation of the Program or on termination of its implementation;
- upon completion of the Program, submits to the Ministry of Economic Development and the Ministry of Finance of Russia a report on the implementation of the Program and on the effectiveness of the use of financial resources for the entire period of its implementation.
- State customers of the Program:
- carry out the current management of the implementation of the Program;
- draw up a detailed organizational and financial plan for the implementation of the Program activities;
- in the event of a reduction in the amount of funding for the Program activities at the expense of the federal budget, they develop additional measures to attract funds from extrabudgetary sources to achieve results characterized by the target indicators of the Program, as well as, if necessary, develop in deadlines proposals for their adjustment;
- make proposals to clarify target indicators and indicators, costs for the implementation of the Program and subprograms, as well as to improve the mechanism for its implementation;
- ensure effective use of funds allocated for the implementation of the Program;
- organize the maintenance of quarterly reporting on the implementation of the Program and subprograms, as well as monitoring the implementation of program activities;
- organize expert reviews of the implementation of individual activities of the Program and subprograms;
- manage the activities of the executors of the Program activities within the framework of the program activities
- select on a competitive basis the contractors of works (services), suppliers of products for each event of the Program and subprograms, as well as the conclusion of state contracts (agreements);
- organize the use of information technologies in order to manage and control the implementation of the Program, ensure the placement on the Internet of the text of the Program, regulatory legal acts, methodological materials in terms of managing the implementation of the Program and monitoring the implementation of its activities, as well as materials on the progress and results of the implementation of the Program;
- agree with the state customer - the coordinator of the Program and the main stakeholders of the Program on the possible dates for the implementation of activities, volumes and sources of funding;
- quarterly provide the state customer - the Program coordinator with statistical, reference and analytical information on the implementation of the Program activities;
- if necessary, submit to the state customer - the coordinator of the Program proposals for extending the period or terminating the implementation of the Program;
- submit annually, by January 25, to the state customer - the coordinator of the Program, in the prescribed form, a report on the progress of the implementation of the Program, the results achieved and the effectiveness of the use of financial resources.
Assessment of the socio-economic efficiency of the program
Evaluation of the effectiveness of the Program is carried out on the basis of comparison with the data for 2005 and taking into account the need to achieve the following indicators:
a decrease in the proportion of complications in diabetes mellitus to 28 percent;
an increase in the average life expectancy of men with type I diabetes mellitus up to 55.3 years, women - up to 59.1 years;
an increase in the average life expectancy of men with type II diabetes mellitus up to 71.5 years, women - up to 73.5 years;
a decrease in the incidence of tuberculosis in correctional institutions of the Federal Penitentiary Service to 1495 cases per 100 thousand people;
an increase in the rate of abacillation of tuberculosis patients registered at the end of the year to 35.9 percent;
reduction of mortality from tuberculosis to 17.8 cases per 100 thousand people, including in correctional institutions of the Federal Penitentiary Service - up to 140 cases per 100 thousand people;
a decrease in the number of newly registered cases of HIV infection during the year to 31 thousand cases, in correctional institutions of the Federal Penitentiary Service - to 1.6 thousand cases;
an increase in the proportion of HIV-infected pregnant women included in the program for the prevention of HIV infection in newborns to 98 percent;
improvement of indicators characterizing the early detection of malignant neoplasms, including an increase in the proportion of patients with visual localizations of the tumor detected at stages I and II of the disease, up to 73.1 percent;
decrease in the proportion of patients who died from malignant neoplasms within a year from the date of diagnosis, among patients first registered in the previous year, to 27.8 percent;
reduction of mortality from malignant neoplasms in men to 171.6 cases per 100 thousand of the population, in women - to 90.1 cases per 100 thousand of the population;
reducing the incidence of syphilis to 50.1 cases per 100 thousand people, including in correctional institutions of the Federal Penitentiary Service - up to 150 cases per 100 thousand people;
reducing the incidence of syphilis among children to 7.2 cases per 100 thousand of the child population;
a decrease in the incidence of gonorrhea in children to 10.2 cases per 100 thousand of the child population;
an increase in the share of specialized medical institutions monitoring the variability of sexually transmitted infection pathogens in the total number of dermatovenerological institutions to 60 percent;
an increase in the number of adolescent specialized centers for the prevention and treatment of sexually transmitted infections to 55;
a decrease in the incidence of acute viral hepatitis B to 2.7 cases per 100 thousand population;
reduction of the incidence of acute viral hepatitis C to 3.8 cases per 100 thousand population;
reducing the incidence of chronic viral hepatitis B and C to 36 cases per 100 thousand population;
an increase in the proportion of patients covered by brigade mental health services in the total number of observed patients to 41 percent;
a decrease in the proportion of patients requiring inpatient psychiatric care in the total number of observed patients to 14.5 percent;
reducing the average duration of treatment of a patient in a psychiatric hospital to 73.9 days;
decrease in the share of repeated hospitalizations in a psychiatric hospital to 17.5 percent during the year;
reduction of the incidence of cerebrovascular diseases in the population to 4680 cases per 100 thousand of the population;
reduction of mortality from cerebrovascular diseases to 270 cases per 100 thousand population;
an increase in the number of newly diagnosed patients with arterial hypertension up to 1000 thousand people per year;
an increase in the number of people trained in health schools for patients with arterial hypertension to 1400 thousand people a year;
maintaining the 95% coverage of children with preventive vaccinations;
a decrease in the incidence of diphtheria to 0.16 cases per 100 thousand of the population;
exclusion of cases of poliomyelitis;
a decrease in the incidence of measles to 0.8 cases per 100 thousand population.
It is assumed that the overall economic effect from the implementation of the Program activities will be achieved by reducing the incidence, disability and mortality of the population with socially significant diseases.
The social effectiveness of the implementation of the Program activities will be expressed in improving the quality and increasing the life expectancy of patients, preserving labor potential, forming the foundations of a healthy lifestyle, reducing social and psychological tension in society due to the threat of the spread of socially significant diseases.
2. The Government of the Russian Federation establishes the procedure for the development and implementation of federal target programs, and the executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation establish the procedure for the development and implementation of regional target programs in the field of health care.
3. Regional target programs in the field of health care, including those aimed at equalizing the differences in the level of medical care to citizens living in various administrative-territorial entities of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation, are created on the basis of federal target programs in the field of health in accordance with the mandatory state norms and standards, taking into account the characteristics, needs and capabilities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. Regional targeted health programs cannot limit government-guaranteed norms and standards included in federal targeted health programs.
4. Federal and regional target programs in the field of health care are formed taking into account state social standards in the field of health care.
5. Organs local government participate in the implementation of federal and regional target programs in the field of health care, including investment and personnel policy. In this case, financing of specific programs is carried out at the expense of the federal budget, the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, other funds in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
6. In the implementation of federal and regional target programs in the field of health care, in accordance with agreements (contracts), health care organizations, regardless of ownership. The selection of health care organizations for the implementation of federal and regional target programs in the field of health care is carried out on a competitive basis.
Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia
State budgetary educational institution
higher professional education
Siberian State Medical University
Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation
(GBOU VPO Siberian State Medical University of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia)
Faculty of Health Economics and Management
Department of Health Organization and Public Health
Course work
in the discipline "Medical and social foundations of health"
FEDERAL TARGETED PUBLIC HEALTH PROGRAMS
Completed: 2nd year student of group 7001
Baldandorzhieva N.A.
Checked by: Dr. med. sciences, professor
CM. Khlynin,
cand. honey. sciences, associate professor O.V. Kudelina
Tomsk 2011
Introduction
At present, a very big problem has arisen before society and health care - this is a decline in the health of the population, primarily the population of working age. In this regard, health care has developed a number of federal targeted programs aimed at reducing morbidity, improving the standard of living of patients suffering from socially significant diseases, as well as developing medical literacy of the population.
So my theme term paper “Federal target programs aimed at protecting public health” is relevant today, since federal target programs are designed to help in solving strategic problems of health and social development, especially in cases where it is necessary to concentrate resources to achieve specific goals within a given time frame.
The purpose of the course work is:
study of federal target programs, its directions, activities.
analysis of implementation, activities, financing of the program
To achieve this goal, it is necessary to solve the following tasks:
To reveal the essence of the federal target program.
Study financing, formation, approval of the target program.
Analyze the implementation of federal target programs in the Russian Federation and their role in financing budget investments.
Chapter 1. Characteristics of federal target programs
1. Basic concepts of a targeted program aimed at protecting public health
In modern civilization, the human right to health protection ceases to be a purely individual property, it becomes the most important value for the state and civil society. The peculiarities of the right to health protection are that it belongs to inalienable rights, belongs to a person even before his birth, is an integral condition of the life of society and is associated not only with the need to take care of his health of every citizen, but also with the responsibility of the state for the preservation and strengthening of health their citizens. Human life and health are the highest values \u200b\u200bfor society, taking into account which all other values \u200b\u200band benefits should be determined.
Public health protection is a set of measures of a political, economic, legal, social, scientific, medical, sanitary-hygienic and anti-epidemic nature aimed at preserving and strengthening the physical and mental health of each person, maintaining his long active life, providing him with medical and medicinal assistance ... Currently, it is generally accepted that the program-target method is the most important tool for the implementation of state social and economic development country and its individual regions, along with forecasting and indicative planning methods.,
The federal target program is a complex of research, development, production, socio-economic, organizational and economic and other activities, linked in terms of tasks, resources and timing of implementation, that provide an effective solution to systemic problems in the field of state, economic, environmental, social and cultural development of the Russian Federation.
Targeted programs are one of the most important means of implementing the structural policy of the state, actively influencing its socio-economic development and should be focused on the implementation of large-scale investment and scientific and technical projects that are most important for the state, aimed at solving systemic problems that fall within the competence of federal executive authorities.
The target program may include several subprograms aimed at solving specific tasks within the program. The division of the target program into subprograms is based on the scale and complexity of the problems to be solved, as well as the need for a rational organization of their solution.
Budget financing can be divided into two parts - financing the volume of services and specific targeted programs. In the first case, funds go to a specific subject of budget expenditures, in the second, financing can go to a number of industries. In this case, funding is directed either directly to the executor, or through the department.
The customer of a long-term target program can be a public authority or a local self-government body for municipal target programs. It is such a body that acts on behalf of the state or municipal formation when developing a long-term target program and its implementation.
Federal target programs are an effective tool for implementing state economic and social policies, especially when solving long-term problems and implementing large infrastructure projects. It is this program-project approach that is used in the countries of the European Union, in the USA, Canada, Japan and others to solve strategic problems of economic and social development, in cases where it is necessary to concentrate resources to achieve specific goals within a given time frame.
1.3. List of federal targeted programs aimed at protecting public health
Federal target program "Prevention and control of socially significant diseases (2007 - 2011)"
1) Subprogram "Diabetes mellitus"
2) Subprogram "Tuberculosis"
) Subprogram "Vaccine prophylaxis"
) Subprogram "HIV infection"
) Subprogram "Oncology"
) Subprogram "Sexually transmitted infections"
) Subprogram "Viral hepatitis"
) Subprogram "Mental disorders"
) Subprogram "Arterial hypertension"
Federal target program "Children of Russia" for 2007 - 2010
· Subprogram "Healthy Generation"
· Subprogram "Children and Family"
Federal target program "Improving road safety in 2006 - 2012".
3.1.
Program "Prevention and fight against socially significant diseases (2007 - 2012)"
The federal target program "Prevention and fight against socially significant diseases (2007 - 2011)" (hereinafter - the Program) was developed in accordance with the order<#"663364.files/image001.gif">
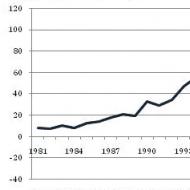
Figure: 1 Source of funding for program activities
Financing of the Program from the federal budget is carried out in the following areas:
· capital investment - 23,064.9064 million rubles;
· Research and development work - 1238.7268 million rubles;
· Other needs - 21149.8245 million rubles, of which subsidies from the federal budget - 1593.716 million rubles.

Figure: 2 Directions of spending funds of the federal target program "Prevention and fight against socially significant diseases 2007-2011"
The fulfillment at the expense of the federal budget of obligations on construction sites and objects that are state-owned by the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and in municipal ownership is carried out in the manner of inter-budgetary relations in accordance with the provisions of the Budget Code<#"663364.files/image003.gif">
Figure: 3 Amount of funding for subprogrammes
Evaluation of the effectiveness of the Program is carried out on the basis of comparison with the data for 2005 and taking into account the need to achieve the following indicators:
an increase in the average life expectancy of men with type I diabetes mellitus to 55.4 years, women - to 59.2 years;
an increase in the average life expectancy of men with type II diabetes mellitus to 71.4 years, women - up to 73.2 years;
an increase in the rate of abacillation of tuberculosis patients who were registered at the end of the year to 36.1 percent;
a decrease in the number of newly registered cases of HIV infection during the year in correctional institutions of the Federal Penitentiary Service to 1.67 thousand cases;
an increase in the proportion of HIV-infected pregnant women included in the program to prevent HIV infection in newborns to 95 percent;
a decrease in the proportion of patients who died from malignant neoplasms within a year from the date of diagnosis in the total number of patients registered for the first time in the previous year to 27.5 percent;
a decrease in mortality from malignant neoplasms in men to 231.2 cases per 100 thousand of the population, in women - to 170 cases per 100 thousand of the population;
decrease in the incidence of syphilis among children to 7.1 cases per 100 thousand of the child population;
a decrease in the incidence of gonorrhea in children to 7.7 cases per 100 thousand of the child population;
an increase in the share of specialized medical institutions monitoring the variability of sexually transmitted infections in the total number of dermatovenerological institutions to 62 percent;
an increase in the number of adolescent specialized centers for the prevention and treatment of sexually transmitted infections to 60;
reduction of the incidence of acute viral hepatitis B to 2.6 cases per 100 thousand population;
a decrease in the incidence of acute viral hepatitis C to 3.7 cases per 100 thousand population;
an increase in the proportion of patients covered by brigade mental health services in the total number of observed patients to 30 percent;
exclusion of cases of poliomyelitis;
reducing the incidence of measles to 0.99 cases per 1 million population.
2.2 The Children of Russia 2007-2010 Program
The implementation of the Program activities will allow:
improve the quality of life and health of children;
improve the quality and availability of social services for families with children, primarily for families with disabled children;
to improve the state system of social protection and support for minors in order to ensure the provision of emergency and prompt assistance to children in difficult life situations, as well as to carry out long-term consistent work to support children in need of special state care.
The implementation of the activities of the Healthy Generation subprogram will allow to continue improving the state support of the motherhood and childhood service, to increase the availability and quality of medical care for women and children, to achieve by 2011:
In the course of implementing the Gifted Children subprogram, state system identification, development and targeted support of gifted children, covering up to 40 percent of the school-age child population, aimed at preserving the country's national gene pool, forming the future highly professional elite in various fields of intellectual and creative activity.
The number of winners of all-Russian contests, competitions, Olympiads, tournaments held within the subprogram will increase by 2011 by 8 percent compared to 2006 data.
The assessment of the implementation of the direction "Prevention of neglect and juvenile delinquency" by 2011 will be carried out according to the following indicators:
· The share of street children in the total child population - 2.17 percent;
· The proportion of children who received social rehabilitation in specialized institutions for minors in the total number of neglected and street children - 83.3 percent.
Evaluation of the implementation of the direction "Family with disabled children" by 2011 will be carried out according to the following indicators:
the proportion of disabled children who received rehabilitation services in specialized institutions for children with disabilities, in the total number of disabled children - 43.1 percent;
the share of families with disabled children who received services in specialized institutions for children with disabilities, in the total number of families with disabled children in need of services - 25.2 percent.
The implementation of the activities of this subprogram will allow to reduce the number of orphans and children left without parental care, transferred to institutions for full state support, to increase the number of orphans and children left without parental care, transferred to families of citizens, to ensure effective socialization of children in a difficult life situationand their integration with society.
The assessment of the implementation of the direction "Orphans" by 2011 will be carried out according to the indicator reflecting the share of orphans and children left without parental care, transferred to families of citizens, in the total number of orphans and children left without parental care, which should reach 72 percent.
Financing
The total amount of funding for the Program is 47845.9 million rubles (in prices of the respective years), including:
at the expense of the federal budget - 10,101.7 million rubles;
at the expense of the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation - 36315.1 million rubles;
at the expense of extra-budgetary sources - 1,429.1 million rubles.
Table 3. Funding source for the activities of the Federal Target Program "Children of Russia 2007-2010"
According to the directions of spending, funds are distributed as follows:
capital investments - 25899.3 million rubles, including:
at the expense of the federal budget - 6917 million rubles;
at the expense of the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation - 18812.3 million rubles;
at the expense of extra-budgetary sources - 170 million rubles;
research and development work - 37.7 million rubles at the expense of the federal budget;
other needs -21908.9 million rubles, including:
at the expense of the federal budget - 3147 million rubles;
at the expense of the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation - 17502.8 million rubles;
at the expense of extra-budgetary sources - 1259.1 million rubles.

Figure: 4 Sources of funding for the program
health population target investment
The executors of the Program events are determined in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The implementation of the Program is supposed to be carried out within 7 years (2006 - 2012) in 2 stages.
At the first stage (2006 - 2007), the main activities were identified for implementation:
· Creation of a system of propagandistic influence on the population in order to form a negative attitude towards offenses in the field of road traffic;
· Ensuring involvement of civil society institutions in preventive work;
· Improvement of the licensing system in the field of driver training, development of a legal basis for control over the implementation by citizens of self-training to obtain the right to drive vehicles of categories "A" and "B";
· Preparation of proposals for the introduction of mechanisms for driving schools to improve the quality of driver training;
· Strengthening control over the availability, serviceability and use of security equipment;
· Increasing the prevention of child road traffic injuries, the active introduction of child restraints;
· Implementation of pilot projects for replacing road patrol service posts with technical automatic systems for monitoring compliance by road users with the Road Traffic Rules of the Russian Federation and the use of helicopters to speed up the arrival at the scene of a road traffic accident;
· Prevention of traffic congestion, optimization of speed modes of movement on sections of the road network;
· Monitoring the dynamics of road traffic injuries, public opinion on road safety problems and the implementation of the Program activities.
At stage II (2008 - 2012), the following activities are envisaged:
· Further increase in the volume of work on the organization of traffic and pedestrians, including the introduction of integrated schemes and projects for the organization of traffic, traffic management of main, regional and city-wide significance;
· Expanding the scope of work on the construction of underground and overground pedestrian crossings;
· Increasing the role of public associations and organizations in carrying out preventive measures;
· Improvement of work on the prevention of child road traffic injuries;
· Improvement of forms and methods of control and supervision over the observance of established standards and rules by road users;
· Improvement of forms and methods of international interaction in the field of road safety;
· Continued monitoring of the dynamics of road traffic injuries, public opinion on road safety problems and the implementation of the Program activities.
Transfer to the constituent entities of the Russian Federation of material and technical resources (equipment that does not require installation, special vehicle) purchased at the expense of the federal budget is carried out by the state customers of the Program in the manner established by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Financing
The total amount of financing for the Program is 47,755.51 million rubles, including:
from the federal budget - 21049.01 million rubles (of which - for research and development work - 2446.23 million rubles, capital investments - 15247.58 million rubles and other needs - 3355.21 million . rubles);
at the expense of the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation - 26245.4 million rubles (of which for capital investments - 21805.9 million rubles and other needs - 4439.5 million rubles);
at the expense of extra-budgetary sources - 461.1 million rubles (of which for capital investments - 359.9 million rubles and other needs - 101.2 million rubles) (as amended by Resolutions of the Government of the Russian Federation of 18.08.2007 N 528, of 15.07.2008 N 538, of 14.02.2009 N 132, of 02.08.2011 N 642) reduction by 2012 of the number of persons who died as a result of road accidents,
Table 4. Sources of funding for the federal target program "Improving road safety in 2006 - 2012"
Figure: 5 Sources of funding for the program

Conclusion
Upon completion of the work, it can be concluded that today federal target programs aimed at protecting the health of the population are one of the most important means of implementing the state's social policy and actively influencing socio-economic development.
Evaluation of the effectiveness of the implementation of the programs under consideration is based on comparison with the data for 2005
Results of the effectiveness of the program "Prevention and control of socially significant diseases for 2007-2011"
a decrease in the proportion of complications in diabetes mellitus to 28.5 percent;
a decrease in the incidence of tuberculosis in correctional institutions of the Federal Penitentiary Service to 1490 cases per 100 thousand people;
reduction in mortality from tuberculosis to 15.2 cases per 100 thousand people, including in correctional institutions of the Federal Penitentiary Service - to 104.9 cases per 100 thousand people;
reducing the incidence of syphilis to 49.2 cases per 100 thousand people, including in correctional institutions of the Federal Penitentiary Service - up to 148 cases per 100 thousand people;
decrease in the incidence of chronic viral hepatitis B and C to 54 cases per 100 thousand population;
improvement of indicators characterizing the early detection of malignant neoplasms, including an increase in the proportion of patients with visual localizations of the tumor detected at stages I and II of the disease, up to 72 percent;
FTP "Children of Russia 2007-2010"
reducing the infant mortality rate to 9.8 per 1000 live births;
reducing the maternal mortality rate to 21 per 100 thousand live births;
decrease in the mortality rate of children aged 0 to 4 years (inclusive) to 10.9 per 1000 newborns of the corresponding year of birth;
increasing the share of children of the 1st health group to 37.5 percent of the total number of children;
a decrease in the primary disability rate for children aged 0 to 17 years (inclusive) to 21.4 per 10 thousand children.
FTP "Improving road safety in 2007-2012"
With the implementation of the program, the number of fatalities in road accidents compared to 2005 will be reduced by 2012 by 1.5 times, and the number of road accidents with victims - by 10 percent. At the same time, within the framework of the implementation of the Program activities, the implementation by the constituent entities of the Russian Federation of the activities of regional programs aimed at improving road safety is taken into account.
Thus, a number of federal targeted programs aimed at protecting public health have significantly improved the health of citizens, but some results are to be expected.
List of used literature
1. Vyalkov, A.I. Contemporary problems state of health of the population of the Russian Federation / A.I. Vyalkov // Probl. health management. 2009. - No. 3.
2. Vyalkov, A.I. Health care management and economics: textbook / ed. A.I. Vyalkova; A.I. Vyalkov, V.Z. Kucherenko, B.A. Raisberg and others - M .: GEOTAR-Media, 2009 .-- 664 p.
Medkov, V.M. Healthcare Management / Under. ed. V.Z. Kucherenko. M .: TEIS, 2007 .-- 448 p.
Trushkina L.Yu., Tleptserishev R.A., Trushkin A.G. and other Economics and health care management.
Federal Target Programs of Russia, Department of State Target Programs and Capital Investments: - electronic resource [access mode
Federal target programs of Russia: electronic resource [access mode
FTP "Improving road safety in 2007-2012" -electr. resource [access mode
Federal Law of July 22, 1993 N 5487-1 Fundamentals of the Legislation of the Russian Federation on the Protection of Citizens' Health (as amended on December 1, 2004, March 7, 2005)
Central Research Institute of Organization and Informatization of Health Care: - electr. resource [access mode
Shilenko Yu.V., Raizberg B.A., Vyalkov A.I. Health care management and economics
Russian Federation
"Health care development"
rules
the provision and distribution of subsidies from the federal budget to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation for one-time compensation payments medical workers (doctors, paramedics) who arrived (moved) to work in rural settlements, or workers' settlements, or urban-type settlements, or cities with a population of up to 50 thousand people
With changes and additions from:
1. These Rules establish the goals, conditions and procedure for the provision and distribution of subsidies from the federal budget to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in order to co-finance the expenditure obligations of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation for the implementation of one-time compensation payments to medical workers (doctors, paramedics) who arrived (moved) to work in rural settlements, or workers' settlements, or urban-type settlements, or cities with a population of up to 50 thousand people (hereinafter referred to as subsidies).
2. Subsidies are provided within the limits budget commitmentscommunicated to the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation as the recipient of federal budget funds for the provision of subsidies for the purposes specified in paragraph 1 of these Rules.
3. The criteria for selecting a constituent entity of the Russian Federation for granting subsidies are:
a) the availability of a list of vacant positions of medical workers in medical organizations and theirs approved by the authorized executive body of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation in the field of healthcare (hereinafter referred to as the authorized body) structural units, upon replacement of which, lump-sum compensation payments are made for the next financial year (program register of positions), developed on the basis of an approximate list of positions of medical workers in medical organizations and their structural units providing primary health care, upon replacement of which, one-time compensation payments are made for the next financial year (program register of positions) approved by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation;
b) the presence of an application from the highest executive body of state power of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation for participation in the event, containing information on the planned number of participants in the event (doctors, paramedics)
4. The subsidy is provided on the basis of a subsidy agreement concluded between the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation and the highest executive body of state power of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation, prepared (formed) using the state integrated information system public finance management "Electronic budget" in accordance with the standard form approved by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the agreement).
5. The conditions for granting a subsidy are:
a) approved by the regulatory legal act of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation the procedure for providing one-time compensation payments to medical workers (doctors, paramedics) who are citizens of the Russian Federation who do not have outstanding financial obligations under a targeted training agreement (with the exception of medical organizations with less than 60 percent staffing) who have arrived (moved) to work to rural settlements, or workers' settlements, or urban-type settlements, or cities with a population of up to 50 thousand people and who have concluded an employment contract with medical organization, subordinate to the executive authority of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation or to the local government, on a full-time basis with the working time established in accordance with Article 350 Labor Code Of the Russian Federation, with the performance of a labor function in a position included in the program register of positions provided for in paragraph 3 of these Rules, in the amount of:
2 million rubles for doctors and 1 million rubles for paramedics who arrived (moved) to work in rural settlements, or workers' settlements, or urban-type settlements located on the territory of the Far Eastern Federal District, in the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas , The Arctic zone of the Russian Federation;
1.5 million rubles for doctors and 0.75 million rubles for paramedics who arrived (moved) to work in rural settlements, or workers' settlements, or urban-type settlements located in remote and inaccessible areas. The list of remote and inaccessible territories is approved by the highest executive body of state power of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation;
1 million rubles for doctors and 0.5 million rubles for paramedics who arrived (moved) to work in rural settlements, or workers' settlements, or urban-type settlements (except for those specified in paragraphs two and three of this subparagraph), or cities with a population of up to 50 thousand people;
b) the presence in the budget of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation of budgetary appropriations provided for financial security expenditure obligations of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation, for the purpose of co-financing which the subsidy is provided, in the amount necessary for the fulfillment of these obligations, including the amount of the subsidy planned to be provided;
c) the conclusion of an agreement in accordance with paragraph 10 of the Rules for the formation, provision and distribution of subsidies from the federal budget to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, approved by the Government of the Russian Federation of September 30, 2014 N 999 "On the formation, provision and distribution of subsidies from the federal budget to the budgets of the constituent entities Russian Federation "(hereinafter - the Rules for the formation, provision and distribution of subsidies).
6. A one-time compensation payment is provided by the authorized body to a medical worker from among the medical workers specified in paragraph 1 of these Rules (hereinafter referred to as medical workers), once on one of the grounds specified in subparagraph "a" of paragraph 5 of these Rules. The authorized body has the right to decide on the provision of a one-time compensation payment to a medical worker:
a) if he has obligations related to targeted training (targeted training), subject to his conclusion employment contract with a medical organization with less than 60 percent staffing;
b) provided that a medical worker who has fulfilled the obligations related to targeted training (targeted training) continues to work in the same medical organization located in a rural settlement, or a workers' settlement, or an urban-type settlement, or a city with a population of up to 50 thousand. person.
7. A medical worker who has entered into an agreement with a medical organization on the provision of a one-time compensation payment (hereinafter referred to as the agreement) undertakes the following obligations:
a) perform labor duties for 5 years from the date of the conclusion of the contract for positions in accordance with the labor contract, subject to the extension of the contract for the period of non-fulfillment of the labor function in full (except for the rest time provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
b) return to the budget of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation a part of the lump-sum compensation payment calculated in proportion to the unworked period from the date of termination of the employment contract to the expiration of the 5-year period (except for cases of termination of the employment contract on the grounds provided for in paragraph 8 of part one of Article 77 and paragraphs 5-7 part one of Article 83 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), as well as in the case of transfer to another position or admission to training in additional professional programs;
c) return to the budget of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation a part of the lump-sum compensation payment calculated in proportion to the unworked period from the date of termination of the employment contract, in the event of dismissal in connection with an appeal for military service (in accordance with paragraph 1 of part one of Article 83 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) or extend the term of the contract for the period of non-performance functional responsibilities (at the choice of a medical professional).
8. The total amount of the subsidy (S total) is determined by the formula:
S total \u003d S 1i + S 2i + S 3i,
S li - the size of the subsidy to the budget of the i-th constituent entity of the Russian Federation participating in the corresponding financial year in the implementation of the measures provided for in paragraph 1 of these Rules, as regards medical workers who arrived (moved) to work in rural settlements or workers' settlements , or urban-type settlements (with the exception of medical workers specified in clauses 10 and these Rules), or cities with a population of up to 50 thousand people;
S 2i - the size of the subsidy to the budget of the i-th constituent entity of the Russian Federation participating in the corresponding financial year in the implementation of the measures provided for in paragraph 1 of these Rules, as regards medical workers who arrived (moved) to work in rural settlements or workers' settlements , or urban-type settlements located on the territory of the Far Eastern Federal District, in the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas, in the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation;
S 3i - the size of the subsidy to the budget of the i-th constituent entity of the Russian Federation participating in the corresponding financial year in the implementation of the measures provided for in paragraph 1 of these Rules, as regards medical workers who arrived (moved) to work in rural settlements or workers' settlements , or urban-type settlements located in remote and hard-to-reach areas.
9. The size of the subsidy to the budget of the i-th constituent entity of the Russian Federation participating in the corresponding financial year in the implementation of the measures provided for in paragraph 1 of these Rules (S 1i), as regards medical workers who have arrived (moved) to work in rural settlements, either workers' settlements, or urban-type settlements (with the exception of medical workers specified in clauses 10 and these Rules), or cities with a population of up to 50 thousand people, is determined by the formula:
S 1i \u003d (V 1plani 1 + F 1plani 0.5) L i,
V 1plani - the number of doctors to whom it is planned to provide one-time compensation payments, in i-th subject The Russian Federation in the relevant financial year;
1 - the amount of a one-time compensation payment provided to a doctor, equal to 1 million rubles;
F 1plani - the number of paramedics to whom it is planned to provide one-time compensation payments in the i-th constituent entity of the Russian Federation in the corresponding financial year;
0.5 - the amount of a one-time compensation payment provided to a medical assistant, equal to 0.5 million rubles;
paragraph 13
10. The size of the subsidy to the budget of the i-th constituent entity of the Russian Federation participating in the corresponding financial year in the implementation of the measures provided for in paragraph 1 of these Rules (S 2i), as regards medical workers who have arrived (moved) to work in rural settlements, either workers' settlements, or urban-type settlements located on the territory of the Far Eastern Federal District, in the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas, the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation, is determined by the formula:
S 2i \u003d (V 2plani 2 + F 2plani 1) L i,
V 2plani - the number of doctors to whom it is planned to provide one-time compensation payments in the i-th constituent entity of the Russian Federation in the corresponding financial year;
2 - the size of a one-time compensation payment provided to a doctor, equal to 2 million rubles;
F 2plani - the number of paramedics to whom it is planned to provide one-time compensation payments in the i-th constituent entity of the Russian Federation in the corresponding financial year;
1 - the amount of a one-time compensation payment provided to a paramedic, equal to 1 million rubles;
L i - the maximum level of co-financing of the expenditure obligation of the i-th subject of the Russian Federation from the federal budget, determined in accordance with paragraph 13 of the Rules for the formation, provision and distribution of subsidies.
11. The size of the subsidy to the budget of the i-th constituent entity of the Russian Federation participating in the corresponding financial year in the implementation of the measures provided for in paragraph 1 of these Rules (S 3i), as regards medical workers who arrived (moved) to work in rural settlements, either workers' settlements, or urban-type settlements located in remote and inaccessible territories, is determined by the formula:
S 3i \u003d (V 3plani 1.5 + F 3plani 0.75) L i,
V 3plani - the number of doctors to whom it is planned to provide one-time compensation payments in the i-th constituent entity of the Russian Federation in the corresponding financial year;
1.5 - the amount of a one-time compensation payment provided to a doctor, equal to 1.5 million rubles;
F 3plani - the number of paramedics to whom it is planned to provide one-time compensation payments in the i-th constituent entity of the Russian Federation in the corresponding financial year;
0.75 - the amount of a one-time compensation payment provided to a medical assistant, equal to 0.75 million rubles;
L i - the maximum level of co-financing of the expenditure obligation of the i-th subject of the Russian Federation from the federal budget, determined in accordance with paragraph 13 of the Rules for the formation, provision and distribution of subsidies.
12. The volume of budget allocations for financial support of expenditure obligations of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation for the implementation of one-time compensation payments to medical workers, for the purpose of co-financing of which the subsidy is provided, is approved by the law of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation on the budget of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation (determined by the consolidated budget list of the budget of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation) based on the need to achieve the values \u200b\u200bof the result of using the subsidy established in the agreement - the share of medical workers who were actually provided with one-time compensation payments in the total number of medical workers who are scheduled to receive these payments.
The amount of a subsidy to the budget of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation in a financial year may not exceed the amount of funds for the fulfillment in a financial year of expenditure obligations of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation related to the implementation of measures provided for in paragraph 1 of these Rules, taking into account the maximum level of co-financing of an expenditure obligation of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation from the federal budget, determined in accordance with paragraph 13 of the Rules for the formation, provision and distribution of subsidies.
13. The subsidy is transferred in accordance with the established procedure to the account opened for the territorial body of the Federal Treasury in the institution The Central Bank Of the Russian Federation for accounting of operations with budgetary funds of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
14. To assess the results of using the subsidy, the indicator is used - the share of medical workers who are actually provided with one-time compensation payments in the total number of medical workers who are planned to provide these payments (percent) (I i), calculated by the formula:
Fact V - the number of doctors who were actually provided with lump-sum compensation payments in the i-th constituent entity of the Russian Federation in the corresponding financial year;
F facti - the number of paramedics who were actually provided with lump-sum compensation payments in the i-th subject of the Russian Federation in the corresponding financial year;
V plan i - the number of doctors to whom it is planned to receive one-time compensation payments in the i-th constituent entity of the Russian Federation in the corresponding financial year;
F plani is the number of paramedics to whom it is planned to receive one-time compensation payments in the i-th constituent entity of the Russian Federation in the corresponding financial year.
15. Evaluation of the effectiveness of the use of a subsidy is carried out by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation on the basis of a comparison of the value of the results of using the subsidy, established in the agreement, and the value of the results of using the subsidy actually achieved at the end of the reporting year, as provided for in paragraph 14 of these Rules.
16. The procedure and conditions for the return of funds from the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation to the federal budget in case of violation of the obligations stipulated by the agreement, as well as the grounds for exempting the constituent entities of the Russian Federation from the application of measures financial responsibility established by clauses 16 - 18 and the Rules for the formation, provision and distribution of subsidies.
17. Control over the implementation by the constituent entities of the Russian Federation of the measures provided for in paragraph 1 of these Rules is carried out Federal Service on health supervision.
18. Control over compliance by the constituent entities of the Russian Federation with the conditions for granting subsidies is carried out by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation and authorized bodies of state financial control.