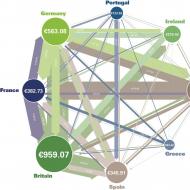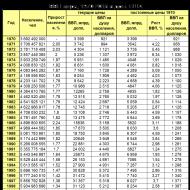
Blocked residential house SNiP. Legislative base of the Russian Federation. Houses residential one-friendly houses
Russian FederationSnip
SNiP 31-02-2001 residential homing houses
- MDS 55-1.2005 Walls with thermal insulation from polystyrene and mineral wool plates with a finishing layer of thin layer plaster. Materials for designing and working drawings of MDS nodes
- Index of regulatory documents on the construction operating in the Russian Federation (as of 01.07.2011) Information material
- SP 55.13330.2011 Houses residential houses. Actualized edition Snip 31-02-2001 SP (rules call)
- SP 23-101-2004 Design of thermal protection of buildings Letter of Gosstroy Russia
- One hundred 58239148-001-2006 Outdoor thermal insulation systems of buildings walls with a finishing layer of thin-layer plaster "Ceresit". Materials for designing and working drawings of nodes. Installation instructions. Technical descriptions STR, standard organization
- SP 31-107-2004 Architectural and planning solutions of apartment buildings Letter of Gosstroy Russia
- Snip 41-01-2003 Heating, ventilation and air conditioning SNIP
- SP 31-105-2002 Design and construction of energy efficient single-sided residential buildings with wooden frame
- Hundred 36554501-012-2008 The use of thermal insulation from plates of polystyrene foamed extrusion polyplex when designing and device of low-boiled foundations on bunched soils Order OJSC "NIC" Construction "
- Hundred 50470372-001-2007 Steel fasteners for mounted facade designs "Diath". Technical conditions STR, standard organization
- Methodical recommendations for organizing training managers and employees of organizations. Fire briefing and fire and technical minimum MR (Methodical Recommendations)
- SP 31-106-2002 Design and construction of engineering systems of single-headed residential buildings Resolution of the Gosstroy Russia
- Method of compulsory certification of sets of building structures of factory manufacture for single-sided residential buildings Information material
install tabmark
install tabmark
Snip 31-02-2001
Construction standards and rules of the Russian Federation
Houses residential one-friendly houses
SINGLE-FAMILY HOUSES
Date of introduction 2002-01-01
Preface
1 Developed by a federal state unitary enterprise - the center of the mission and standardization methodology in construction (FSUE "TSNS") with the participation of the team of specialists from leading research and design organizations
Made by the management of standardization, technical rationing and certification of the state system of Russia
2 Accepted and enforced from January 1, 2002 resolution of the State Construction of Russia of March 22, 2001 N 35
3 introduced for the first time
Amendments made approved by the Office of Technical Regulation, Standardization and Certification in the Construction and Housing and Communal Services of the Gosstroy of Russia on May 26, 2004
Introduction
These construction standards and rules have been developed in connection with the increasing volume of construction and the development of the market for single-family residential buildings. This type of construction gets more and more widespread in the world, and therefore the Technical Committee of 59 "Construction of buildings" of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has begun to develop a number of standards for the performance of "single-sided separately standing and blocked residential buildings".
These norms establish a set of mandatory regulatory requirements for the operational characteristics of single-family houses, including security issues, regardless of their constructive systems and used building materials.
Norms should be applied to homes, regardless of whether they are built at the expense of the state or municipal budget, the funds of developers organizations engaged in the aim of subsequent sale or lease, or at the expense of individual developers building houses for their own needs.
Single residential buildings started by construction on project documentation developed and approved before January 1, 2002 may continue to be built and commissioned without adjusting project documentation for compliance with the requirements of these construction standards and rules.
It is envisaged to develop arrangements of the rules of a recommendatory nature on the design and construction of single-family residential buildings. Among the first, the rules for the design and construction of houses with carrying walls of the frame structure and on engineering systems of single-family houses are developed.
These construction standards and rules have been developed with the support of the Canadian Mortgage Corporation and Housing and the National Research Council of Canada.
The development of SNiP was attended by: L.A.Viktorova, Cand. Archite.; V.A.Glukharev; Yu.G.G. G., Cand. tehn sciences; V.N.zify Corn, Cand. tehn sciences; S.V. Krolevts, Cand. Archite.; D.M. Lakovsky; Yu.A. Matrosov, Cand. tehn sciences; S.Nestech, Cand. tehn sciences; E.Yu. Performs, Cand. Archite.; N.N. Polyakov; A.V.Saregradsky; E.P.Shastitko; L.S. Eksler.
1 AREA OF USE
These standards and rules apply to newly built and reconstructed single-family residential buildings, intended for permanent residence of people (hereinafter referred to as home), and establish requirements for their safety and other operational characteristics, compliance with all legal entities and individuals carrying out the design and construction of houses .
These norms also apply to blocked at home, the residential blocks of which are autonomous and are considered as separate single-sided homes if they are:
do not have premises located above the premises of other residential blocks;
do not have common entrances, auxiliary premises, attics, subliments, mines of communications;
they have independent heating and ventilation systems, as well as individual entries and connections to external networks of centralized engineering systems.
Blocked houses that do not meet these conditions are designing and built in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 31-01.
When designing and building houses in accordance with these norms and rules, the provisions of other more general rules and rules extending to residential one-quality houses should also be applied if they do not contradict the requirements of this document.
2 Regulatory references
In these standards and rules, references to regulatory documents are used, the list of which is given in Appendix A.
3 Terms and Definitions
Definitions of terms used in this document are given in Appendix B.
4 General
5 Beneficial Ability and Deformative Designs
Adjacent residential blocks should be separated by deaf fireproof walls with the fire resistance limit of at least Rei 45 and the fire hazard class is not lower than K1. Blocking houses of classes of constructive fire hazard C2 and NW additionally must be separated by deaf fireproof walls of the 1st SNIP 21-01 with the fire resistance limit of at least Rei 150 and fire hazard class not lower than K0 on fire compartments area of \u200b\u200bno more than 600 m, including One or more residential blocks.
6.3 To houses up to two floors, the requirements for the degree of fire resistance and the class of structural fire danger are not presented.
6.4 In houses 3 floors, basic structures must comply with the requirements for the designs of buildings III degree of fire resistance to SNIP 21-01: the limit of fire resistance of the carrier elements should be at least R 45, overlaps - Rei 45, non-external walls - E 15, undelated walls Coatings - Re 15, open farms, beams and beams of unbeliving coatings - R 15. The limit of fire resistance of interior partitions is not regulated. The class of constructive fire danger at home should be no lower than C2.
At floor area up to 150 m, it is allowed to take the limit of fire resistance of carrier elements of at least R 30, overlaps - at least Rei 30.
6.5 Houses of 4th floor height should not be lower than III degree of fire resistance and class structural fire danger not lower than C1.
6.6 Each house (residential unit) must have a minimum of one evacuation output directly outward, including on the staircase of the type of SNiP 21-01. An independent evacuation output should also have public premises related to the individual entrepreneurial activities of residents of the house, as well as the premises of basement or basement floors, if they have a heat generator on a gaseous or liquid fuel and (or) stored such fuel.
It is allowed to provide evacuation outputs from the specified premises of the basement and basement floors through the above floor, which has an output directly. At the same time, such a room should be additionally equipped with an emergency output of 6.20, g *Snip 21-01. The exit from the basement to the first floor should be equipped with a door with a device for self-blocking and with a seal in the focus. This door should not go into the bedroom.
6.7 In houses of 2 floors height as evacuation allowed to use internal open stairs (2nd SNIP 21-01), as well as screw staircases and stairs with overtook steps. The limit of fire resistance and the class of fire hazard elements of the stairs, as well as its width and bias are not regulated.
6.8 In houses 3 floors height, open internal stairs is allowed to be considered as evacuation, if it should be climbed or descended to go outside or descend or descend.
If in these houses to exit from the top floor it is necessary to go down to two levels (floors), the open internal stairs are allowed to be considered as evacuation only when both the following conditions are complianced by the following conditions:
a) each room that can be used for sleep must have at least one window located at an altitude of no more than 1 m above the floor level;
b) the specified premises must have a way out directly in the corridor or in the hall with a balcony;
c) the height of the above-mentioned windows and balconies above the ground level should be no more than 7 m.
With a staircase device in the house with a height of no more than three floors in its volume it is allowed to place the entrance lobby and floor halls. The designs of the walls and overlaps of such staircases, including the lobbies and halls, should have a limit of fire resistance not lower than Rei 45 and the class of structural fire danger is not lower than K1. The staircase may not have light openings in the walls, but to be lit by the upper light. Stairs can be wooden.
6.9 Houses and residential blocks of 4 floors should have evacuation outputs from each floor, in addition to the first, in the staircase or on the 3rd type staircase on SNiP 21-01.
6.10 When designing and building blocked houses, measures should be taken to prevent the spread of fire to neighboring residential blocks and fire compartments, bypassing fire barriers. For this, fireproof walls should cross all the designs of the house, made of combustible materials.
At the same time, the Film Walls of the 1st type on SNIP 21-01, separating the house for fire compartments, should rise above the roof and perform for the outer cladding of the walls at least by 15 cm, and when used in the coating, with the exception of the roof, combustibility groups GZ and G4 - rise above the roof at least 60 cm and perform for the outer surface of the wall at least 30 cm.
Fire walls separating residential blocks of the house may not cross the roof and external cladding of the walls provided that the gaps between the fire wall and the roof, as well as between the fire wall and the wall cladding are tightly filled with non-combustible material for the entire thickness of the fire wall.
The direct distance horizontally between any openings located in the adjacent fire compartments must be at least 3 m, and in neighboring residential blocks - do not change 1.2 m.
When the outer walls of adjacent residential blocks or fire compartments at an angle of 135 ° and less section of the outer wall forming this angle, a total length of at least 1.2 m for adjacent residential blocks and at least 3 m for adjacent fire compartments should be made in this way So that it meets the requirements for the corresponding fire wall.
6.11 The built-in parking lot for two or more machines should be separated from other rooms at home (block) by partitions and overlaps with the limit of fire resistance at least Rei 45.
The door between the parking lot and residential premises should be equipped with a seal in the raids, a device for self-blocking and should not go into a sleep room.
6.12 Building structures at home should not contribute to the hidden spread of burning. Empties in the walls, partitions, floors and coatings, limited by the materials of the combustibility groups G3 and G4 and having a minimum size of more than 25 mm, as well as the sinuses of the attic and the attic to be separated by deaf diaphragms on the sections, the dimensions of which should be limited to the contour of the enclosed room. Deaf diaphragms should not be performed from thermoplastic foams.
6.13 Houses Three floors high and more should be equipped with autonomous optical-electronic flue fire detectors, relevant to the requirements of NPB 66, or other detectors with similar characteristics. On each floor of the house, taking into account the need for a timely alert about the emergence of the fire focus, at least one fire detector should be installed. Smoke detectors should not be installed in the kitchen, as well as in bathrooms, shower, toilets, etc. Premises.
Built-in parking lots and public premises must be equipped with indicated detectors and, moreover, primary fire extinguishing agents.
6.14 In the absence of centralized heat supply as sources of thermal energy operating on gas or liquid fuel, automated heat generators of complete factory readiness should be applied. These heat generators should be installed in the ventilated room at home in the first or basement floor, in the basement or roof. The generators of thermal power up to 35 kW are allowed to be installed in the kitchen.
A room in which a heat generator operating on gas or liquid fuel is located must have a window with an area of \u200b\u200bat least 0.03 m per 1 m.
Entering the gas pipeline should be carried out directly into the kitchen or room for the placement of the heat generator. The domestic gas pipeline in the house must meet the requirements for low pressure gas pipelines Snip 42-01.
In the absence of centralized gas supply for the supply of kitchen stoves, the use of gas plates placed outside the house is allowed. Inside the house is allowed to install a balloon with a capacity of no more than 50 liters.
6.15 Heat generators, including furnaces and fireplaces on solid fuel, cooking plates and chimneys should be made with the implementation of constructive measures that provide fire safety at home in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 41-01. Heat generators and cooking plates of factory manufacturers should also be established taking into account the safety requirements contained in the instructions of manufacturers.
Storage solid fuel is allowed to be placed in the first, basement floor or in the basement of the house.
6.16 Gas fireplaces must be factory manufacture. The removal of combustion products should be provided in the chimney. Placing fireplaces and equipping their gas-melting devices with security automation should be carried out in compliance with the requirements available in the manufacturer's instructions.
6.17 The electrical installations must meet the requirements of the "rules of electrical installations" (PUE) and state standards on the electrical installation of buildings, taking into account the provisions of this clause and be equipped with a protective shutdown (RCD) devices.
Wiring, mounted directly on the surface of building structures or hidden inside of them, must be made by cable or insulated wires having shells that do not propagate burning. It is allowed to skip such a wire or cable directly through the design of the house (without using bushings or tubes).
Electric devices used for a steam sauna must have automatic protection and a disabling device after 8 hours of continuous operation.
6.18 Houses The height of four floors and above is not allowed to erect outside the radius of the departure of fire units, which have an auto expense.
6.19 In the design and construction of houses, the requirements for ensuring water for outdoor fire extinguishing should be taken into account in accordance with SNiP 2.04.02.
7 Security when using
Walls separating residential blocks of a blocked house must have an air noise insulation index not lower than 50 dB.
8.9 Natural lighting should be provided in residential and kitchen. The ratio of the area of \u200b\u200blight openings to the floor area of \u200b\u200bresidential premises and kitchens should be at least 1: 8. For mansard floors, it is allowed to take this attitude at least 1:10.
The need for natural lighting for embedded public premises is set to SNiP 2.08.02. The level of natural lighting of these premises must comply with the requirements of SNiP 23-05.
8.10 House-enclosing house designs must have thermal insulation, air insulation from the penetration of outer cold air and vapor barrier from the diffusion of water vapor from interior, providing:
the required temperature on the inner surfaces of the structures and the absence of moisture condensation indoors;
preventing moisture accumulation in structures.
The difference in the temperature of the inner air and the inner surface of the designs of the outer walls at the calculated temperature of the inner air should not exceed 4 ° C, and for the structures of the floor of the first floor - 2 ° C. The temperature of the inner surface of the design elements should not be below 3 ° C at the calculated temperature of the outer air.
The premises of the house must be protected from the penetration of rain, melt, groundwater and domestic water leaks.
8.11 The supply of home drinking water should be provided from the centralized network of water supply in the settlement.
It is allowed to provide individual and collective sources of water supply from underground aquifers or from water bodies at the calculation of the daily flow of economic and drinking water of at least 60 liters per person. In areas with limited water resources, the estimated daily flow consumption is allowed to be reduced by coordination with local bodies of the Ministry of Health of Russia. The quality of drinking water must comply with hygienic standards approved by the Ministry of Health of Russia.
8.12 To remove wastewater, a sewage system should be provided - centralized, local or individual, including cesspool, absorbing or with sanitary individual biotrocess.
The collection and removal of solid household waste and waste from the operation of public premises should be organized in accordance with the rules of the operation of the Housing Fund, adopted by local authorities.
Wastewater and solid waste should be removed without contamination of the territory and aquifers.
9 Energy Saving
systems of heating, ventilation, air conditioning and hot water supply have automatic or manual regulation;
engineering systems of the house with centralized supply are equipped with thermal energy metering devices, cold and hot water, electricity and gas.
9.4 When evaluating the energy efficiency of the house according to the integrated indicator of the specific energy consumption on its heating, the requirements of these standards are considered to be fulfilled if the calculated value of the specific energy consumption To maintain the normalized parameters of the microclimate and air quality, does not exceed the maximum allowable regulatory value given in SNiP 23-02.
Table 1 is excluded.
At the same time, engineering systems of the house must have automatic or manual regulation and with centralized supply must be equipped with heat consumption, cold and hot water, electricity and gas.
9.5 Estimated value of the specific consumption of thermal energy on the heating of the projected home q. Determine as the amount of heat loss through the enclosing structures and with the outgoing air through the ventilation system for the heating period, referred to 1 m of the heated room at home and the number of degree and day of the heating period.
9.6 In order to achieve the optimal technical and economic characteristics of the house and further reduction in the specific energy consumption for heating, it includes:
volume-planning solutions of the house, ensuring the improvement of its compactness indicators;
the most rational orientation of the house and its premises in relation to the countries of light, taking into account the prevailing areas of cold wind and solar radiation streams;
the use of efficient engineering equipment of the relevant nomenclature series with increased efficiency;
disposal of heat of exhaust air, wastewater, the use of renewable sources of solar energy, wind, etc.
If, as a result of these measures, compliance with conditions 9.4 is ensured with smaller impedance values \u200b\u200bof heat transfer of enclosing structures than the required SNiP 23-02 , It is allowed to reduce the indicators of the resistance of the wall heat transfer compared to the required SNiP 23-02.
9.7 Depending on the ratio of the maximum permissible regulatory value of the specific consumption of thermal energy on the heating of the house to the settlement () house refer to one of the following categories of energy efficiency:
at 1.25 - high energy efficiency house;
at 1.25-1.1 - house of increased energy efficiency;
at 1.1-1.0 - the house of normal energy efficiency.
The category of energy efficiency is in a passport of the house when it is commissioned and clarified by the results of operation and taking into account the measures taken by energy saving.
9.8 The norms of this section do not apply to the traditional houses built by their own forces with chopped walls of logs at the area of \u200b\u200bheated premises not more than 60 m.
10 Durability and maintainability
10.1 When complying with the established rules, the House operated must maintain its properties in accordance with the requirements of these standards and the Rules during the alleged service life, which can be installed in the design task.
10.2 Basic unrestracted elements of the house, which determine its strength, stability and service life as a whole, should maintain their properties within acceptable limits, taking into account the requirements GOST 27751 and building standards and rules for building structures from the corresponding materials.
10.3 Elements, details, equipment with smaller service life than the estimated service life of the house must be replaced in accordance with the interremary deadlines established in the project, taking into account the design requirements for design. The decision to apply less or more durable elements, materials or equipment with an appropriate increase or decrease in interremmer periods is established by technical and economic calculations.
10.4 Construction and parts should be made of materials with resistance to possible moisture, low temperatures, aggressive medium, biological and other adverse factors according to SNiP 2.03.11.
In the necessary cases, appropriate measures should be taken from the penetration of rain, melt, groundwater into the thickness of carrier and enclosing house structures, as well as the formation of an unacceptable amount of condensing moisture in outdoor enclosing structures by sufficient sealing of structures or ventilation devices of closed spaces and air suits.
In accordance with the requirements of existing regulatory documents, the necessary protective formulations and coverage should be applied.
10.5 Button compounds of prefabricated elements and layered structures should be calculated on the perception of temperature-humidary deformations and efforts arising from uneven bases of bases and with other operational impacts. Sealing and sealing materials used in the joints should maintain elastic and adhesive properties when exposed to negative temperatures and wetting and be resistant to ultraviolet rays. Sealing materials should be compatible with the materials of protective and protective and decorative coatings of structures in the places of their conjugation.
10.6 The possibility of access to equipment, fittings and devices of engineering systems at home and their compounds for inspection, maintenance, repair and replacement should be provided.
Equipment and pipelines whose work can adversely affect low temperatures, should be protected from their impact.
10.7 During the construction of houses in areas with complex geological conditions, susceptible to seismic effects, part-time, drawdowns and other soil movements, including frosty, engineering communications should be carried out, taking into account the need to compensate for possible reasons.
Equipment and pipelines must be fixed on building structures at home so that their performance is not impaired with possible movements of structures.
Appendix B.
(mandatory)
TERMS AND DEFINITIONS
Definition |
|
1. House, plot |
|
1.1 House residential one-friendly house SINGLE-FAMILY HOUSE (Separately standing - Detached Single-Family House) | The house intended for a permanent joint residence of one family and related related bonds or other people's close relationships |
1.2 House residential blocked Note - This document applies to blocked houses consisting of two or more autonomous residential blocks attached to each other, each of which has direct access to the pillage |
|
1.3 block residential autonomous Unit of Attached Single-Family Houses | Residential block, which has independent engineering systems and individual connections to external networks, not having common with adjacent residential blocks of attics, subliments, mines of communications, auxiliary premises, external inputs, as well as rooms located above or under other residential blocks |
1.4 Apartment plot | |
2. Floor |
|
2.1 Floor | Part of the house between the top of the overlap or floor on the ground and the overlapping located above it |
2.2 floor above ground |
|
3.9 underground Crawl Space. | Designed for the placement of pipelines of engineering systems space between the overlap of the first or basement floor and the surface of the soil |
3.10 The underground ventilated |
The text of the document is drilled by:
Official edition
M.: FSUE CPP, 2005
Act Editorial 27.12.2010
| Name Document | "SP 55.13330.2011. A set of rules of the house Residential one-quality updated editors SNiP 31-02-2001" (approved by the Order of the Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation of 27.12.2010 N 789) |
| Document type | order, Rules, SP |
| Accepted by | ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation |
| Document Number | 789 |
| Date of adoption | 20.05.2012 |
| Date of editorial | 27.12.2010 |
| Date of registration in the Ministry of Justice | 01.01.1970 |
| Status | act |
| Publication |
|
| Navigator | Notes |

"SP 55.13330.2011. A set of rules of the house Residential one-quality updated editors SNiP 31-02-2001" (approved by the Order of the Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation of 27.12.2010 N 789)
Note Rules Preface
Objectives and principles of standardization in the Russian Federation are established by the Federal Law of December 27, 2002 N 184-FZ "On Technical Regulation", and the rules of development - the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 19, 2008 N 858 "On the procedure for the development and approval of rules ".
Information about the rules1. Contractor - OJSC "Center for Production Methodology and Standardization in Construction".
2. Made by the Technical Committee on Standardization TC 465 "Construction".
3. Prepared for approval by the Department of Architecture, Construction and Urban Planning Policy.
4. Approved by order of the Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation (Ministry of Regional Development of Russia) dated December 27, 2010 N 789 and put into action from May 20, 2011
5. Registered by the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology (Rosstandart). Revision SP 55.13330.2010.
Information on changes to this Sport of Rules is published in the "National Standards" information index published annually, and the text of the amendments and amendments - in the monthly issues of the Information Pointers "National Standards". In case of revision (replacement) or the cancellation of this Code of Rules, the appropriate notification will be published in the "National Standards" information index published. Relevant information, notification and texts are also posted in the public information system - on the official website of the developer (Ministry of Regional Development) on the Internet.
1 area of \u200b\u200buseThis set of rules extends to newly under construction and reconstructed separate residential buildings (hereinafter - at home) with the number of floors not more than three, intended for the residence of one family (individual housing facilities).
The real set of rules also extends to newly under construction and reconstructed houses with the number of floors no more than three, consisting of several blocks, the number of which does not exceed ten and each of which is intended to stay one family, has a common wall (common walls) without opening with adjacent By block or adjacent blocks, located on a separate land plot and has access to public areas (Blocked building residential buildings) if they are:
do not have premises located above the premises of other residential blocks;
do not have common entrances, auxiliary premises, attic;
have independent ventilation systems;
Have independent heating systems or individual entries and connecting to external thermal networks.
Blocked houses that do not meet these conditions are design and built in accordance with the requirements of the SP 54.13330. When designing and building homes in accordance with this Code of Rules, the provisions of other more general arrangements of the rules extending to residential one-quality houses should also be applied if they do not contradict the requirements of this document.
2. Regulatory referencesRegulatory documents, which in the text of this Code of Rules have references, are given in Appendix A.
Note. When using this Code of Rules, it is advisable to check the action of reference standards and classifiers in the public information system - on the official website of the National Body of the Russian Federation on the standardization on the Internet or on the National Standards annually published information indicator, which is published as of January 1 of the current year , and according to the corresponding monthly information indicators published in the current year. If the reference document is replaced (changed), then when using this Code of Rules should be guided by a replaced (modified) document. If reference material is canceled without replacement, the position in which the reference is given to it is applied in a part that does not affect this link.
3. Terms and definitionsIn this Code of Rules, the Terms and their definitions provided in Appendix B.
4. General provisions4.1. In embedded or home-built public premises, trade facilities, production workshops and warehouses, which are sources of noise, vibration, ultrasonic and electromagnetic fields, pollution of drainage and other harmful factors of environmental impact are not allowed. It is not allowed to place shops with the presence of explosion hazardous substances and materials, as well as household service enterprises, which use flammable liquids (with the exception of hairdressing, watch repair workshops and shoes).
4.2. The composition of the premises of the house, their size and functional relationship, as well as the composition of engineering equipment are determined by the developer. The house should create conditions for recreation, sleep, hygienic procedures, preparation and meals, as well as for other activities commonly implemented in the home.
In homes belonging to the State and Municipal Housing Fund, including the Housing Fund of Social Use, the minimum area of \u200b\u200bthe apartment and the number of rooms in them is recommended to be taken according to SP 54.13330.
4.3. The house should include at least the following premises: residential room (s), kitchen (kitchen-niche) or kitchen-dining room, bathroom or shower, toilet, storeroom or built-in cabinets; In the absence of centralized heat supply - the containing heat generator.
The house should provide heating, ventilation, water supply, sewage, power supply.
In homes belonging to the State and Municipal Housing Fund, including the Housing Fund of Social Use, the composition of the premises is recommended to take 54.13330, the area of \u200b\u200bthe room - according to SP 54.13330, the equipment of the premises - according to SP 54.13330.
The area of \u200b\u200bpremises of the house is determined taking into account the arrangement of the necessary set of furniture and equipment and should be at least: a total residential room - 12 m2; Bedrooms - 8 m2 (when placing it in the attic - 7 m2); Kitchens - 6 m2. The width of the room should be at least: the kitchen and kitchen area in the kitchen-dining room - 1.7 m; Anterior - 1.4 m, intravarter corridors - 0.85 m; bathroom - 1.5 m; Toilet - 0.8 m. The depth of the toilet should be at least 1.2 m when opening the door and at least 1.5 m - when opening the door inside.
4.4. The height (from the floor to the ceiling) of residential rooms and kitchens in climatic regions IA, IB, IG, ID and IIA (SNIP 23-01) must be at least 2.5 m, in the rest - at least 2.5 m. Height residential rooms, kitchens and other premises located in the attic, and, if necessary, in other cases defined by the developer, allowed not to take at least 2.3 m. In the corridors and with the device, the height of the premises can be taken at least 2.1 m.
4.5. In residential buildings belonging to the State and Municipal Housing Fund, including the Housing Fund of Social Use, conditions must be provided for the livelihoods of small groups of the population, the availability of a plot, houses and its premises for people with children's wheelchairs, for disabled people and the elderly in accordance with SP 59.13330 and SP 35-101. To this end, the necessary dimensions of the tracks on the plot and ramps, as well as the corresponding dimensions of doors, tambours, corridors and kitchens, restrooms and bathrooms, should be provided.
4.6. The project documentation for the house is allowed to include the operating instructions for the house.
The instruction manual of the house must contain the data required by the home owner to ensure safety during operation, including information about the main designs and engineering systems, the location of the hidden frameworks, hidden wiring and engineering networks, as well as the limit values \u200b\u200bof the loads on the elements of the house designs And on its power grid. These data can be represented as copies of executive documentation.
4.7. The rules for counting the area of \u200b\u200bthe premises, the determination of the volume and floor sites of the house and the number of floors take on SP 54.13330.
4.8. Redevelopment and reorganization of houses belonging to the State and Municipal Housing Fund, including the Housing Fund of Social Use, should be carried out in accordance with the Housing Code of the Russian Federation.
5. Bearing ability and deformativity of structures5.1. The bases and supporting structures of the house must be designed and erected in such a way that in the process of its construction and in the calculated operating conditions the possibility of destruction or damage to structures leading to the need to stop operating at home; Invalid deterioration in the operational properties of structures or house as a whole due to deformations or formation of cracks.
5.2. The designs and bases of the house must be calculated on the perception of regulatory loads and impacts.
Regulatory values \u200b\u200bof loads, accounted for adverse combinations of loads or their corresponding efforts, limit values \u200b\u200bof deflection and movements of structures, as well as the values \u200b\u200bof reliability coefficients for load should be taken in accordance with the requirements of the SP 20.13330. The additional requirements of the customer (for example, loads from furnaces, fireplaces, heavy elements of hinged equipment, etc.) also should be taken into account also specified in the design task.
5.3. The methods of calculating their bearing capacity and permissible deformability used in the design of structures should meet the requirements of existing regulatory documents on the design of the relevant materials.
When placing a house on the territory being worked out, on sedentary soils, in seismic areas, as well as in other complex geological conditions, additional requirements of the relevant rules should be taken into account.
5.4. The foundations of the house must be designed taking into account the physico-mechanical characteristics of the soils provided for in the SP 22.13330 (for the perpetrators of the soils - in SP 25.13330), the characteristics of the hydrogeological regime on the construction site, as well as the degree of aggressiveness of soils and groundwater relative to the foundations and underground engineering networks . Foundations should provide the necessary uniformity of the base precipitate under the elements of the house.
6. Fire safety6.1. At home belong to the class F1.4 functional fire hazard in accordance with the technical regulations on fire safety requirements.
In the design and construction of houses, the measures established by this Code for the prevention of fire prevention, ensuring the possibility of timely evacuation of people from the house to the territory adjacent to it, the non-proliferation of fire to neighboring buildings and residential blocks, as well as ensuring the access of the personnel of fire units to the house For events for fire extinguishing and rescue people. At the same time, the possibility of fire inside any room and the exit to the surface of the house is taken into account.
6.2. Fire distances between the houses, as well as other structures, must comply with the requirements of the Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements.
Adjacent residential blocks should be separated by deaf fireproof walls with the fire resistance limit of at least Rei 45 and the fire hazard class is not lower than K1. Blocked houses of constructive fire hazard C2 and C3 classes additionally should be in accordance with the technical regulations on fire safety requirements and SP 4.13130 \u200b\u200bare separated by deaf fire walls of the 1st type with the limit of fire resistance at least Rei 150 and the fire hazard class not lower than K0 for fire compartments area The floor is not more than 600 m2, including one or more residential blocks.
6.3. To single and two-storey houses, the requirements for the degree of fire resistance and the class of structural fire hazard are not presented.
6.4. In homes with the number of floors equal to three (three-story), the main structures must comply with the requirements for the designs of buildings III degree of fire resistance in Table 21 of the Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements: The limit of fire resistance of the carrier elements must be at least R 45, overlaps - Rei 45 , non-outer outdoor walls - e 15, covertile coatings - Re 15, open farms, beams and beams of unbelief coatings - R 15. The limit of fire resistance of interior partitions is not regulated. The class of constructive fire danger at home should be no lower than C2.
It is allowed to design three-storey houses to perform IV degree of fire resistance if the floor area does not exceed 150 m2, while the limit of fire resistance of the carrier elements is not less than R 30, overlaps - at least Rei 30.
6.5. Each house (residential unit) must have a minimum of one evacuation exit directly outward, including the 3rd type staircase, in accordance with the technical regulations on the requirements of fire safety and SP 1.13130.
6.6. In two-storey buildings, internal open stairs (2nd-type 2) are allowed as evacuation in accordance with the technical regulations on fire safety requirements and SP 1.13130, as well as screw staircases and ladders with overtook steps. The limit of fire resistance and the class of fire hazard elements of the stairs, as well as its width and bias are not regulated.
6.7. In three-storey houses, open internal stairs is allowed to be viewed as evacuation, if it should be climbed or descended to go outside or descend, no more than one level (floor).
If in three-storey buildings to exit from the top floor, it is necessary to go down to two levels (floors), the open internal staircases are allowed to be considered as evacuation only while complying with the following conditions:
A) each room that can be used for sleep must have at least one window located at an altitude of no more than 1 m above the floor level;
B) the specified premises must have a way out directly in the corridor or in the hall with a balcony;
c) the height of the above-mentioned windows and balconies above the ground level should be no more than 7 m.
With a staircase device in three-storey houses in its volume it is allowed to place the input lobby and floor halls. The designs of the walls and overlaps of such staircases, including the lobby and halls, should have a limit of fire resistance not lower than Rei 45 and the class of structural fire danger is not lower than K1 in accordance with a table 21 of the Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements.
The staircase may not have light openings in the walls, but to be lit by the upper light. Stairs can be wooden.
6.8. When designing and building blocked houses, measures should be taken to prevent fire spread to neighboring residential blocks and fire compartments, bypassing fire barriers. For this, fireproof walls should cross all the designs of the house, made of combustible materials.
At the same time, the fire-prevention walls of the 1st type of technical regulations on fire safety, separating the house for fire compartments, must rise above the roof and perform for the outer cladding of the walls at least by 15 cm, and when used in the coating, with the exception of the roof, materials of groups The flammability G3 and G4 is to rise above the roof at least 60 cm and perform for the outer surface of the wall at least 30 cm.
Fire walls separating residential blocks of the house may not cross the roof and external cladding of the walls provided that the gaps between the fire wall and the roof, as well as between the fire wall and the wall cladding are tightly filled with non-combustible material for the entire thickness of the fire wall.
The direct distance horizontally between any openings located in the adjacent fire compartments must be at least 3 m, and in neighboring residential blocks - at least 1.2 m.
When the outer walls of adjacent residential blocks or fire compartments at an angle of 135 ° and less section of the outer wall forming this angle, a total length of at least 1.2 m for adjacent residential blocks and at least 3 m for adjacent fire compartments should be made in this way So that it meets the requirements for the corresponding fire wall.
6.9. Built-in parking for two cars and more should be separated from other rooms at home (block) by partitions and overlaps with the limit of fire resistance at least Rei 45.
The door between the parking lot and residential premises should be equipped with a seal in the raids, a device for self-blocking and should not go into a sleep room.
6.10. Building structures at home should not contribute to the hidden spread of burning. Empties in the walls, partitions, floors and coatings, limited by the materials of the combustibility groups G3 and G4 and having a minimum size of more than 25 mm, as well as the sinuses of the attic and the attic to be separated by deaf diaphragms on the sections, the dimensions of which should be limited to the contour of the enclosed room. Deaf diaphragms should not be performed from thermoplastic foams.
6.11. Three-storey houses should be equipped with autonomous optical electronic smoke detectors that meet the requirements of NPB 66, or other detectors with similar characteristics. On each floor of the house, taking into account the need for a timely alert about the emergence of the fire focus, at least one fire detector should be installed. Smoke detectors should not be installed in the kitchen, as well as in bathrooms, shower, toilets, etc. Premises.
Built-in parking lots and public premises must be equipped with indicated detectors and, moreover, primary fire extinguishing agents.
6.12. In the absence of centralized heat supply as sources of thermal energy operating on gas or liquid fuel, automated heat generators of complete factory readiness should be applied. These heat generators should be installed in the ventilated room at home in the first or basement floor, in the basement or roof. The generators of thermal power up to 35 kW are allowed to be installed in the kitchen.
A room in which a heat generator operating on gas or liquid fuel must comply with the requirements of the safety set out in SP 61.13330 and SP 62.13330.
Entering the gas pipeline should be carried out directly into the kitchen or to the room heat generator. The domestic gas pipeline in the house must meet the requirements for low pressure gas pipelines 62.13330.
In the absence of centralized gas supply for the supply of kitchen stoves, the use of gas plates placed outside the house is allowed. Inside the house is allowed to install a balloon with a capacity of no more than 50 liters.
6.13. Heat generators, including furnaces and fireplaces on solid fuel, cooking plates and chimneys should be made with the implementation of constructive activities that provide fire safety at home in accordance with the requirements of the SP 60.13330 and SP 7.13130. Heat generators and cooking plates of factory manufacturers should also be established taking into account the safety requirements contained in the instructions of manufacturers.
Storage solid fuel is allowed to be placed in the first, basement floor or in the basement of the house.
6.14. Gas fireplaces must be factory manufacture. The removal of combustion products should be provided in the chimney. Placing fireplaces and equipping their gas-melting devices with security automation should be carried out in compliance with the requirements available in the manufacturer's instructions.
6.15. The electrical installations must meet the requirements of the rules of the electrical installation (PUE) and state standards on the electrical installation of buildings, taking into account the provisions of this paragraph and be equipped with a protective shutdown (RCD) devices.
Wiring, mounted directly on the surface of building structures or hidden inside of them, must be made by cable or insulated wires having shells that do not propagate burning. It is allowed to skip such a wire or cable directly through the design of the house (without using bushings or tubes).
Electric devices used for a steam sauna must have automatic protection and a disabling device after 8 hours of continuous operation.
6.16. During the design and construction of houses, the requirements for the provision of water for external fire extinguishing should be taken into account in accordance with Table 7 of the Technical Regulation on Fire Safety Requirements.
7. Security when using7.1. The house should be designed, erected and equipped in such a way as to prevent the risk of injury by tenants when moving inside and near the house, at the entrance and outlet of the house, as well as when using it with moving elements and engineering equipment.
7.2. The bias and width of the staircase marches and ramps, the height of the steps, the width of the extex, the width of the staircase, the height of the passages along the stairs, the basement, the attic, the floor level drops, as well as the dimensions of the doorways must provide the convenience and safety of the movement and the possibility of moving the equipment of the room facilities at home . In the necessary cases, handrails must be provided. The use of stairs with different heights of steps is not allowed.
7.3. The height of the stairs, balconies, balconies, loggias, terraces, roofs and in other places of dangerous height drops should be sufficient to prevent the fall and be at least 0.9 m.
Fences must be continuous, equipped with handrails and are designed to perceive the loads of at least 0.3 kN / m.
7.4. The house and at the site should include the necessary measures to protect against unauthorized invasion.
7.5. Structural solutions of elements of the house (including the location of emptiness, methods of sealing the places of passing pipelines through structures, the device of the ventilation holes and the placement of thermal insulation, etc.) should provide for protection against rodents and insect penetration.
7.6. Engineering systems of the house should be designed and mounted taking into account the safety requirements contained in the relevant regulatory documents, and the instructions of the equipment manufacturers instructions. At the same time: the temperature of the surfaces of the available parts of the heating devices and the supply pipelines of heating should not exceed 70 ° C if measures are not taken to prevent the touch by the person, and 90 ° C in other cases; The temperature of the surfaces of other pipelines and chimneys should not exceed 40 ° C; The temperature of hot air at a distance of 10 cm from the outlet of the air heating devices should not exceed 70 ° C; The temperature of the hot water in the hot water system should not exceed 60 ° C.
7.7. Units and devices whose displacement can lead to a fire or explosion, in the house erected in the seismic area, must be securely fixed.
8. Ensuring sanitary and epidemiological requirements8.1. When designing and building houses, the measures established by this Code of the Regulation must be provided to ensure the implementation of sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the protection of human health and the environment.
8.2. The heating system and the enclosing house designs must be designed to provide in rooms at home during the heating period with the calculated parameters of the outer air for the respective areas for the construction of the internal air temperature in the permissible limits set by GOST 30494, but not lower than 20 ° C for all rooms with a permanent stay. People (for SP 60.13330), and in the kitchens and restrooms - 18 ° C, in bathrooms and shower - 24 ° C.
Under the device in the house of the air heating system with forced air supply during the cold period of the year, this system must be calculated in the premises of the house of the optimal values \u200b\u200bof the microclimate parameters according to GOST 30494 (temperature, relative humidity and speed of air, the resulting temperature of the room and its local asymmetry) . When the air conditioning system device, the optimal parameters must be provided in the warm period of the year.
8.3. The ventilation system should maintain the purity (quality) of the air in the premises in accordance with the sanitary requirements and the uniformity of its receipt and distribution. Ventilation can be:
with the natural motion of air removal through ventilation channels;
with mechanical motivation of the inflow and air removal, including combined with air heating;
combined with a natural influx and air removal through ventilation channels with partial use of mechanical motivation.
Air removal should be provided from the kitchen, restroom, bathtubs and, if necessary, from other premises of the house.
Air from premises in which there may be harmful substances or unpleasant odors, should be removed directly to out and not fall into other rooms, including through ventilation channels.
To ensure natural ventilation, it should be possible to carry out the premises of the house through the windows, windows, fraamuga, etc.
8.4. The minimum performance of the ventilation system at home in service mode should be determined at the rate of at least one-time exchange of air volume for an hour in rooms with a permanent stay of people. From the kitchen in service mode should be removed at least 60 m3 of air per hour, from the bath, restroom - 25 m3 air per hour.
The multiplicity of air exchange in other rooms, as well as in all ventilated premises, in non-working mode should be at least 0.2 volume of the room per hour.
8.5. During the construction of houses in areas where, according to engineering and environmental surveys, there are allocations of soil gases (radon, methane, thorin), measures must be taken to insulate in contact with the soil and walls of basements to prevent the penetration of soil gas from the soil to the house , and other measures contributing to the reduction of its concentration in accordance with the requirements of sanitary standards.
8.6. Soundproofing of outdoor and internal furnace structures of residential premises, air ducts and pipelines should reduce sound pressure from external noise sources, as well as from the noise of equipment of engineering systems to a level not exceeding allowed by SP 51.13330.
Walls separating residential blocks of a blocked house must have an air noise insulation index not less than 52 dB.
8.7. Natural lighting should be provided in residential and kitchen. The level of natural lighting must comply with the requirements of the SP 52.13330. The ratio of the area of \u200b\u200blight openings to the floor area of \u200b\u200bresidential premises and kitchens should be at least 1: 8. For mansard floors, it is allowed to take this attitude at least 1:10.
The need for natural lighting for embedded public premises is set to SNiP 31-06. The level of natural lighting of these premises must comply with the requirements of the SP 52.13330.
8.8. Fencing house designs must have thermal insulation, air insulation from the penetration of outer cold air and vapor barrier from diffusion of water vapor from interior, providing:
the required temperature on the inner surfaces of the structures and the absence of moisture condensation indoors;
preventing moisture accumulation in structures.
The difference in the temperature of the inner air and the inner surface of the designs of the outer walls at the calculated temperature of the inner air should not exceed 4 ° C, and for the floor designs of the first floor - 2 ° C. The temperature of the inner surface of the structural elements of the windows should not be below 3 ° C at the calculated temperature of the outer air.
The premises of the house must be protected from the penetration of rain, melt, groundwater and domestic water leaks.
8.9. The supply of home drinking water should be provided from the centralized water supply network of the settlement.
It is allowed to provide individual and collective sources of water supply from underground aquifers or from water bodies at the calculation of the daily flow of economic and drinking water of at least 60 liters per person. In areas with limited water resources, the estimated daily flow consumption is allowed to be reduced by coordination with the relevant supervisory authorities. The quality of drinking water must comply with hygienic standards.
8.10. To remove wastewater, the sewage system should be provided - centralized, local or individual, including cesspool, absorbing or with sanitary individual biotrocess.
The collection and removal of solid household waste and waste from the operation of public premises should be organized in accordance with the rules of the exploitation of the Housing Fund, adopted by local governments.
Wastewater and solid waste should be removed without contamination of the territory and aquifers.
8.11. Insolation of the premises of the house should be provided in accordance with the requirements of SanPiN 2.1.2.2645.
9. Energy saving9.1. The house should be designed and erected in such a way that, when performing established requirements for internal microclimate of premises and other conditions of residence, it was ensured by the effective and economical spending of non-renewable energy resources during its operation.
9.2. Compliance with the requirements for energy saving standards are evaluated by either characteristics of the main elements of the house - building structures and engineering systems, or according to the integrated indicator of the specific energy consumption for the heating of the house.
9.3. When evaluating the energy efficiency of the house according to the characteristics of its building structures and engineering systems, the requirements of this Code of Rules are considered to be fulfilled if the following conditions are followed:
The reduced heat transfer resistance and the breathability of the enclosing structures are not lower than those required by the SP 50.13330;
Systems of heating, ventilation, air conditioning and hot water supply have automatic or manual regulation;
engineering systems of the house with centralized supply are equipped with thermal energy metering devices, cold and hot water, electricity and gas.
9.4. When evaluating the energy efficiency of the house according to the integrated indicator of the specific energy consumption on its heating, the requirements of this Code of Rules are considered to be fulfilled if the calculated value of the specific energy consumption Q to maintain the normalized microclimate parameters and air quality does not exceed the maximum allowable regulatory value given in the SP 50.13330.
At the same time, engineering systems of the house must have automatic or manual regulation and with centralized supply must be equipped with heat consumption, cold and hot water, electricity and gas.
9.5. The calculated value of the specific flow rate of thermal energy on the heating of the projected house Q is determined as the amount of heat loss through the fencing structures and with the outgoing air through the ventilation system for the heating period, referred to 1 m2 of the area of \u200b\u200bheated at home and the number of degree in the heating period.
9.6. In order to achieve the optimal technical and economic characteristics of the house and further reduce the specific energy consumption for heating, it includes:
volume-planning solutions of the house, ensuring the improvement of its compactness indicators;
the most rational orientation of the house and its premises in relation to the countries of light, taking into account the prevailing areas of cold wind and solar radiation streams;
The use of efficient engineering equipment of the relevant nomenclature series with increased efficiency;
the use of energy-saving sources of artificial lighting;
disposal of heat of exhaust air, wastewater, the use of renewable sources of solar energy, wind, etc.
If, as a result of these measures, compliance with conditions 9.4 is provided with smaller impedance values \u200b\u200bof heat transfer of enclosing structures than the required SP 50.13330, then it is allowed to reduce the results of the heat transfer resistance of the walls compared to the required SP 50.13330.
9.7. Depending on the ratio of the maximum allowable regulatory value of the specific consumption of thermal energy on the heating of the house to the settlement house refer to one of the following categories of energy efficiency:
with K\u003e 1.25 - high energy efficiency house;
with K \u003d 1.25 - 1.1 - house of increased energy efficiency;
at k \u003d 1.1 - 1.0 - the house of normal energy efficiency.
The category of energy efficiency is in a passport of the house when it is commissioned and clarified by the results of operation and taking into account the measures taken by energy saving.
9.8. The norms of this section do not apply to the traditional houses built by their own forces with chopped walls of logs at an area of \u200b\u200bheated premises not more than 60 m2.
9.9. When developing an engineering support of a residential building, the use of renewable natural sources of energy (solar, wind, etc.) is allowed.
10. Durability and maintenance10.1. If the established rules are met, the operating house must maintain its properties in accordance with the requirements of this Code of Rules during the alleged service life, which can be installed in the design task.
10.2. The main unrestracted elements of the house, which are determined by its strength, stability and service life of the house as a whole, should maintain their properties within acceptable limits, taking into account the requirements of GOST 27751 and the arrangement of the rules for building structures from the corresponding materials.
10.3. Elements, details, equipment with smaller service life than the estimated service life of the house must be replaced in accordance with the interremary deadlines established in the project, taking into account the requirements of the design task. The decision to apply less or more durable elements, materials or equipment with an appropriate increase or decrease in interremmer periods is established by technical and economic calculations.
10.4. Designs and parts should be made of materials with resistance to possible impacts of moisture, low temperatures, aggressive medium, biological and other adverse factors according to SP 28.13330.
In the necessary cases, appropriate measures should be taken from the penetration of rain, melt, groundwater into the thickness of carrier and enclosing house structures, as well as the formation of an unacceptable amount of condensing moisture in outdoor enclosing structures by sufficient sealing of structures or ventilation devices of closed spaces and air suits.
In accordance with the requirements of existing regulatory documents, the necessary protective formulations and coverage should be applied.
10.5. The butt compounds of prefabricated elements and layered structures should be calculated on the perception of temperature and humidity deformations and efforts arising from uneven base precipitate and with other operational impacts. Sealing and sealing materials used in the joints should maintain elastic and adhesive properties when exposed to negative temperatures and wetting and be resistant to ultraviolet rays. Sealing materials should be compatible with the materials of protective and protective and decorative coatings of structures in the places of their conjugation.
10.6. The possibility of access to equipment, reinforcement and devices of engineering systems of the house and their compounds for inspection, maintenance, repair and replacement should be provided.
Equipment and pipelines whose work can adversely affect low temperatures, should be protected from their impact.
10.7. When building houses in areas with complex geological conditions, susceptible to seismic effects, part-time, drawdowns and other movements of the soil, including frosty trips, engineering communications should be carried out, taking into account the need to compensate for possible reasons.
Equipment and pipelines must be fixed on building structures at home so that their performance is not impaired with possible movements of structures.
ApplicationsFederal Law of the Russian Federation of December 30, 2009 N 384-FZ "Technical Regulations on the Safety of Buildings and Facilities"
SP 20.13330.2011 "Snip 2.01.07-85 * Loads and Impact"
SP 22.13330.2011 "Snip 2.02.01-83 * Bases of buildings and structures"
SP 25.13330.2010 "SNiP 2.02.04-88 Basis and foundations on perpetrators of soils"
SP 28.13330.2010 "Snip 2.03.11-85 Protection of building structures from corrosion"
SP 31.13330.2011 "Snip 2.04.02-84 * Water supply. External networks and structures"
SP 42.13330.2011 "Snip 2.07.01-89 * Urban planning. Planning and building of urban and rural settlements"
SNiP 23-01-99 * "Construction climatology"
SP 50.13330.2010 "Snip 23-02-2003 Thermal protection of buildings"
SP 51.13330.2011 "Snip 23-03-2003 Noise Protection"
SP 52.13330.2011 "Snip 23-05-95 * Natural and Artificial Lighting"
SP 54.13330.2011 "SNiP 31-01 buildings residential complexity"
SNiP 31-06-2009 Public buildings and structures
SP 59.13330.2010 "Snip 35-01-2001 Availability of buildings and structures for low-car groups"
SP 60.13330.2010 "Snip 41-01-2003 Heating, ventilation and air conditioning
SP 61.13330.2010 "Snip 41-03-2003 Heavy insulation of equipment and pipelines"
SP 62.13330.2011 "Snip 42-01-2002 Gas distribution systems"
GOST 27751-88 Reliability of building structures and grounds. Basic provisions for the calculation
GOST 30494-96 Buildings Residential and public. Parameters of the microclimate indoor
SP 1.13130.2009 Fire protection systems. Evacuation paths and outputs
SP 4.13130.2009 Fire protection systems. Restriction of fire distribution at protection objects. Requirements for volume-planning and constructive solutions
SP 7.13130.2009 Heating, ventilation and air conditioning. Firefire requirements
Sanpin 2.1.2.2645-2010 Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for living conditions in residential buildings and premises.
with adjacent residential blocks of attics, subliments, mines of communications, auxiliary premises, outdoor inputs, as well as premises located above or under other residential blocksRules of electrical installation devices (PUE)
NPB 66-97 Fire detectors Autonomous. General technical requirements.
Test methods
SP 35-101-2001 Design of buildings and structures, taking into account accessibility for small groups of the population. General provisions
The site "Zakonbase" is presented "SP 55.13330.2011. A set of rules of the house residential one-quality updated editors of SNiP 31-02-2001" (approved by the Order of the Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation dated December 27, 2010 No. 789) in the latest edition. Observe all the requirements of the legislation simply, if you familiarize yourself with the relevant sections, chapters and articles of this document for 2014. To search for the necessary legislation on the topic of interest, it is worth using convenient navigation or expanded search.
You will find on the site "Zakonbase" you will find "SP 55.13330.2011. A set of rules of the house Residential one-quality updated editors of SNiP 31-02-2001" (approved by the Order of the Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation of 27.12.2010 N 789) in the fresh and full version in which all are made Changes and corrections. This ensures the relevance and accuracy of the information.
At the same time, download "SP 55.13330.2011. A set of house rules residential single-service updated editors SNIP 31-02-2001" (approved by the order of the Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation of December 27, 2010 N 789) can be completely free of charge, both fully and separate chapters.
Below is a typical sample document. Documents are designed without taking into account your personal needs and possible legal risks. If you want to develop a functional and competent document, contract or contract of any complexity Contact professionals.
System of regulatory documents in construction
Houses residential one-friendly houses
Snip 31-02-2001
State Committee of the Russian Federation
For construction and housing and communal complex
(Gosstroy Russia)
Moscow 2001.
Preface
1 Developed by a federal state unitary enterprise - the center of the mission methodology and standardization in construction (FSUE "TSNS") with the participation of the team of specialists from leading research and design organizations
Made by the management of standardization, technical rationing and certification of the state system of Russia
2 Accepted and enforced from January 1, 2002 by a decree of the Gosstroy of Russia of March 22, 2001 No. 35
3 introduced for the first time
CONTENT
Introduction
1
Application area
2
Normative references
3
Terms and Definitions
4
General provisions
5
Beneficial ability and deformity of structures
6
Fire safety
7
Security with use
8
Ensuring sanitary and epidemiological requirements
9
Energy saving
10
Durability and maintainability
Appendix A.
The list of regulatory documents on which there are links in the text
Appendix B.
Terms and Definitions
Introduction
These construction standards and rules have been developed in connection with the increasing volume of construction and the development of the market for single-family residential buildings. This type of construction is gaining more widespread in the world, and therefore the Technical Committee of 59 "Construction of buildings" of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has begun to develop a number of standards for the performance of "single-member separately standing and blocked residential buildings".
In accordance with the principles of SNiP 10-01-94, the system of regulatory documents in construction. The main provisions "These norms establish a set of mandatory regulatory requirements for the operational characteristics of single-family houses, including security issues, regardless of their constructive systems and used building materials.
Norms should be applied to homes, regardless of whether they are built at the expense of the state or municipal budget, the funds of developers organizations engaged in the aim of subsequent sale or lease, or at the expense of individual developers building houses for their own needs.
Single residential buildings started by construction on project documentation developed and approved before January 1, 2002 may continue to be built and commissioned without adjusting project documentation for compliance with the requirements of these construction standards and rules.
In connection with the introduction of these norms and rules, the area of \u200b\u200bdistribution of SNiP 2.08.01-89 * "Residential buildings" is limited only by apartment building buildings. It is also envisaged to develop arms of the Rules for the design and construction of single-sided residential buildings. Among the first, the rules for the design and construction of houses with carrying walls of the frame structure and on engineering systems of single-family houses are developed.
These construction standards and rules have been developed with the support of the Canadian Mortgage Corporation and Housing and the National Research Council of Canada.
The development of SNiP was attended by: L.A. Viktorova, Cand. arch.; V.A. Glukharev; SOUTH. Brank, Cand.Tehn. Nauk; V.N. Ziegern Corn, Cand.Tehn. Nauk; S.V. Krolets, Cand. arch.; D.M. Lakovsky; Yu.A. Matrosov, Kand.Tehn. Nauk; S.N. Nerses, Cand.Tehn. Nauk; E.Yu. Peresvetov, Cand. arch.; N.N. Poles; A.V. Tsareghadsky; E.P. Shastitko; L.S. EXler.
Construction standards and rules of the Russian Federation
Houses residential one-friendly houses
Sindle-Family Houses
Date of introduction 2002-01-01
1 AREA OF USE
These standards and rules apply to newly built and reconstructed single-family residential buildings, intended for permanent residence of people (hereinafter referred to as home), and establish requirements for their safety and other operational characteristics, compliance with all legal entities and individuals carrying out the design and construction of houses .
These norms also apply to blocked at home, the residential blocks of which are autonomous and are considered as separate single-sided homes if they are:
Do not have premises located above the premises of other residential blocks;
do not have common entrances, auxiliary premises, attics, subliments, mines of communications;
They have independent heating and ventilation systems, as well as individual entries and connections to external networks of centralized engineering systems.
Blocked houses that do not meet these conditions are designed and built in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 2.08.01.
When designing and building houses in accordance with these norms and rules, the provisions of other more general rules and rules extending to residential one-quality houses should also be applied if they do not contradict the requirements of this document.
2 Regulatory references
In these standards and rules, references to regulatory documents are used, the list of which is given in Appendix A.
3 Terms and Definitions
Definitions of terms used in this document are given in Appendix B
4 General
4.1 Building houses should be carried out in accordance with the requirements of these construction standards and rules and other regulatory documents establishing the rules of design and construction, on the basis of a construction permit, certifying the right of ownership, owner, a user, a land tenant (hereinafter - developer) to implement its development According to project documentation, coordinated and approved in the prescribed manner.
With the individual construction of houses, simplified procedures for the development, coordination, approval of project documentation, supervision in the construction process, acceptance of the house and commissioning in accordance with the procedure established by the authority of the subject of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation on the basis of general requirements of legislation and relevant regulatory documents on Construction.
4.2 Placement of the house and household buildings on the site, the distance from them to buildings in the next section, as well as the composition, purpose and area of \u200b\u200bembedded or attached to the house of public premises, including those associated with the owner's individual entrepreneurial activities, must comply with the restrictions established in Construction permit and (or) architectural planning task in accordance with current legislation, regulatory documents on design and construction and requirements arising from the laws protected by the rights of residents of neighboring houses (residential blocks).
In embedded or attached to the house of public premises, building materials, shops with explosion hazardous substances and materials, as well as household service enterprises, which use flammable liquids (with the exception of hairdressers, watches and shoe repair workshops).
4.3 Composition of the premises of the house, their size and functional relationship, as well as the composition of engineering equipment are determined by the developer. The house should create conditions for recreation, sleep, hygienic procedures, preparation and meals, as well as for other activities commonly implemented in the home.
4.4 The house must include at least the following premises: residential room (s), kitchen (kitchen-niche) or kitchen-dining room, bathroom or shower, restroom, storeroom or built-in cabinets; In the absence of centralized heat supply - a room for a thermal unit.
The house should provide heating, ventilation, water supply, sewage, power supply and broadcasting.
The area of \u200b\u200bthe premises of the house is determined taking into account the arrangement of the necessary set of furniture and equipment and must be at least: a total residential room - 12 m2 bedrooms - 8 m2 (when it is placed in the attic - 7 m2); Kitchens - 6 m2.
The width of the premises should be at least: the kitchen and kitchen area in the kitchen-dining room - 1.7 m, front - 1.4 m, intra-quarter corridors - 0.85 m, bathroom - 1.5 m, restroom - 0.8m. The depth of the restroom must be at least 1, 2 m when opening the door to the outside and not less than 1.5 m when the door is opened inside.
4.5 Height (from floor to ceiling) residential rooms and kitchens in climatic regions IA, IB, IG, ID and IIA (SNIP 23-01) must be at least 2.7 m, in the remaining - at least 2.5 m. The height of residential rooms, kitchens and other premises located in the attic, and, if necessary, in other cases defined by the developer, allowed to take at least 2.3 m. In the corridors and during the device, the height of the premises can be taken at least 2.1 m.
4.6 During the design and construction of the house, conditions must be provided for small inhabitants, and if necessary, also for people with disabilities using wheelchairs. For this purpose, the necessary dimensions of the tracks on the site and ramps should be provided, as well as the corresponding dimensions of doors, tambourines, corridors and kitchens, restrooms and bathrooms.
4.7 At the request of the developer as part of the documentation on the house should be a thermal power passport and instruction manual at home.
The heat and power passport is designed to establish the thermal power characteristics of the thermal protection of the house and its energy consumption. It is compiled in the order and in the form established in the current regulatory documents, taking into account the provisions of section 9 of these standards and the rules. The passport indicates the category of energy efficiency at home. The heat and power passport is not intended for settlement of utility and other services provided by the owner of the house.
The instruction manual of the house must contain the data required by the home owner to ensure safety during operation, including information about the main designs and engineering systems, the location of the hidden frameworks, hidden wiring and engineering networks, as well as the limit values \u200b\u200bof the loads on the elements of the house designs And on its power grid. These data can be represented as copies of executive documentation.
4.8 The rules for counting the area of \u200b\u200bthe premises, the determination of the volume and floor sites of the house are taken by SNiP 2.08.01.
5 carrier ability
And deformativity of structures
5.1 The foundations and supporting structures of the house should be designed and built in such a way that in the process of its construction and in the calculated operating conditions the possibility of:
destruction or damage to structures leading to the need to stop operating at home;
Invalid deterioration in the operational properties of structures or house as a whole due to deformations or formation of cracks.
5.2 Designs and bases of the house must be calculated on the perception of the following loads and influences:
constant loads from their own weight of carrier and enclosing structures;
temporary uniformly distributed and concentrated loads on overlap;
snow loads for this construction area;
Wind loads for this construction area.
The regulatory values \u200b\u200bof the listed loads accounted for adverse combinations of loads or their corresponding efforts, limit values \u200b\u200bof the deflection and movement of structures, as well as the values \u200b\u200bof the reliability coefficients for load should be taken in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 2.01.07. The additional requirements of the Customer (for example, to loads from furnaces, fireplaces, heavy elements of hinged equipment, etc.) also should be taken into account.
5.3 The methods of calculation of their bearing ability and deformativity used in the design of structures must meet the requirements of existing regulatory documents on the design of the relevant materials.
When housed the house on the territory being worked out, on sedentary soils, in seismic areas, as well as in other complex geological conditions, additional requirements should be taken into account with the relevant standards and rules.
5.4 The foundations of the house should be designed taking into account the physicomechanical characteristics of the soils provided for in SNIP 2.02.01 (for the perplexed soils - in SNIP 2.02.04), the characteristics of the hydrogeological mode at the construction site, as well as the degree of aggressiveness of soils and groundwater in relation to Foundations and underground engineering networks and should ensure the necessary uniformity of the base precipitate under the elements of the house.
5.5 In the construction of traditional houses in rural areas up to two floors inclusive, which are erected by developers with its own, a decision on the possibility of applying technical solutions to the foundations and supporting structures of the house can be accepted when issuing a construction permit based on the results of previous construction and operation of houses.
6 Fire safety
6.1 Single residential buildings belong to the class F 1.4 functional fire hazard on SNIP 21-01. In this regard, in the design and construction of houses, the measures established by these norms to prevent the emergence of a fire, to ensure the possibility of timely evacuation of people from the house on the territory adjacent to it, the non-proliferation of fire to neighboring buildings and residential blocks, as well as ensuring the access of the personnel of firefighters Divisions to the house for events for fire extinguishing and rescue people. At the same time, the possibility of fire inside any room and the exit to the surface of the house is taken into account.
6.2 Fire distances between the houses, as well as other structures, must meet the requirements of SNiP 2.07.01.
Related residential blocks should be separated by deaf fireproof walls with the limit of fire resistance at least REI 45 and the fire hazard class is not lower than K1. Blocking houses of classes of constructive fire danger C2 and SZ additionally should be separated by deaf fireproof walls of the 1st-type SNIP 21-01 with the fire resistance limit of at least 150 and the fire hazard class not lower than the fire compartments of the floor area not more than 600 m2, including One or more residential blocks.
6.3 To houses up to two floors, the requirements for the degree of fire resistance and the class of structural fire danger are not presented.
6.4 In houses 3 floors. Basic structures must comply with the requirements for the structures of buildings III degree of fire resistance to SNIP 21-01: the limit of fire resistance of the carrier elements should be at least R 45, overlaps - REI 45, non-exterior walls - E 15, bench-ending flooring. Coatings - RE 15, open farms, beams and beams of unbeliving coatings - R 15. The limit of fire resistance of interior partitions is not regulated. The class of constructive fire danger at home should be no lower than C2.
At floor area up to 150 m2, it is allowed to take the limit of fire resistance of carrier elements of at least R 30, overlaps - no less than REI 30.
6.5 Houses of 4th floor height should not be lower than III degree of fire resistance and class structural fire danger not lower than C1.
6.6 Each house (residential unit) must have a minimum of one evacuation output directly outward, including on the 3rd type staircase on SNIP 21-01, independent evacuation output should also have public premises associated with the individual entrepreneurial activities of residents of the house, and Also, the premises of the basement or basement floors, if they have a heat generator on a gaseous or liquid fuel and (or) stored such fuel.
It is allowed to provide evacuation outputs from the specified premises of the basement and basement floors through the above floor, which has an output directly. At the same time, such a room should be additionally equipped with an emergency yield of 6.20, R SNIP 21-01. The exit from the basement to the first floor should be equipped with a door with a device for self-blocking and with a seal in the focus. This door should not go into the bedroom.
6.7 In the houses of two floors height as evacuation allowed to use internal open stairs (2nd-type SNIP 21-01), as well as screw staircases and stairs with running steps. The limit of fire resistance and the class of fire hazard elements of the stairs, as well as its width and bias are not regulated.
6.8 In houses 3 floors height, open internal stairs is allowed to be considered as evacuation, if it should be climbed or descended to go outside or descend or descend.
If in these houses to exit from the top floor it is necessary to go down to two levels (floors), the open internal stairs are allowed to be considered as evacuation only when both the following conditions are complianced by the following conditions:
a) each room that can be used for sleep must have at least one window located at an altitude of no more than 1 m above the floor level;
b) the specified premises must have a way out directly in the corridor or in the hall with a balcony;
c) the height of the above-mentioned windows and balconies above the ground level should be no more than 7 m.
With a staircase device in the house with a height of no more than three floors in its volume it is allowed to place the entrance lobby and floor halls. The design of the walls and overlaps of such staircases, including the lobby and halls, should have a limit of fire resistance not lower than REI 45 and the class of structural fire danger is not lower than K1. The staircase may not have light openings in the walls, but to be lit by the upper light. Stairs can be wooden.
6.9 Houses and residential blocks of 4 floors should have evacuation outputs from each floor, in addition to the first, in the staircase or on the 3rd type staircase on SNiP 21-01.
6.10 When designing and building blocked houses, measures should be taken to prevent the spread of fire to neighboring residential blocks and fire compartments, bypassing fire barriers. For this, fireproof walls should cross all the designs of the house, made of combustible materials.
At the same time, the Film Walls of the 1st type on SNIP 21-01, separating the house for fire compartments, should rise above the roof and perform for the outer cladding of the walls at least by 15 cm, and when used in the coating, with the exception of the roof, combustibility groups GZ and G4 - rise above the roof at least 60 cm and perform for the outer surface of the wall at least 30 cm.
Fire walls separating residential blocks of the house may not cross the roof and external cladding of the walls provided that the gaps between the fire wall and the roof, as well as between the fire wall and the wall cladding are tightly filled with non-combustible material for the entire thickness of the fire wall.
The direct distance horizontally between any openings located in the adjacent fire compartments must be at least 3 m, and in neighboring residential blocks - do not change 1.2 m.
When the outer walls of adjacent residential blocks or fire compartments at an angle of 135 (and less section of the outer wall forming this angle, a total length of at least 1.2 m for adjacent residential blocks and at least 3 m for adjacent fire compartments should be made in this way So that it meets the requirements for the corresponding fire wall.
6.11 The built-in parking lot for two cars and more should be separated from other rooms at home (block) by partitions and overlaps with the limit of fire resistance at least REI 45.
The door between the parking lot and residential premises should be equipped with a seal in the raids, a device for self-blocking and should not go into a sleep room.
6.12 Building structures at home should not contribute to the hidden spread of burning. Empties in walls, partitions, overlaps and coatings, limited material
MI of the combustibility groups of GZ and G4 and having a minimum size of more than 25 mm, as well as the sinuses of the attic and the attic to be separated by deaf diaphragms on the sections, the dimensions of which must be limited by the contour of the enclosed room. Deaf diaphragms should not be performed from thermoplastic foams.
6.13 Houses Three floors high and more should be equipped with autonomous optical-electronic flue fire detectors, relevant to the requirements of NPB 66, or other detectors with similar characteristics. On each floor of the house, taking into account the need for a timely alert about the emergence of the fire focus, at least one fire detector should be installed. Smoke detectors should not be installed in the kitchen, as well as in bathrooms, shower, toilets, etc. Premises.
Built-in parking lots and public premises must be equipped with indicated detectors and, moreover, primary fire extinguishing agents.
6.14 In the absence of centralized heat supply as sources of thermal energy operating on gas or liquid fuel, automated heat generators of complete factory readiness should be applied. These heat generators should be installed in the ventilated room at home in the first or basement floor, in the basement or roof. The generators of heat power up to 60 kW are allowed to be installed in the kitchen.
The room in which the heat generator-ranger is located on gas or liquid fuel must have a window with an area of \u200b\u200bat least 0, 03 m2 per 1 m3 of the room.
Entering the gas pipeline should be carried out directly into the kitchen or room for the placement of the heat generator. The domestic gas pipeline in the house must meet the requirements for low pressure gas pipelines on SNIP 2.04.08.
In the absence of centralized gas supply for the supply of kitchen stoves, the use of gas plates placed outside the house is allowed. Inside the house is allowed to install a balloon with a capacity of no more than 50 liters.
6.15 Heat generators, including furnaces and fireplaces on solid fuel, cooking plates and chimneys should be made with the implementation of constructive activities that provide fire safety at home in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 2.04.05. Heat generators and cooking plates of factory manufacturers should also be established taking into account the safety requirements contained in the instructions of manufacturers.
Storage solid fuel is allowed to be placed in the first, basement floor or in the basement of the house.
6.16 Gas fireplaces must be factory manufacture. The removal of combustion products should be provided in the chimney. Placing fireplaces and equipping their gas-melting devices with security automation should be carried out in compliance with the requirements available in the manufacturer's instructions.
6.17 electrical installations must meet the requirements of the rules of the electrical installation device (PUE) and state standards on the electrical installation of buildings, taking into account the provisions of this item and be equipped with a protective shutdown (RCD) devices.
Wiring, mounted directly on the surface of building structures or hidden inside of them, must be made by cable or insulated wires having shells that do not propagate burning. It is allowed to skip such a wire or cable directly through the design of the house (without using bushings or tubes).
Electric devices used for a steam sauna must have automatic protection and a disabling device after 8 hours of continuous operation.
6.18 Houses The height of four floors and above is not allowed to erect outside the radius of the departure of fire units, which have an auto expense.
6.19 In the design and construction of houses, the requirements for ensuring water for outdoor fire extinguishing should be taken into account in accordance with SNiP 2.04.02.
7 Security when using
7.1 The house should be designed, erected and is equipped in such a way as to prevent the risk of injuries with tenants when moving inside and near the house, at the entrance and outlet of the house, as well as when using it with moving elements and engineering equipment.
7.2 Blope and width of staircase marches and ramps, height of steps, width of the extex, width of the staircase, the height of the passages along the stairs, the basement, the attic, the floor level drops, as well as the dimensions of the doorways must ensure the convenience and safety of the movement and the ability to move the equipment of the room equipment at home. In the necessary cases, handrails must be provided. The use of stairs with different heights of steps is not allowed.
7.3 Height of the fences of stairs, balconies, loggias, terraces, roofs and in other places of dangerous height drops should be sufficient to prevent fall and be at least 0.9 m.
Fences must be continuous, equipped with handrails and are designed to perceive the loads of at least 0.3 kN / m.
7.4 The house and the site should include the necessary measures to protect against unauthorized invasion.
7.5 Constructive solutions of house elements (including the location of emptiness, methods for sealing pipelines of pipelines through structures, the device of the ventilation holes and the placement of thermal insulation, etc.) should provide protection against the penetration of rodents and insects.
7.6 Engineering systems of the house must be designed and mounted, taking into account the requirements of the security contained in the relevant regulatory documents of the state supervision authorities, and instructions of the equipment manufacturers of equipment. Wherein:
The temperature of the surfaces of the available parts of heating devices and supplying heating pipelines should not exceed 70 (C, if measures are not taken to prevent the touch of them, and 90 (C in other cases; the temperature of the surfaces of other pipelines and chimneys should not exceed 40 (C;
The temperature of hot air at a distance of 10 cm from the outlet of the air heating devices should not exceed 70 (C;
The temperature of the hot water in the hot water system should not exceed 60 (C.
7.7 Aggregates and devices (for example, gas water heaters), whose displacement can lead to a fire or explosion, in the house erected in the seismic area must be securely fixed.
8 Sanitary provision
Epidemiological requirements
8.1 When designing and building houses, measures established by these norms and rules to ensure the implementation of sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the protection of human health and the environmental environment.
8.2 The system of heating and enclosing house designs should be designed to provide in rooms at home during the heating period at the calculated parameters of the outer air for the respective areas for the construction of the internal air temperature in the permissible limits set by GOST 30494, but not lower than 20 (C for all rooms with constant stay of people (on SNiP 04.04.05), and in the kitchens and restrooms - 18 (C, in bathrooms and shower - 24 (C.
Under the device in the house of the air heating system with forced air supply during the cold period of the year, this system must be calculated in the premises of the house of the optimal values \u200b\u200bof the microclimate parameters according to GOST 30494 (temperature, relative humidity and speed of air, the resulting temperature of the room and its local asymmetry) . When the air conditioning system device, the optimal parameters must be provided in the warm period of the year.
8.3 The ventilation system should maintain the purity (quality) of the air in the premises in accordance with the sanitary requirements and the uniformity of its receipt and distribution. Ventilation may be;
- with the natural motivation of air removal through ventilation channels;
- with the mechanical motivation of the inflow and removal of air, including combined with air heating;
- Combined with natural influx and air removal through ventilation channels with partial use of mechanical motivation.
Air removal should be provided from the kitchen, restroom, bathtubs and, if necessary, from other premises of the house.
Air from premises in which there may be harmful substances or unpleasant odors, should be removed directly to out and not fall into other rooms, including through ventilation channels.
To ensure natural ventilation, it should be possible to carry out the premises of the house through the windows, windows, fraamuga, etc.
8.4 Minimum performance of the ventilation system of the house in service mode should be determined at the rate of at least one-time exchanging of the air volume for one hour in rooms with a permanent stay of people. From the kitchen in the service mode should be removed at least 60 m3 of air per hour, from the bath, restroom - 25 m ...
Snip 31-02-2001
Construction standards and rules of the Russian Federation
Houses residential one-friendly houses
SINGLE-FAMILY HOUSES
Text comparison SNiP 31-02-2001 with SP 55.13330.2011 See reference.
Note database manufacturer.
___________________________________________________________
Date of introduction 2002-01-01
Preface
1 Developed by a federal state unitary enterprise - the center of the mission and standardization methodology in construction (FSUE "TSNS") with the participation of the team of specialists from leading research and design organizations
Made by the management of standardization, technical rationing and certification of the state system of Russia
2 Accepted and enforced from January 1, 2002 by the Resolution of the State Sunday of Russia of March 22, 2001 N 35
3 introduced for the first time
Amendments made approved by the Office of Technical Regulation, Standardization and Certification in the Construction and Housing and Communal Services of the Gosstroy of Russia on May 26, 2004
Introduction
These construction standards and rules have been developed in connection with the increasing volume of construction and the development of the market for single-family residential buildings. This type of construction gets more and more widespread in the world, and therefore the Technical Committee of 59 "Construction of buildings" of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has begun to develop a number of standards for the performance of "single-sided separately standing and blocked residential buildings".
These norms establish a set of mandatory regulatory requirements for the operational characteristics of single-family houses, including security issues, regardless of their constructive systems and used building materials.
Norms should be applied to homes, regardless of whether they are built at the expense of the state or municipal budget, the funds of developers organizations engaged in the aim of subsequent sale or lease, or at the expense of individual developers building houses for their own needs.
Single residential buildings started by construction on project documentation developed and approved before January 1, 2002 may continue to be built and commissioned without adjusting project documentation for compliance with the requirements of these construction standards and rules.
It is envisaged to develop arrangements of the rules of a recommendatory nature on the design and construction of single-family residential buildings. Among the first, the rules for the design and construction of houses with carrying walls of the frame structure and on engineering systems of single-family houses are developed.
These construction standards and rules have been developed with the support of the Canadian Mortgage Corporation and Housing and the National Research Council of Canada.
The development of SNiP was attended by: L.A.Viktorova, Cand. Archite.; V.A.Glukharev; Yu.G.G. G., Cand. tehn sciences; V.N.zify Corn, Cand. tehn sciences; S.V. Krolevts, Cand. Archite.; D.M. Lakovsky; Yu.A. Matrosov, Cand. tehn sciences; S.Nestech, Cand. tehn sciences; E.Yu. Performs, Cand. Archite.; N.N. Polyakov; A.V.Saregradsky; E.P.Shastitko; L.S. Eksler.
1 AREA OF USE
These standards and rules apply to newly built and reconstructed single-family residential buildings, intended for permanent residence of people (hereinafter referred to as home), and establish requirements for their safety and other operational characteristics, compliance with all legal entities and individuals carrying out the design and construction of houses .
These norms also apply to blocked at home, the residential blocks of which are autonomous and are considered as separate single-sided homes if they are:
do not have premises located above the premises of other residential blocks;
do not have common entrances, auxiliary premises, attics, subliments, mines of communications;
they have independent heating and ventilation systems, as well as individual entries and connections to external networks of centralized engineering systems.
Blocked houses that do not meet these conditions are designing and built in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 31-01.
When designing and building houses in accordance with these norms and rules, the provisions of other more general rules and rules extending to residential one-quality houses should also be applied if they do not contradict the requirements of this document.
In these standards and rules, references to regulatory documents are used, the list of which is given in Appendix A.
3 Terms and Definitions
Definitions of terms used in this document are given in Appendix B.
4 General
4.1 Building houses should be carried out in accordance with the requirements of these construction standards and rules and other regulatory documents establishing the rules of design and construction, on the basis of a construction permit, certifying the right of ownership, owner, a user, a land tenant (hereinafter - developer) to implement its development According to project documentation, coordinated and approved in the prescribed manner.
With the individual construction of houses, simplified procedures for the development, coordination, approval of project documentation, supervision in the construction process, acceptance of the house and commissioning in accordance with the procedure established by the authority of the subject of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation on the basis of general requirements of legislation and relevant regulatory documents on Construction.
4.2 Placement of the house and household buildings on the site, the distance from them to buildings in the next section, as well as the composition, purpose and area of \u200b\u200bembedded or attached to the house of public premises, including those associated with the owner's individual entrepreneurial activities, must comply with the restrictions established in Construction permit and (or) architectural planning task in accordance with current legislation, regulatory documents on design and construction and requirements arising from the laws protected by the rights of residents of neighboring houses (residential blocks).
In embedded or attached to the house of public premises, building materials, shops with explosion hazardous substances and materials, as well as household service enterprises, which use flammable liquids (with the exception of hairdressers, watches and shoe repair workshops).
4.3 Composition of the premises of the house, their size and functional relationship, as well as the composition of engineering equipment are determined by the developer. The house should create conditions for recreation, sleep, hygienic procedures, preparation and meals, as well as for other activities commonly implemented in the home.
4.4 The house must include at least the following premises: residential room (s), kitchen (kitchen-niche) or kitchen-dining room, bathroom or shower, restroom, storeroom or built-in cabinets; In the absence of centralized heat supply - a room for a thermal unit.
The house should provide heating, ventilation, water supply, sewage, power supply and broadcasting.
The area of \u200b\u200bthe premises of the house is determined taking into account the arrangement of the necessary set of furniture and equipment and must be at least: a total residential room - 12 m; Bedrooms - 8 m (when placing it in the attic - 7 m); Kitchens - 6 m.
The width of the room should be at least: the kitchen and kitchen area in the kitchen-dining room - 1.7 m, front - 1.4 m, intra-quarter corridors - 0.85 m, bathroom - 1.5 m, restroom - 0.8 m. The depth of the restroom should be at least 1.2 m when the door is opened up and at least 1.5 m when the door is opened inside.
4.5 Height (from floor to ceiling) residential rooms and kitchens in climatic areas I A, I B, I G, I D and II A (SNIP 23-01) must be at least 2.7 m, in the rest - at least 2.5 m. The height of residential buildings, kitchens and other premises located in the attic, and, if necessary, in other cases defined by the developer, allowed to take at least 2.3 m. In the corridors and during the device, the height of the premises can be taken at least 2 ,1m.
4.6 During the design and construction of the house, conditions must be provided for small inhabitants, and if necessary, also for people with disabilities using wheelchairs. For this purpose, the necessary dimensions of the tracks on the site and ramps should be provided, as well as the corresponding dimensions of doors, tambourines, corridors and kitchens, restrooms and bathrooms.
4.7 At the request of the developer as part of the documentation on the house should be a thermal power passport and instruction manual at home.
The heat and power passport is designed to establish the thermal power characteristics of the thermal protection of the house and its energy consumption. It is compiled in the order and in the form established in the current regulatory documents, taking into account the provisions of section 9 of these standards and the rules. The passport indicates the category of energy efficiency at home. The heat and power passport is not intended for settlement of utility and other services provided by the owner of the house.
The instruction manual of the house must contain the data required by the home owner to ensure safety during operation, including information about the main designs and engineering systems, the location of the hidden frameworks, hidden wiring and engineering networks, as well as the limit values \u200b\u200bof the loads on the elements of the house designs And on its power grid. These data can be represented as copies of executive documentation.
4.8 The rules for counting the area of \u200b\u200bthe premises, the determination of the volume and floor sites of the house are accepted by SNiP 31-01.
5 Beneficial Ability and Deformative Designs
5.1 The foundations and supporting structures of the house should be designed and built in such a way that in the process of its construction and in the calculated operating conditions the possibility of:
destruction or damage to structures leading to the need to stop operating at home;
invalid deterioration in the operational properties of structures or house as a whole due to deformations or formation of cracks.
5.2 Designs and bases of the house must be calculated on the perception of the following loads and influences:
constant loads from their own weight of carrier and enclosing structures;
temporary uniformly distributed and concentrated loads on overlap;
snow loads for this construction area;
wind loads for this construction area.
The regulatory values \u200b\u200bof the listed loads accounted for adverse combinations of loads or their corresponding efforts, limit values \u200b\u200bof the deflection and movement of structures, as well as the values \u200b\u200bof the reliability coefficients for load should be taken in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 2.01.07. The additional requirements of the customer (for example, to loads from furnaces, fireplaces, heavy elements of hinged equipment, etc.) should also be taken into account.
5.3 The methods of calculation of their bearing ability and deformativity used in the design of structures must meet the requirements of existing regulatory documents on the design of the relevant materials.
When housed the house on the territory being worked out, on sedentary soils, in seismic areas, as well as in other complex geological conditions, additional requirements should be taken into account with the relevant standards and rules.
5.4 The foundations of the house should be designed taking into account the physicomechanical characteristics of the soils provided for in SNIP 2.02.01 (for the perplexed soils - in SNIP 2.02.04), the characteristics of the hydrogeological mode at the construction site, as well as the degree of aggressiveness of soils and groundwater in relation to Foundations and underground engineering networks and should ensure the necessary uniformity of the base precipitate under the elements of the house.
5.5 In the construction of traditional houses in rural areas up to two floors inclusive, which are erected by developers with its own, a decision on the possibility of applying technical solutions to the foundations and supporting structures of the house can be accepted when issuing a construction permit based on the results of previous construction and operation of houses.
6 Fire safety
6.1 Single residential buildings belong to the class F 1.4 functional fire hazard on SNIP 21-01. In this regard, in the design and construction of houses, the measures established by these norms to prevent the emergence of a fire, to ensure the possibility of timely evacuation of people from the house on the territory adjacent to it, the non-proliferation of fire to neighboring buildings and residential blocks, as well as ensuring the access of the personnel of firefighters Divisions to the house for events for fire extinguishing and rescue people. At the same time, the possibility of fire inside any room and the exit to the surface of the house is taken into account.
6.2 Fire distances between the houses, as well as other structures, must meet the requirements of SNiP 2.07.01.
Adjacent residential blocks should be separated by deaf fireproof walls with the fire resistance limit of at least Rei 45 and the fire hazard class is not lower than K1. Blocking houses of classes of constructive fire hazard C2 and NW additionally must be separated by deaf fireproof walls of the 1st SNIP 21-01 with the fire resistance limit of at least Rei 150 and fire hazard class not lower than K0 on fire compartments area of \u200b\u200bno more than 600 m, including One or more residential blocks.
6.3 To houses up to two floors, the requirements for the degree of fire resistance and the class of structural fire danger are not presented.
6.4 In houses 3 floors, basic structures must comply with the requirements for the designs of buildings III degree of fire resistance to SNIP 21-01: the limit of fire resistance of the carrier elements should be at least R 45, overlaps - Rei 45, non-external walls - E 15, undelated walls Coatings - Re 15, open farms, beams and beams of unbeliving coatings - R 15. The limit of fire resistance of interior partitions is not regulated. The class of constructive fire danger at home should be no lower than C2.
At floor area up to 150 m, it is allowed to take the limit of fire resistance of carrier elements of at least R 30, overlaps - at least Rei 30.
6.5 Houses of 4th floor height should not be lower than III degree of fire resistance and class structural fire danger not lower than C1.
6.6 Each house (residential unit) must have a minimum of one evacuation output directly outward, including on the staircase of the type of SNiP 21-01. An independent evacuation output should also have public premises related to the individual entrepreneurial activities of residents of the house, as well as the premises of basement or basement floors, if they have a heat generator on a gaseous or liquid fuel and (or) stored such fuel.
It is allowed to provide evacuation outputs from the specified premises of the basement and basement floors through the above floor, which has an output directly. At the same time, such a room should be additionally equipped with an emergency output of 6.20, g * Snip 21-01. The exit from the basement to the first floor should be equipped with a door with a device for self-blocking and with a seal in the focus. This door should not go into the bedroom.
6.7 In houses of 2 floors height as evacuation allowed to use internal open stairs (2nd SNIP 21-01), as well as screw staircases and stairs with overtook steps. The limit of fire resistance and the class of fire hazard elements of the stairs, as well as its width and bias are not regulated.
6.8 In houses 3 floors height, open internal stairs is allowed to be considered as evacuation, if it should be climbed or descended to go outside or descend or descend.
If in these houses to exit from the top floor it is necessary to go down to two levels (floors), the open internal stairs are allowed to be considered as evacuation only when both the following conditions are complianced by the following conditions:
a) each room that can be used for sleep must have at least one window located at an altitude of no more than 1 m above the floor level;
b) the specified premises must have a way out directly in the corridor or in the hall with a balcony;
c) the height of the above-mentioned windows and balconies above the ground level should be no more than 7 m.
With a staircase device in the house with a height of no more than three floors in its volume it is allowed to place the entrance lobby and floor halls. The designs of the walls and overlaps of such staircases, including the lobbies and halls, should have a limit of fire resistance not lower than Rei 45 and the class of structural fire danger is not lower than K1. The staircase may not have light openings in the walls, but to be lit by the upper light. Stairs can be wooden.
6.9 Houses and residential blocks of 4 floors should have evacuation outputs from each floor, in addition to the first, in the staircase or on the 3rd type staircase on SNiP 21-01.
6.10 When designing and building blocked houses, measures should be taken to prevent the spread of fire to neighboring residential blocks and fire compartments, bypassing fire barriers. For this, fireproof walls should cross all the designs of the house, made of combustible materials.
At the same time, the Film Walls of the 1st type on SNIP 21-01, separating the house for fire compartments, should rise above the roof and perform for the outer cladding of the walls at least by 15 cm, and when used in the coating, with the exception of the roof, combustibility groups GZ and G4 - rise above the roof at least 60 cm and perform for the outer surface of the wall at least 30 cm.
Fire walls separating residential blocks of the house may not cross the roof and external cladding of the walls provided that the gaps between the fire wall and the roof, as well as between the fire wall and the wall cladding are tightly filled with non-combustible material for the entire thickness of the fire wall.
The direct distance horizontally between any openings located in the adjacent fire compartments must be at least 3 m, and in neighboring residential blocks - do not change 1.2 m.
When the outer walls of adjacent residential blocks or fire compartments at an angle of 135 ° and less section of the outer wall forming this angle, a total length of at least 1.2 m for adjacent residential blocks and at least 3 m for adjacent fire compartments should be made in this way So that it meets the requirements for the corresponding fire wall.
6.11 The built-in parking lot for two or more machines should be separated from other rooms at home (block) by partitions and overlaps with the limit of fire resistance at least Rei 45.
The door between the parking lot and residential premises should be equipped with a seal in the raids, a device for self-blocking and should not go into a sleep room.
6.12 Building structures at home should not contribute to the hidden spread of burning. Empties in the walls, partitions, floors and coatings, limited by the materials of the combustibility groups G3 and G4 and having a minimum size of more than 25 mm, as well as the sinuses of the attic and the attic to be separated by deaf diaphragms on the sections, the dimensions of which should be limited to the contour of the enclosed room. Deaf diaphragms should not be performed from thermoplastic foams.
6.13 Houses Three floors high and more should be equipped with autonomous optical-electronic flue fire detectors, relevant to the requirements of NPB 66, or other detectors with similar characteristics. On each floor of the house, taking into account the need for a timely alert about the emergence of the fire focus, at least one fire detector should be installed. Smoke detectors should not be installed in the kitchen, as well as in bathrooms, shower, toilets, etc. Premises.
Built-in parking lots and public premises must be equipped with indicated detectors and, moreover, primary fire extinguishing agents.
6.14 In the absence of centralized heat supply as sources of thermal energy operating on gas or liquid fuel, automated heat generators of complete factory readiness should be applied. These heat generators should be installed in the ventilated room at home in the first or basement floor, in the basement or roof. The generators of thermal power up to 35 kW are allowed to be installed in the kitchen.
A room in which a heat generator operating on gas or liquid fuel is located must have a window with an area of \u200b\u200bat least 0.03 m per 1 m.
Entering the gas pipeline should be carried out directly into the kitchen or room for the placement of the heat generator. The domestic gas pipeline in the house must meet the requirements for low pressure gas pipelines 42-01.
In the absence of centralized gas supply for the supply of kitchen stoves, the use of gas plates placed outside the house is allowed. Inside the house is allowed to install a balloon with a capacity of no more than 50 liters.
6.15 Heat generators, including furnaces and fireplaces on solid fuel, cooking plates and chimneys should be made with the implementation of constructive measures that provide fire safety at home in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 41-01. Heat generators and cooking plates of factory manufacturers should also be established taking into account the safety requirements contained in the instructions of manufacturers.
Storage solid fuel is allowed to be placed in the first, basement floor or in the basement of the house.
6.16 Gas fireplaces must be factory manufacture. The removal of combustion products should be provided in the chimney. Placing fireplaces and equipping their gas-melting devices with security automation should be carried out in compliance with the requirements available in the manufacturer's instructions.
6.17 The electrical installations must meet the requirements of the "rules of electrical installations" (PUE) and state standards on the electrical installation of buildings, taking into account the provisions of this clause and be equipped with a protective shutdown (RCD) devices.
Wiring, mounted directly on the surface of building structures or hidden inside of them, must be made by cable or insulated wires having shells that do not propagate burning. It is allowed to skip such a wire or cable directly through the design of the house (without using bushings or tubes).
Electric devices used for a steam sauna must have automatic protection and a disabling device after 8 hours of continuous operation.
6.18 Houses The height of four floors and above is not allowed to erect outside the radius of the departure of fire units, which have an auto expense.
6.19 In the design and construction of houses, the requirements for ensuring water for outdoor fire extinguishing should be taken into account in accordance with SNiP 2.04.02.
7 Security when using
7.1 The house should be designed, erected and is equipped in such a way as to prevent the risk of injuries with tenants when moving inside and near the house, at the entrance and outlet of the house, as well as when using it with moving elements and engineering equipment.
7.2 Blope and width of staircase marches and ramps, height of steps, width of the extex, width of the staircase, the height of the passages along the stairs, the basement, the attic, the floor level drops, as well as the dimensions of the doorways must ensure the convenience and safety of the movement and the ability to move the equipment of the room equipment at home. In the necessary cases, handrails must be provided. The use of stairs with different heights of steps is not allowed.
7.3 Height of the fences of stairs, balconies, loggias, terraces, roofs and in other places of dangerous height drops should be sufficient to prevent fall and be at least 0.9 m.
Fences must be continuous, equipped with handrails and are designed to perceive the loads of at least 0.3 kN / m.
7.4 The house and the site should include the necessary measures to protect against unauthorized invasion.
7.5 Constructive solutions of house elements (including the location of emptiness, methods for sealing pipelines of pipelines through structures, the device of the ventilation holes and the placement of thermal insulation, etc.) should provide protection against the penetration of rodents and insects.
7.6 Engineering systems of the house must be designed and mounted, taking into account the requirements of the security contained in the relevant regulatory documents of the state supervision authorities, and instructions of the equipment manufacturers of equipment. Wherein:
the surface temperature of the available parts of heating devices and feeding heating pipelines should not exceed 70 ° C, if measures are not taken to prevent touching them with a person, and 90 ° C in other cases; The temperature of the surfaces of other pipelines and chimneys should not exceed 40 ° C;
the temperature of hot air at a distance of 10 cm from the outlet of the air heating devices should not exceed 70 ° C;
the temperature of the hot water in the hot water supply system should not exceed 60 ° C.
7.7 Aggregates and devices (for example, gas water heaters), whose displacement can lead to a fire or explosion, in the house erected in the seismic area must be securely fixed.
8 Ensuring Sanitary and Epidemiological Requirements
8.1 When designing and building houses, measures established by these norms and rules to ensure the implementation of sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the protection of human health and the environmental environment.
8.2 The system of heating and enclosing house designs should be designed to provide in rooms at home during the heating period at the calculated parameters of the outside air for the respective areas for the construction of the internal air temperature in the permissible limits set by GOST 30494, but not lower than 20 ° C for all rooms with constant Stay of people (by SNIP 41-01), and in the kitchens and restrooms - 18 ° C, in bathrooms and shower - 24 ° C.
Under the device in the house of the air heating system with forced air supply during the cold period of the year, this system must be calculated in the premises of the house of the optimal values \u200b\u200bof the microclimate parameters according to GOST 30494 (temperature, relative humidity and speed of air, the resulting temperature of the room and its local asymmetry) . When the air conditioning system device, the optimal parameters must be provided in the warm period of the year.
8.3 The ventilation system should maintain the purity (quality) of the air in the premises in accordance with the sanitary requirements and the uniformity of its receipt and distribution. Ventilation can be:
With the natural motion of air removal through ventilation channels;
With mechanical motivation of the inflow and air removal, including combined with air heating;
Combined with a natural influx and air removal through ventilation channels with partial use of mechanical motivation.
Air removal should be provided from the kitchen, restroom, bathtubs and, if necessary, from other premises of the house.
Air from premises in which there may be harmful substances or unpleasant odors, should be removed directly to out and not fall into other rooms, including through ventilation channels.
To ensure natural ventilation, it should be possible to carry out the premises of the house through the windows, windows, fraamuga, etc.
8.4 Minimum performance of the ventilation system of the house in service mode should be determined at the rate of at least one-time exchanging of the air volume for one hour in rooms with a permanent stay of people. From the kitchen in service mode should be removed at least 60 m of the air per hour, from the bath, restroom - 25 m of the air per hour.
The multiplicity of air exchange in other rooms, as well as in all ventilated premises, in non-working mode should be at least 0.2 volume of the room per hour.
8.5 excluded.
8.6 Materials and products used in construction, subject to hygienic assessment in accordance with the Ministry of Summary of Products and Goods approved by the Ministry of Health of Russia, should have a hygienic conclusion issued by the authorities and agencies of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Service.
8.7 During the construction of houses in areas where, according to engineering and environmental surveys, there are allocations of soil gases (radon, methane, thorin), measures must be taken to insulate the basements in contact with the soil and walls in order to prevent the penetration of soil gas from the soil in House, and other measures contributing to the reduction of its concentration in accordance with the requirements of sanitary standards.
8.8 Soundproofing of outdoor and internal enclosing designs of residential premises, air ducts and pipelines should reduce sound pressure from external noise sources, as well as from the noise of equipment of engineering systems to a level not exceeding the permissible SNiP 23-03.
Walls separating residential blocks of a blocked house must have an air noise insulation index not lower than 50 dB.
8.9 Natural lighting should be provided in residential and kitchen. The ratio of the area of \u200b\u200blight openings to the floor area of \u200b\u200bresidential premises and kitchens should be at least 1: 8. For mansard floors, it is allowed to take this attitude at least 1:10.
The need for natural lighting for embedded public premises is set to SNiP 2.08.02. The level of natural lighting of these premises must comply with the requirements of SNiP 23-05.
8.10 House-enclosing house designs must have thermal insulation, air insulation from the penetration of outer cold air and vapor barrier from the diffusion of water vapor from interior, providing:
the required temperature on the inner surfaces of the structures and the absence of moisture condensation indoors;
preventing moisture accumulation in structures.
The difference in the temperature of the inner air and the inner surface of the designs of the outer walls at the calculated temperature of the inner air should not exceed 4 ° C, and for the structures of the floor of the first floor - 2 ° C. The temperature of the inner surface of the design elements should not be below 3 ° C at the calculated temperature of the outer air.
The premises of the house must be protected from the penetration of rain, melt, groundwater and domestic water leaks.
8.11 The supply of home drinking water should be provided from the centralized network of water supply in the settlement.
It is allowed to provide individual and collective sources of water supply from underground aquifers or from water bodies at the calculation of the daily flow of economic and drinking water of at least 60 liters per person. In areas with limited water resources, the estimated daily flow consumption is allowed to be reduced by coordination with local bodies of the Ministry of Health of Russia. The quality of drinking water must comply with hygienic standards approved by the Ministry of Health of Russia.
8.12 To remove wastewater, a sewage system should be provided - centralized, local or individual, including cesspool, absorbing or with sanitary individual biotrocess.
The collection and removal of solid household waste and waste from the operation of public premises should be organized in accordance with the rules of the operation of the Housing Fund, adopted by local authorities.
Wastewater and solid waste should be removed without contamination of the territory and aquifers.
9 Energy Saving
9.1 The house should be designed and erected in such a way that, when implementing the established requirements for the internal microclimate of premises and other conditions of residence, the effective and economical spending of non-renewable energy resources during its operation was provided.
9.2 Compliance with the requirements for energy saving standards are evaluated or according to the characteristics of the main elements of the house - building structures and engineering systems, or by the integrated indicator of the specific energy consumption for the heating of the house.
9.3 When evaluating the energy efficiency of the house according to the characteristics of its building structures and engineering systems, the requirements of these standards are considered to be fulfilled if the following conditions are followed:
the reduced heat transfer resistance and the breathability of the enclosing structures are not lower than those required by SNiP 23-02;
systems of heating, ventilation, air conditioning and hot water supply have automatic or manual regulation;
engineering systems of the house with centralized supply are equipped with thermal energy metering devices, cold and hot water, electricity and gas.
9.4 When evaluating the energy efficiency of the house according to the integrated indicator of the specific energy consumption on its heating, the requirements of these norms are considered to be fulfilled if the calculated value of the specific energy consumption for maintaining the normalized parameters of the microclimate and air quality does not exceed the maximum allowable regulatory value given in SNiP 23-02.
Table 1 is excluded.
At the same time, engineering systems of the house must have automatic or manual regulation and with centralized supply must be equipped with heat consumption, cold and hot water, electricity and gas.
9.5 Estimated value of the specific consumption of thermal energy on the heating of the projected home q. Determine as the amount of heat loss through the enclosing structures and with the outgoing air through the ventilation system for the heating period, referred to 1 m of the heated room at home and the number of degree and day of the heating period.
9.6 In order to achieve the optimal technical and economic characteristics of the house and further reduction in the specific energy consumption for heating, it includes:
volume-planning solutions of the house, ensuring the improvement of its compactness indicators;
the most rational orientation of the house and its premises in relation to the countries of light, taking into account the prevailing areas of cold wind and solar radiation streams;
the use of efficient engineering equipment of the relevant nomenclature series with increased efficiency;
disposal of heat of exhaust air, wastewater, the use of renewable sources of solar energy, wind, etc.
If, as a result of these measures, the observance of conditions 9.4 is ensured with smaller impedance values \u200b\u200bof heat transfer of the enclosing structures than the required SNOP 23-02, then it is allowed to reduce the resistance of the heat transfer rates compared to the desired SNiP 23-02.
9.7 Depending on the ratio of the maximum permissible regulatory value of the specific consumption of thermal energy on the heating of the house to the settlement () house refer to one of the following categories of energy efficiency:
at 1.25 - high energy efficiency house;
at 1.25-1.1 - house of increased energy efficiency;
at 1.1-1.0 - the house of normal energy efficiency.
The category of energy efficiency is in a passport of the house when it is commissioned and clarified by the results of operation and taking into account the measures taken by energy saving.
9.8 The norms of this section do not apply to the traditional houses built by their own forces with chopped walls of logs at the area of \u200b\u200bheated premises not more than 60 m.
10 Durability and maintainability
10.1 When complying with the established rules, the House operated must maintain its properties in accordance with the requirements of these standards and the Rules during the alleged service life, which can be installed in the design task.
10.2 Basic unrestracted elements of the house, which determines its strength, stability and service life as a whole, should maintain their properties within acceptable limits, taking into account the requirements of GOST 27751 and building standards and rules for building structures from the respective materials.
10.3 Elements, details, equipment with smaller service life than the estimated service life of the house must be replaced in accordance with the interremary deadlines established in the project, taking into account the design requirements for design. The decision to apply less or more durable elements, materials or equipment with an appropriate increase or decrease in interremmer periods is established by technical and economic calculations.
10.4 Construction and parts should be made of materials with resistance to possible moisture, low temperatures, aggressive medium, biological and other adverse factors according to SNiP 2.03.11.
In the necessary cases, appropriate measures should be taken from the penetration of rain, melt, groundwater into the thickness of carrier and enclosing house structures, as well as the formation of an unacceptable amount of condensing moisture in outdoor enclosing structures by sufficient sealing of structures or ventilation devices of closed spaces and air suits.
In accordance with the requirements of existing regulatory documents, the necessary protective formulations and coverage should be applied.
10.5 Button compounds of prefabricated elements and layered structures should be calculated on the perception of temperature-humidary deformations and efforts arising from uneven bases of bases and with other operational impacts. Sealing and sealing materials used in the joints should maintain elastic and adhesive properties when exposed to negative temperatures and wetting and be resistant to ultraviolet rays. Sealing materials should be compatible with the materials of protective and protective and decorative coatings of structures in the places of their conjugation.
10.6 The possibility of access to equipment, fittings and devices of engineering systems at home and their compounds for inspection, maintenance, repair and replacement should be provided.
Equipment and pipelines whose work can adversely affect low temperatures, should be protected from their impact.
10.7 During the construction of houses in areas with complex geological conditions, susceptible to seismic effects, part-time, drawdowns and other soil movements, including frosty, engineering communications should be carried out, taking into account the need to compensate for possible reasons.
Equipment and pipelines must be fixed on building structures at home so that their performance is not impaired with possible movements of structures.
Appendix A.
(mandatory)
The list of regulatory documents on which there are links in the text
SNIP 21-01-97 * Fire safety of buildings and structures
SNIP 23-01-99 * Construction climatology
SNiP 23-05-95 * Natural and artificial lighting
Snip 2.01.07-85 * Loads and Impact
Snip 2.02.01-83 * Bases of buildings and structures
SNIP 2.02.04-88. Bases and foundations on perpetrators of soils
Snip 2.03.11-85 Protection of building structures from corrosion
SNiP 2.04.02-84 * Water supply. External networks and facilities
SNiP 2.07.01-89 * urban planning. Planning and building of urban and rural settlements
SNiP 2.08.02-89 * Public buildings and structures
SNiP 23-02-2003 thermal protection of buildings
SNiP 23-03-2003 Noise Protection
SNiP 31-01-2003 Buildings Residential Multi-Fire
Snip 41-01-2003 Heating, ventilation and air conditioning
Snip 42-01-2002 Gas distribution systems
GOST 27751-88 Reliability of building structures and grounds. Basic provisions for the calculation
GOST 30494-96 Buildings Residential and public. Parameters of the microclimate indoor
Rules of electrical installation devices (PUE)
NPB 66-97 Fire detectors Autonomous. General technical requirements. Test methods
Appendix B.
(mandatory)
TERMS AND DEFINITIONS
|
Definition |
|
|
1. House, plot |
|
|
1.1 House residential one-friendly house SINGLE-FAMILY HOUSE (Separately standing - Detached Single-Family House) |
The house intended for a permanent joint residence of one family and related related bonds or other people's close relationships |
|
1.2 House residential blocked ROW HOUSES. |
Snip 31-01 Note - This document applies to blocked houses consisting of two or more autonomous residential blocks attached to each other, each of which has direct access to the pillage |
|
1.3 block residential autonomous Unit of Attached Single-Family Houses |
Residential block, which has independent engineering systems and individual connections to external networks, not having common with adjacent residential blocks of attics, subliments, mines of communications, auxiliary premises, external inputs, as well as rooms located above or under other residential blocks |
|
1.4 Apartment plot |
Snip 31-01 |
|
2. Floor |
|
|
2.1 Floor |
Part of the house between the top of the overlap or floor on the ground and the overlapping located above it |
|
2.2 floor above ground Above-Ground Storey |
Snip 31-01 |
|
2.3 Floor First First Storey. |
Lower Overhead Floor House |
|
2.4 Floor attic (attic) ATTIC FLOOR; Mansard |
Snip 31-01 |
|
2.5 Floor Cologway Basement Storey. |
Snip 31-01 |
|
2.6 Floor basement |
Snip 31-01 |
|
3. Premises, open, semi-open and closed spaces |
|
|
3.1 Premises |
The space inside the house having a certain functional purpose and limited by construction structures |
|
Note - Terms characterizing the purpose of various premises (for example, bedroom, kitchen, bathroom, corridor, storeroom, etc.), are generally accepted and here are not given. Purpose of premises indicate the project at home |
|
|
3.2 Public Premises |
Built into residential houses or a premises attached to it intended for individual entrepreneurial and other social activities living in the house of people |
|
3.3 Parking Storage Garage. |
Placed within the home, in an extension to it or in a separate building, a room designed for storage or parking cars, not equipped for their repair or maintenance |
|
3.4 veranda Verandah |
Snip 31-01 |
|
3.5 Cherdak |
Snip 31-01 |
|
3.6 Balcony |
Snip 31-01 |
|
3.7 Loggia |
Snip 31-01 |
|
3.8 Terrace |
Snip 31-01 |
|
3.9 underground Crawl Space. |
Designed for the placement of pipelines of engineering systems space between the overlap of the first or basement floor and the surface of the soil |
|
3.10 The underground ventilated Underfloor Space. |
Snip 31-01 |
The text of the document is drilled by:
official publication M.: FSUE CPP, 2005
Individual housing construction (Izhs) implies the construction of private low-rise buildings intended for living, breeding livestock, storage of materials and products.
The building and the plot on which it will be located must comply with the construction standards and the rules specified in the legislation.
Dear readers! The article tells about the typical ways to solve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to know how solve your problem - Contact a consultant:
Applications and calls are accepted around the clock and seven days a week..
It is fast i. IS FREE!
If you ignore these requirements, you can stay without home and money spent on its construction.
Existing rules
The plot under Izhs must comply with several requirements:
- convenient location near the roads;
- conducted communications;
- developed infrastructure of the district.
The plot must comply with the requirements of the owners of future houses.
One of the important conditions for individual construction is - fertile soil, remoteness from industrial plants and good development of the area.
But construction is possible and when these requirements are inconsistent, which does not affect the strength of the foundation and security of accommodation in the house.
Therefore, in the first place becomes building standards and rules.
Without their observance, it is impossible to build a private and commercial structure.
Individual housing construction should be carried out in strict accordance with the existing rules.
Their disregard can lead to the requirement to demolish the construction in court, and the owner will oblige to pay a fine.
If the building was built without obtaining the appropriate, then legalizing the construction will have to be in court, proving that the house was erected by all construction rules and fire safety standards.
Reflection in law
When designing and building residential type houses, it is necessary to focus on the rules provided for by SNiP 31.02.2001.
They contain technical requirements for buildings, land plots and their target use.
Getting permission
To get a private house, you need to contact the BTI of the Municipal District or the architectural department of the city.
Video: New order of building of suburban properties
It is necessary to have a document in which the land plot is issued.
The owners of the land will need to provide the following documents:
In the BTI bodies, a statement is written to which copies and originals need to be attached:
- Plot.
- On the assignment of land ownership.
- The future structure compiled by BTI staff.
For consideration of documents and the issuance of permission goes, on average, about 14 days.
Refuse to the applicant may if a complete package of documents was provided.
The permit is issued in the form of a document valid for 10 years from the date of receipt.
During this time, the applicant can build a house according to the existing project.
Snip individual housing construction
If the site is called the name of the ILS, then it can only build buildings of a residential type.
These include at home, as well as additional buildings necessary for a comfortable stay (shed, bath, etc.).
It is forbidden to carry out the construction of industrial organizations.
During the construction of a private home for accommodation, you must focus on the rules provided for.
It indicates that construction materials are used refractory, resistant to the formation of mold and rotting, not subject to life and health of people danger.
SNiP implies the beginning of the construction of the house while complying with several rules:







On the territory allowed the construction of other buildings:
- compost sites;
- biotales;
- toilets with cesspools;
- shed.
Placement of buildings
Buildings should be located at a distance of more than 5 meters from the highway and at least 3 meters from the streets with a small movement.
Economic buildings are located in the depths of the site, the first, relative to the road, always becomes a residential building.











Special attention is paid to the distance between buildings and fence. For the most part, the value has a hygienic side of the question, and not fire safety.
The reason is the possible darkening of the neighboring area, if at home will be too close to their territory.
The lower standards of the location of buildings near the fence are indicated.
| Distance between two sites | it should be at least 3 meters (with the written consent of the parties a decrease in this indicator) |
| Buildings for livestock and birds | must be located at a distance of more than 4 meters from the fence |
| Bath, Household Buildings, Toilet and Shower | at a distance of at least 2.5 meters |
| Greenhouses on the site should be located at a distance of more than 4 meters | to prevent shading in the neighboring section and getting sewed with milking fertilizers dissolved in them |
| Garage and Building for Storage Materials (Inventory) | may be 1 meter from the fence |
The optimal option is the location of buildings at a distance of 3 meters. This will prevent conflict with neighbors due to the shading of their plot.
Successors and trees deserve separate attention. They must be located in the site so as not to shade the neighboring plot.
This provides for several rules:
Do not rely on the fact that green plantings or buildings will not cause harm if they are located in chaotic order.
The high tree on the plot can grow for a long time, while a person will not be settled in a neighboring house who will not like the shadow from the tall plants.
And in this case, not only conflict is possible, but also a judicial proceedings ending with the requirement to remove the objective object and pay a penalty for violations of the rules of SNiP.
Distance between buildings
The location of the surplus buildings is regulated by SNiP 30-02-97. It contains the rules for the placement of houses for fire safety.















In the event of a fire fire, the fire quickly reinfects the adjacent area, which will lead to the ignition of a residential building.
Therefore, during construction, it is important to follow the standards provided for by legislative norms.
The distance between the residential buildings is determined depending on the material of the structure:
The location of the houses is allowed to closely, if the structure has a system "2 host on 1 house".
The distance is measured in a straight line, ranging from the house, not the fence of neighbors.
If there are no buildings on the adjacent territory, then primary construction in priority. In the future, measuring the distance between houses will have to neighbors.
The distance between the buildings in the site is also indicated in SNiP.
However, non-compliance with the described standards may result in difficulties in the residential area, therefore it is recommended to follow the rules regarding the location of the buildings:
Snip contains information about the location of objects relative to each other.
For example, the well must be at a distance of more than 20 meters from the compost pit, toilet and away from the fence.
This is the likelihood of toxic substances to the water used in drinking purposes.
Separate attention is paid to baths. In most cases, they are made of wood, which increases fire danger on the site.
For this reason, the bath must be at a distance of more than 8 meters from residential buildings (including neighbor).
Building garage
Previously, the requirements for the construction of the garage were not presented. In 2019, changes in SNiP were introduced.
The garage should be at a distance of more than 1 meter from the fence. If it is equipped within a residential building, additional ventilation should be equipped.
Height of fences
Construction rules contain some requirements and to the fencing of the site.
The fence between adjacent areas should not be higher than 1.5 meters in height.
It is allowed to create a continuous fence, but only half to prevent shading in the neighboring area.
As for the external fence, they do not have special requirements.
But it should not be a height of more than 2 meters, otherwise it will be necessary to further coordinate the structure with controlling authorities.
For the manufacture of the fence you can use any material.
Norms for IZhS
The construction rules are governed not only the location of buildings on the site, but the nature of the buildings themselves.
Having studied the regulatory documents, you can familiarize yourself with the existing standards:
The ground floor must be a height of more than 2 meters, if it is planned to be used for storage of things and inventory. Camping residential in basements is prohibited.
Engineering Communication
For comfortable accommodation in a private house, you must sum up engineering communications or think about the possibility of installing their analogues.
Heating
What to install heating is solved by the owner of the house. It can be a wood-burning furnace, a fireplace, a gas boiler.
Heating radiators are installed under the windows of the house to increase heat transfer.
If there is an opportunity, a house with permission serving organization, connects to the general heating system.
Gas supply
Gas supply can be used in a private house in two ways:
- By connecting to the general highway.
- From gas cylinders.
Connecting to the central gas highway, it is necessary to properly pave the pipes and make parts connections. It is forbidden to carry out communication through residential rooms at home.
Pipes must be supplied to the kitchen or heating stove. Exceptions are at home, where a shut-off crane is installed near the entrance to the residential premises.
Communication is laid outside the building, and not through the foundation. Elements are connected by welding method.
Shut-off valves can be installed using threaded parts.


If the gas cylinders are planned for cooking or heating the premises, then you need to buy containers with a volume of no more than 12 liters.
The exploitation of larger cylinders is allowed only under the condition of their content in a specially designated building, located away from the residential building.
Mandatory condition for the installation of gas supply is the use of at least two devices operating from this fuel.
As a rule, they include a stove for cooking and a heating boiler.
Power supply
Electricity to private homes is summarized due to the installation of air power transmission lines (power lines).
The main condition - the wires should not be on the road and interfere with the roadway.
The installation of wires at an altitude of 2.75 meters are allowed to install wires at a height of 2.75 meters.
If the area is livenily, people often go near the house and cars pass, then the distance from the Earth should be at least 6 meters.
This prevents threats and does not interfere with the movement of people and vehicles.
The distance between the supports should be no more than 25 meters. If the house is located at a greater distance, it is necessary to decide an additional intermediate post.
Between the wires there is a distance of 20 cm. When taking power lines, accounting devices are installed. They are mounted in a special box outside at home or inside.
Wiring in the building is necessarily riveted with insulating material and is attached to the corners of the rooms or on the ceiling.
Work on wiring should be carried out only by professional electricians!
Water supply and sanitation
Water supply in a private house is carried out in several ways:
- through the central system;
- method of drilling wells;
- water delivery.
24-hour cold water without additional manipulations is a connection to the central water supply system.
If hot water is required, the water heaters are installed.
Caliation arrangement is carried out with little requirements:
If the house is equipped with a toilet, then the issue of arranging a cesspool is considered.
It can be separate from sewage from the kitchen or combined.
In a private house, ventilation is not required. Windows and windows open to ventilation.
Ventilation is installed in the bathroom and toilet, provided that there is no inflow of fresh air, that is, there are no windows in the room.
Fire safety standards
Snip does not provide a separate chapter for fire safety standards.
But the basic rules can be allocated from the basic requirements for the construction of the house:
| Distance between house and expensive | must be at least 6 meters. For the entry of fire trucks should not be obstacles |
| Between neighboring houses | the distance must be from 6 meters, not less. This, provided that the building is made from refractory material, and there are no windows and doors from the side of the adjoint. In other cases, the distance increases to 8 or more |
| Wiring is laid according to the PUE rules | when installing power supply in a wooden house, a metal corrugated tube is used. She protects the house from fire in the event of a short smoke of wiring or sparking. Before commissioning, wiring is checked by Ochenergo employees |
| Regular check of electrical wiring | feeding the heating devices is a measure of fire warning in a private house |
| You can not store large gas cylinders in the house | and flammable substances in the unclosed container. For these materials there must be a separate metal box |