Countries with the largest public debt. The only countries in the world that have no debts. What is the debt of the state
Currently, many Russians are interested in information regarding external debt not only of our state, but also other countries of the world. Whose foreign debt is the smallest, and who has the greatest? Our experts will help to deal with these issues.
External debt
Before drawing up the rating of the countries of the world largest and the size of external debt, this concept should be considered. It is established primarily at the legislative level. So, in our country there is a budget code, according to which the foreign debt of any country in front of other states is understood as financial credit debt in foreign currency.
In the economic terms, this concept is considered in the form of a total monetary obligations that the borrower must be returned to a certain period of the Leices state. In the amount of such credit debt, the loan itself will be included, and interest for its use requiring payments. For the country, this amount of debt includes liabilities:
- international banks;
- governments of other countries of the world;
- private banks that belong to foreigners.
External debt distinguish between two types:
- The current (one you want to return to foreign creditors this year, that is, in 2019).
- The general state (accumulated over several years along with unpaid interest, it should be reimbursed in subsequent years).
To assess the magnitude of the external debt of a separate state, specialists working in the field of economy and finance use the relationship between credit debts to foreign creditors and the gross domestic product of the debtor's country itself. In this case, GDP (gross domestic product) is a macroeconomic indicator representing the total amount of all that the country has earned a year on produced products and services.
External debt performance
Experts argue that foreign debt is reflected not only on the economic sphere of the borrower country, but also can lead to long-term political dependence. This is determined by the critical level of overall debt indicators:
- The solvency of the country (the ability to fully fulfill all the obligations assumed at the expense of its own resources), which includes:
- dependence on export goods;
- attitude to state GDP (i.e., to the main base of home resources);
- repayment of debt due to state budget revenues.
- Liquidity (the ability of existing assets, such as securities, to rapid sale at market prices), taking into account:
- term of duty (short-term or for a long period of time);
- sufficiency of international reserves;
- monitoring the risks of non-missing debt.
- Indicators for the Gosseltor, namely:
- influence of tax revenues for public debt;
- changes in foreign currency rate to home.
Thanks to these indicators affecting almost all spheres of the economy, it is possible to calculate how quickly the debtor will return funds borrowed from other countries of the world. For example, about the safe level of debt shows the rating of debt to export income, not exceeding 200% (if this indicator will be higher than 275%, then the external debt may be partially written off as unpaid).
In relation to local GDP, the critical debt level will be considered from 60% (according to the calculations of the IMF) and from 80-100% (according to the calculations of the World Bank). The excess of this limit figure suggests that the repayment of financial debts from other countries of the world is due to the repayment of resources. Instead of the production of goods and services for the internal needs of the state, their production is underway for export trade.
Also, to predict the return of debt obligations with interest should be considered:
- the ratio of these obligations (they may be due to a number of preferential conditions);
- degree of openness of the external capital market;
- real exchange rate mode;
- the likelihood of economic crisis.
If access to its own and international reserves is limited in the country, then any solvency can also be speech. Therefore, many developing states have difficulties with the refund of cash loans. They are on the payment of external debt there is all profit from the internal production, and the current costs of their own activities are taken from new credit revenues.
Positive aspects of the external debt of the state from countries of the world
It would seem that credit financial debt to other countries for the state does not carry anything good in itself - it is an ineffective use of money received on credit, maintenance of credit obligations, economic dependence on the creditor country leading to a change in political relations between states. But experts of the economy and finance and external debt find positive parties:
- any foreign loan improves the economic situation of the borrower country;
- the influx of foreign capital helps in the development of certain areas of the economy (for example, transport, energy, etc.);
- the general budget of the state is restored.
But these positive aspects begin to work only in case of effective distribution of borrowed funds.
Rating countries of the world by external debt
Experts working in the global banking system annually calculate all possible prospects for repaying external debt for the countries of the whole world. Also in the sphere of their activities includes the preparation of rating tables on external debt with the miscalculation of the percentage of the debt of this type to nominal GDP. For 2019, the top 10 countries of the world, who have the smallest foreign debt:
| The name of the country | External debt (million dollars) | External debt to GDP (%) |
| USA | 16 893 000 | 101 |
| Great Britain | 9 836 000 | 396 |
| Germany | 5 624 000 | 159 |
| France | 5 633 000 | 188 |
| Netherlands | 3 733 000 | 309 |
| Japan | 2 719 000 | 46 |
| Spain | 2 570 000 | 165 |
| Italy | 2 684 000 | 101 |
| Ireland | 2 357 000 | 1060 |
| Luxembourg | 2 146 000 | 3411 |
As a result of the analysis of these tables, it can be concluded that countries that do not have external debt, surprisingly small quantity - only three (Brunei, Macau and the Republic of Palau), unlike other states that should almost all of the world.
There are countries that are both borrowers and lenders in relation to each other. So why will they not make their financial debts going on? But it depends not only on the political relationship between them, but also on the conditions of the loan loan - the maturity, interest payments, etc., etc., the mutual debt can not only reset the debt, but also seriously affect the working capital of state financial companies. This situation in turn can lead to the crisis of the economy of both states.
The state debt of the countries of the world is the dominant factor in destabilizing not only the financial situation in the world, but also the economic. The only way out of the situation is to search for the reduction in world debt, with a decrease in its growth inclusive. According to world analysts, while the first global crisis arose as a result of the active growth of the debts of the financial sector, corporate economy and household, the crisis of the 21st century will be caused by the growth of state debts of most countries of the world. The financial market experts with concern say that the debt obligations of countries by 2015 have every chance to turn into simple paper.
What does 2014 statistics mean?
The state debt of the countries of the world as of the end of 2014 has frightening volumes.
- Japan - public debt corresponds to 234% of GDP.
- Greece - 183%.
- Portugal - 148%.
- Italy - 139%.
- Belgium - 135%.
The analytical world company McKinsey introduced to the top ten countries in the size of public debt, Spain (132%) and Ireland (115%), Singapore (105%), France (104%) and the United Kingdom (92%). Interesting the fact that America in this ranking got 11th place from 89% of GDP. Immediately it is worth noting that in accordance with the official state statistics, in 2011, the state overcame the mark of 100% of GDP. As for the 2013 statistics, the volume of debt increased to 106.6%. According to preliminary calculations in 2014, America's debt must be at the level of 109.9%. At the moment, countries are actively policy to reduce government debts. Efficiency of events and final figures of 2015 can be evaluated only in December.
The lowest indicators of public debt
- Norway - the public debt is 34% of GDP.
- Colombia - 32%.
- China - 31%.
- Australia - 31%.
- Indonesia - 22%.
States that practically do not have debts and whose debt is less than 20% of GDP - this is Peru (19%) and Argentina (19%), Chile (15%), Russia (9%) and Saudi Arabia (3%) .
The relationship of national debt and the level of development of countries of the world

The state debt of the countries of the world allows you to establish a certain connection between the debt and the level of development of the state. It is worth saying that the least attracts funds to overlapping the states that are at the stage of active development. In countries that are considered economically developed, it arises much more often, and in debt they are systematically. If we consider the debt not as a percentage of GDP, but in the monetary equivalent, in this category the leadership went to America. Her national debt has long oversail a limit of 18 trillion dollars. World economic analysts talk about increasing debt by the end of 2015 to 19 trillion dollars. The second place in the category is occupied by Japan, with its debts in the amount of 10.5 trillion dollars. Next follows China - 5.5 trillion. These three countries account for about 58-60% of the total world debt. At the same time, Russia, which in mid-2014 had a debt corresponding to 0.1% of the world, today is made to the "garbage rating" of countries for which it is almost impossible to get a loan on the international market.
Dynamics of the situation

The national debt of the countries of the world has a positive trend, it systematically increases. Only for the period from 2007 to 2014 to increase their debt several times not only by the countries of PIGS, carrying the danger to the EU (Portugal, Ireland, Italy, Greece and Spain), but also the leaders of the international market, in particular Japan, Italy and France. America also surpassed all states of the PIGS group. According to preliminary forecasts, the situation in the world will only heat up. Absolute and relative arrears increases, most likely, will be characterized by countries with a high level of economic development.
Why do countries with developed economies have inbox state debts?

The reason for the phenomenon is that the rate of extension of the economy does not allow not only to repay, but also to serve the preoccupied loans. For most, not only zero, but also the minority of the economic pace of the economy are economically characteristic. Experts of the McKinsey Agency after a careful analysis of the situation came to the conclusion that it is harder to refuse to receive a loan to refinance its debts will be such countries as Spain and Japan, Italy, Portugal, United Kingdom and France. Experts see the solution to the problem in the complex restructuring of the economy, by its full dislocation from state debt.
Trends and observations
- The more public debt in the country, the more in its policies such concepts as democracy and liberalism are proteisure.
- Developed countries spend funds from the budget without focusing on the actual state of the economy. Say a simple language "live is not by means." The more developed by the country, the more external debt.
- The economic development of the country fully corresponds to the growth of debt. The processes proceed in parallel and almost identical.
Strange statistics, or what shows the external state debt of the countries of the world

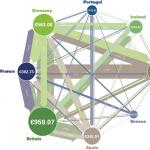
The above observations from the specialists of the "Spiegel" edition are confirmed by the actual situation in the world. Consider large international alliances. So, the "big seven", in theory, combined the economies of the strongest countries of the world. If you compare GDP and the national debt of the countries of the world from this alliance, you can see the following indicators:
- United Kingdom - debt volume corresponds to 92% of GDP.
- Germany - 72%.
- Canada - 86%.
- Italy - 139%.
- USA - 109.9%
- France - 98%.
- Japan - 234%.
Comparing these indicators with indicators of states that are members of BRICS, specialists make certain conclusions. So, Russia (9% of GDP), Brazil (65% of GDP), China (31% of GDP) and South Africa (50% of GDP) looks on the background of world leaders more "economically healthy." It is worth saying that at least 0.5 billion people live on the territory of the Great Seven states, which consume more of more goods and services, rather than about 3 billion people in the territory of the BRICS countries.
What does the analysis of the situation of 2015 say?

The state debt of the countries of the world in real time is to evaluate problematic, since official data will be presented only by the end of 2015. According to preliminary estimates, taking into account the fact that the growth of debts in connection with the economic situation in the world continues to be active at their service, this year will take about 6.3% more than 6.3%. Representatives of the Bloomberg agency report that the strongest states of the world are engaged in active refinancing of their debts due to the design of new loans from the IMF. From the official sources it became known that by the end of 2015 the BRICS and the Great Seven states should pay off debt obligations in the amount of 6.96 trillion dollars. From experts, you can hear opinions on the fact that 2015 will be favorable, and the amount of debts will become less, which seems an unrealistic forecast at this stage.
The mid-2016 seven states (among the largest countries) have a debt above 100% of GDP- Japan (211%), Italy (136%), Spain (100%), Belgium (109%), Singapore (108%), Greece ( 176%) and Portugal (129%) and two countries under 100% - the United States and France. Among the developed countries, only Germany and Switzerland tend to reduce debt burden. As for developing countries, most of the national debt balancing near 50%, the exception is Brazil and Hungary with a debt of about 75%.
In the horizontal table, the color encoding of the trend change in the public debt in% to GDP for 15 years, where the transition from green to red means an increase. In the last column, color coding vertically, showing transitions from the smallest public debt to the greatest.
There is no universal measure of the cost of the public debt, because for some countries, 100% and above may be a normal level in which the state can without any problems to serve current obligations and produce new borrowing, and for the other 50% is a red feature, critical level.
From the point of view of the state and the ability to attract the influence of the following factors:
- The degree of state control over the largest financial institutions in the national currency zone.
- Capacity of the national financial system and developed debt instruments with modulation mechanisms of global cash flows in the right direction. Roughly speaking, the ability of the state to redirect financial flows of institutional units from some tools to others at a certain time with specified criteria.
- Long-term confidence of institutional investors to the public debt market and the lack of negative experience in the appeal of debt securities.
- The international authority of the state and the ability to force, influence international investors, including foreign states.
- Developed monetary mechanisms for control of excess liquidity in the system in the framework of the monetization of the public debt. In other words, the ability of the Central Bank to redeem the public debt without negative consequences in financial markets for national currency and economy.
- The presence of a stable surplus of operational cash flow among private structures.
In the US, on the contrary. Having a shortage of national net cash flows capable of absorbing in the public debt, the United States has methods of force coercion to the Trezeris of International Investors (if necessary, then with the help of the aircraft group, a public debate and panic in domestic markets). If it does not have enough, they buy debt without any consequences through the Fed, reinforcing all this with propaganda in absolute stability Trezeris.
Japan cannot force international investors as the United States, but has an exceptional, close to absolute control on national financial institutions, the capacious domestic market and the ability to monetize without consequences.
Spain does not have the essence of anything and exists in the model of the cross-allrow distribution of euro liquidity flows in which Germany, United Kingdom and France are in the first stage, and what will remain within loyalty and solidarity gets the second, third group and so on the links of the food chain. Therefore, if the conjuncture allows and there is an excess of liquidity, then Spain, Greece and Portugal goes out. If not, then as in 2010-2012.
The dynamics of the public debt to GDP in% 


In this regard, speaking of the redundancy of the public debt, it is necessary to imagine the potential of the state and the structure of the national financial system and the ability of both attracting and servicing the public debt.
Last:
- The magnitude of net interest expenses regarding the budget income and expenditures.
- The degree of public coating by the liquid funds of the state, the amount of pure state.
- The normalized amount of state repayments to the magnitude of the whole state and budget revenues.
- The current and potential need for pure borrowing relative to the entire state. Dolgar and budget revenues.
Value of the public debt in billion dollars 


The total debt of developed countries about 44 trillion dollars, a rise in 15 years by almost 29 trillion, with a crisis of 2008 15 trillion growth, but in dollars, the growth of the national debt developed countries ceased in 2013, which is primarily due to the fall of national currencies relative to the dollar. 44-45 trillion is about 82% for all selected countries. In the group of developing countries, China occupies exactly half, and without taking into account the growth of China's state holder, the remaining developing countries practically did not increase dollar debt from 2011-2012.
In general, the total debt situation is normalized, both through a decrease in the need for new borrowing and a decrease in weighted average rates, which makes it possible to bring the amount of debt service to the pre-crisis level. The US is now paying less than in 2007, although the debt itself has grown from 8 to 18 trillion!
In all cases, we are talking about the debt for the federal and municipal government.
Below is the ratio of public debt of each country to GDP
Top 15 countries with the largest external debt. Photo: Penge.dk.
Since 1979, the World Economic Forum, WEF (World Economic Forum, WEF) is rated countries based on 12 competitiveness indicators. One of the indicators is the level of public debt, which shows how well the same country can cope with debts without significantly harm for the financial system. The lower the settlement of the public debt to GDP, the better.
Below are 15 countries of the world with the largest external debt.
15. France
State Dolg: 96.8%.
Due to the low productivity and low salaries this year, the public debt of France in relation to GDP increased significantly.
14. Singapore
State Dolg: 98.2%.
Despite the fact that Singapore is one of the richest countries of the world, its public debt towards GDP is 98.2%. And this is despite the fact that the indicator managed to reduce from 103.8% last year.
13. Spain
State Dolg: 99%.
Spain has been trying to overcome unemployment for several years in a row, increase productivity and stimulate the growth of the economy after the country has received billionth loans from the EU to maintain the economy.
12. Barbados.
State Dolg: 103%.
Barbados is the richest and developed country in the east of the Caribbean region. She is also a tax refuge. Nevertheless, the country still cannot come to himself after the credit crisis of 8 years ago, and its inhabitants are forced to live in hard savings.
11. USA
State Dolg: 105.8%.
The United States is on the eve of the presidential elections, which will be held on November 8, where the Americans will choose a new head of state who will be either Hillary Clinton from the Democratic Party or Donald Trump - Candidate of Republicans. It is also worth noting that the country is expected to increase the interest rate of the Fed at the end of 2016.
10. Belgium
State Dolg: 106.3%.
Despite the status of the capital of the European Union, which the capital of Belgium, Brussels possesses, is quite high public debt, and there are difficulties with labor and tax legislation, noted in WEF.
9. Cyprus
State Dolg: 108.7%.
Despite the fact that Cyprus managed to reduce the State debt in relation to GDP from last year's value of 112%, the country is still in the process of recovery from the banking crisis.
8. Butane
State Dolg: 115.7%.
A small Asian Bhutan country seriously depends on India in terms of financial assistance and specialists in the construction of infrastructure.
7. Cape Verde
State Dolg: 119.3%.
About 82% of food in Cape Verde - imported, which makes the country's economy dependent on market oscillations.
State Dolg: 124.3%.
The service sector provides about 80% of Jamaica GDP. Among the most serious problems in the country can be called a high level of crime, corruption and unemployment.
5. Portugal
State Dolg: 128.8%.
The country has already received billionth credit tranches for maintaining the economy.
4. Italy
State Dolg: 132.6%.
State duty towards Italy's GDP is the second in size in the Eurozone. Toma, the Italians will soon be solved on a referendum, whether to make the reform package proposed by the Prime Minister.
3. Lebanese
State Dolg: 139.1%.
In the country, war in Syria extremely negatively affected. Internal political contradictions were added to this. The combination of these negative factors has negatively affected Lebanon, as in the tourist direction and, as a result, on the economy of the country as a whole.
2. Greece
State Dolg: 178.4%.
Greece continues to allocate all new packages of assistance, and the country's government continues to drive the population into an increasingly stringent framework of savings. Nevertheless, international loans do not have a positive effect on the country's economy.
1. Japan.
State Dolg: 248.1%.
The country's economy grows as slow the pace that recently the Central Bank introduced negative interest rates.
The public debt of Ukraine in relation to GDP has already reached 80%. Experts predict the growth of the indicator to 90%.
Thus, states, business and citizens together owed the amount of 3.25 times higher than the size of global GDP. The volume of public debt issues increased by three times compared to 2015 and reached $ 855 billion.
In debt leaders the so-called developed countries of the world. In 2016, they increased their debt by 6%. In the first place of the EU. The volume of external debt of the European Union reached 405% of GDP. US foreign debt reached 335% of GDP - $ 67.3 trillion.
The debt of developing countries in 2016 rose by 4.3% and reached 217% of the GDP produced. Only China increased its $ 710 billion debt.
In Russia, foreign debt did not increase due to the introduced anti-Russian sanctions. On July 1, 2016, it was $ 521 billion.
Experts are alarming, recalling that about 75% of the debt is nominated in American dollars - in fact, the amount of interest payments on these loans depends on the US Federal FRAS policy.
Since the American regulator does not print money, but raises the rates, it means that the debt maintenance becomes more expensive.
In general, the global economy is now facing a double problem.
The increase in the value of borrowing and strengthening the dollar, that is, it is obvious that the cost of refinancing already existing debts is growing accelerated pace, and this process cannot be left without consequences.