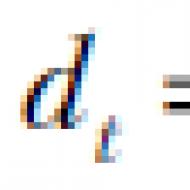There are three states of the system. Find a state with efficient production. Social policy sets its goal. Added value is defined as
Topic “National economy: goals and results of development”
1. The purpose of macroeconomic analysis is:
D) Research national economy, as an integral system;
2. Macroeconomics, as a branch of economic theory, studies:
C) The behavior of the national economy as a whole from the point of view of ensuring conditions for sustainable economic growth, full employment of resources and stability general level prices;
3. A Russian citizen temporarily works in the USA, in an American private company. His income includes:
a) Russian GNP and US GDP
4. Gross domestic product serves as an indicator:
D) The market value of the gross output of final goods and services in the country;
5. Nominal GNP is the value of goods and services measured in:
a) current prices
6. National income (GNI) of a country is:
C) The totality of primary income received by all participants in production in various forms
7. What is gross domestic product (GDP):
e) the sum of all final goods and services produced in the country by both domestic and foreign producers.
8. GDP differs from GNP in that it includes:
a) only final products produced domestically by national and foreign producers
9. Real GDP is measured in:
D) Base period prices.
10. GDP is the sum of the prices of all goods and services:
C) Produced during the year in the country;
11. To calculate the contribution of a company to the created GDP, calculated by the amount of added value, it is necessary from market value created products subtract:
C) Costs for the purchase of raw materials, materials, semi-finished products, fuel, energy, etc.;
12. The maximum possible volume of gross domestic product per year is most often limited to:
D) Insufficient production resources.
13. The GNP deflator is equal to the ratio:
b) nominal GNP to real
14. Despite the harsh repressive measures taken by law enforcement agencies against the businessmen of the shadow economy, it is being revived again because:
C) Profits from underground business are very large;
15. The national wealth of the country is:
E) The totality of material, intellectual and spiritual values that a country has at each stage of its development, including Natural resources, involved in economic turnover.
16. To determine the value national income need to:
b) subtract the amount from GNP depreciation charges for the year, the amount of indirect taxes and government subsidies
17. GDP volume indicator:
A) reflects the possible level of well-being in society
18. To go from GNP to CNP, you need to subtract from GNP:
A) depreciation
19. Real GDP is the value of final goods and services produced in a country during the year, calculated:
B) at base prices
20. A Finnish citizen permanently residing in St. Petersburg receives annual dividends on his shares of a Finnish corporation. This income included in:
a) GNP of Finland
d) Russia's GDP
21. What scientific works represent macroeconomics:
A) Klas Eklund "Efficient economy. The Swedish model." M., 1991
B) A. Pigou "Economic Theory of Welfare". T. 1. 2 M., 1985
D) D. M. Keynes " General theory employment, interest and money". M., Progress, 1978.
22. If the volume of nominal GNP and the price level increased, then:
e) this information does not allow us to determine how GNP has changed
23. Indicate what shifts in the economy led to the change reproductive structure(the numbers are hypothetical):
B) The ratio between the production of means of production and the production of consumer goods has changed from 75: 25 to 60: 40;
E) Gross Investment into the economy grew from 15% to 20% of GDP.
24. Which of the following values is included in GNP, calculated based on the amount of expenses:
a) government procurement
b) gross investment
d) net exports
25. Find appropriate definitions for the following categories:
- a) final product
- b) gross domestic product
- c) net national product
- d) gross national product
1. GNP minus depreciation (3c)
II. The sum of all goods and services produced by national producers in the country and abroad (4g)
III. The sum of all goods and services produced in the country by domestic and foreign producers. (2b)
IV. Goods and services purchased for final use.(1a)
26. The volume of gross national product can be calculated:
a) through income
b) through expenses
c) through production (at added value)
27. The ultimate goal macro economic development is:
d) increase standard of living people based on economic growth.
28. What is net export:
e) the difference between exports and imports.
29. If real GDP decreased by this year by 5% compared to last year, and the population in the same year decreased by 3%, then real GDP per capita per population:
a) decreased
30. What prices are used when analyzing the dynamics of GNP by year:
b) comparable
31. Calculating GDP by production allows you to determine:
c) the contribution of each industry to the creation of GDP.
32. National income includes:
b) corporate profits
c) rent payments
e) interest on capital
33. Transfer payments are:
a) benefits
b) pensions
d) scholarship
Topic: “Fundamentals of the dynamics of the national economy”
1. Economic growth is measured by the following indicators:
c) The growth rate of national income per capita
2. Economic growth can be illustrated by:
c) the movement of a point along the production possibilities curve;
3. Proponents of the theory of economic growth cite the following arguments in defense of their concept:
a) economic growth leads to an increase in living standards;
4. B Keynesian theory The main sources of economic growth are:
A) Investments
D) Savings of the population
5. Identify the demand factors that influence economic growth:
a) income level
d) level of taxes;
e) the population's propensity to save.
6. What factors are considered intensive factors of economic growth:
b) improving the quality of the workforce;
c) improvement of technologies;
e) improving the quality of physical capital;
f) improving the organization and management of production and sales.
7. The two-factor model of economic growth includes:
A) Labor and capital
8. The rate of economic growth of the USSR in the 70-80s. XX century were determined by:
B) government plans
9. The main remedy for overcoming an economic downturn:
c) increased government intervention in the economy.
10. When we talk about the economic cycle, we mean:
c) the period of time between two crises
11. The frequency of crises is based on:
a) the rate of obsolescence of fixed capital
12. What policies base economic growth policies on incentives? aggregate demand:
b) Keynesian
13. The essence of the acceleration principle is that:
b) minor changes in the demand for consumer goods lead to a sharp change in demand for services
14. The crisis that Russia experienced in the 90s of the 20th century was mainly caused by:
c) transformational nature.
15. The main indicators of economic growth are:
a) increase in national income
d) GDP growth,
e) GDP per capita growth.
16. The main condition for ensuring a new quality of economic growth is:
C) Acceleration of scientific and technical progress
17. The new quality of economic growth is achieved mainly due to:
18. Find the corresponding definitions:
4 a) economic growth
3 b) intensive economic growth
1 c) extensive economic growth
2 d) economic cycle
1. Increasing production and consumption volumes attracting additional labor and additional means of production.
2. The period of time from one crisis to another.
3. Increasing the volume of production and consumption through the use of scientific and technological advances.
4. Increasing the volume and structure of production and consumption due to their qualitative improvement, leading to an increase in prosperity in the country
19. A decline in economic growth leads to:
B) a decrease in the standard of living in the country
20. Find a correspondence between the phases of the classical economic cycle and the following phenomena:
1 a) crisis
3 b) depression
4 c) revival
2 d) rise
1. Overproduction of goods
2. Increased production, higher prices and reduced unemployment
3. Suspension of falling prices and growth of loan interest
4. Slight increase in production levels
21. What activities does the state carry out during the recession phase:
c) increase in government spending
22. Features modern structure Russian economy are:
a) accelerated development of industries in the extractive complex
c) accelerated development of trade and intermediary activities
23. B last years V modern Russia The trend is clear:
a) to equalize the levels of economic development of regions
24. The structure of the national economy must correspond to:
c) the structure of society's needs
25. Basic proportion reproductive structure of the economy:
c) the proportion between consumption and accumulation in national income
26. Regulation of the structure of the economy in market conditions is carried out mainly:
a) economic methods
27. Economic growth is intensive if:
c) growth in labor productivity outpaces growth in the number of employees
28. The numerical value of which of the following indicators decreases after the start of the climb and growing after the recession:
a) the volume of inventory in the manufacturing industry
29. High rates of economic growth are achieved through:
a) maximum use of all intensive development factors
30. Intensive factors of economic growth include:
c) introduction of more productive equipment and technology
31. Extensive factors of economic growth include:
d) increase in shift ratio
32. Cycles lasting 45-60 years were studied by:
d) Nikolay Kondratyev
Topic "Mechanism of macroeconomic equilibrium"
1. Which factor will cause the curve to shift aggregate supply:
A) Natural disasters led to the loss of 30% of capacity in the mining industry
2. Where will the aggregate supply curve shift with the accelerated development of scientific and technical progress:
A) Right
3. What led to the shift of the aggregate demand curve to the left in Russia during the years of economic reforms:
A) Fall in production volume
D) Dramatic reduction in investment in industry
4. A shift in the aggregate demand curve occurs when:
B) incomes of the population are growing
5. On the aggregate supply graph vertical section reflects:
A) full employment during the recovery phase:
6. Increase your savings according to the identity I = S leads to:
A) growth in GDP volumes
7. The sum of the marginal propensities to consume and save is equal to one:
D) Always
8. This year the government has increased spending on education by reducing the cost of maintaining the state apparatus. Consequently:
D) ND, GDP have not changed.
9. In accordance with the multiplier theory, the increase in NNP is greater than the increase in investment due to the fact that:
B) Investment growth also increases other components of aggregate demand;
10. Necessity government regulation macroeconomic equilibrium first substantiated in theory:
B) Keynesians
11. A shift in the aggregate demand curve can occur under the influence of changes in:
B) Income
12. Aggregate demand consists of:
A) Personal consumption
D) Investments
G) Government spending
H) Net exports
13. Between the price level in the country and aggregate demand there is:
B) inverse relationship,
14. Investment costs in aggregate demand depend on:
A) Interest rates
B) Expected profit,
d) Tax level
15. The aggregate supply curve consists of:
B) Three segments,
16. The Keynesian (horizontal) segment of the aggregate demand curve in the short term is characterized by:
B) Excess resources
17. The intermediate section of the aggregate demand curve is characterized by:
A) Rising prices
18. The vertical segment of the aggregate supply curve reflects:
A) Full time
D) Lack of reserves of factors of production
19. The shift in the aggregate supply curve is influenced by:
B) Increase in labor productivity
D) Rising prices for resources
20. The marginal propensity to consume is:
a) the share of consumption in each additional unit of disposable income.
21. The marginal propensity to save is:
c) the share of savings in each unit of additional income.
22. The marginal propensity to consume can be equal to:
b) Unit
23. In total, consumption and savings in society are equal to:
b) income
24. An increase in consumption simultaneously reduces:
c) saving
25. The main factor on which investments depend:
B) Interest rate
26. Check the reasons that directly affect investment in Russia
A) Low profits of enterprises
B) Low level income of the population
D) High taxes
27. The equilibrium state of a market economy is maintained through:
A) market mechanism
B) government regulation
28. Sources of investment are:
a) savings of the population
b) bank loans
d) profit of enterprises.
29. Investments in human capital include:
b) construction of hospitals
30. The investment structure always corresponds to:
A) goals and objectives of the development of society:
31. Factors that shift the aggregate demand curve to the right:
d) an increase in the money supply in the country
32. The Keynesian segment of the aggregate supply curve is characterized by:
b) change in the volume of GNP at constant prices
33. The classic segment of the aggregate demand curve is characterized by:
d) change in the price level with a constant volume of GNP
The topic is “Inflation and Unemployment.”
1. Select from the listed options those that characterize inflationary price increases.
c) there is a process of depreciation of money, as a result of the overflow of circulation channels with the money supply;
2. Suppressed inflation manifests itself as:
a) deterioration in the quality of goods and services with stable prices for them;
c) development of the “black market”;
e) chronic shortage of goods;
3. Inflation is:
A) Depreciation of money
D) Rising prices
4. Modern economic theory identifies the costs of inflation, called “costs of worn-out shoes.” These include:
c) more frequent visits by the population to banking institutions to withdraw money from accounts;
5. Okun's Law states that:
B) GNP affects the unemployment rate
D) Unemployment affects the size of GNP
6. The main goal of the state anti-inflationary policy is:
c) bringing inflation to a moderate level;
7. Unemployment is understood as:
b) forced unemployment;
e) imbalance between supply and demand in the labor market.
8. The unemployed include:
B) laid off but constantly looking for work
D) young people looking for work for the first time
9. The unemployment rate (in%) is defined as the ratio of the total number of unemployed to:
a) the working population
10.Upon reaching full employment:
B) there may be natural unemployment
11. Negative economic consequences unemployment consists of:
b) defending the real GNP from the potential;
d) underutilization of the economic potential of society;
12. The relationship between the unemployment rate and the volume of GNP was identified and studied:
d) A. Okun;
13. The “Phillips curve” demonstrates the relationship between the level:
c) inflation and unemployment;
14. What comes first in the development of inflation:
a) Money supply growth
15. Which definition most fully reflects the content of inflation:
c) Depreciation of money, accompanied by the loss of part of its functions
e) Decrease purchasing power money while prices rise.
16. Open inflation is characterized by:
a) Constantly increasing prices
c) By washing out cheap goods from the assortment
17. Select a control measure from the following with negative consequences unemployment:
c) large-scale use of public works paid for from the budget;
18. The Phillips curve characterizes:
C) The relationship between the growth rate of unemployment and inflation
19. The following is used as an indicator of the inflation rate in the country:
c) Consumer Price Index
c) Change in the average price level
21. Demand inflation occurs when:
c) when the increase in demand cannot be satisfied due to the increase in supply due to the lack of reserves of factors of production
22. Which group of the population benefits from inflation:
c) Borrowers
23. The mechanisms of open inflation that ensure its reproduction are:
a) The mechanism of adaptive inflation expectations
c) Demand inflation
d) Cost-push inflation
24. Hyperinflation occurs when the annual price increase is:
25. The consequences of inflation for the population are:
a) Decline in living standards
c) Loss of savings
26. Anti-inflationary strategy affects:
c) On the causes of inflation
27. Anti-inflationary tactics involve:
c) a reduction in demand without a reduction in supply
28. Which of these people is considered unemployed:
b) Who looks through newspapers in search of suitable work
d) Who is fired and has been looking for a job for 3 months.
29. Stagflation is:
B) Simultaneous increase in inflation and unemployment
30. Demand inflation can be caused by:
d) an increase in income for the country with a lagging increase in production volume
31. American economist Arthur Okun showed the relationship between:
d) changes in the number of unemployed and the volume of GNP
32. If the total population is 100 million people, the labor force is 50 million, and the actual workers are 47 million, then unemployment will be:
33. Cyclical unemployment is also called:
d) unemployment insufficient demand
Topic: “Finance and financial policy of the state”
1. If the government annually strives to balanced budget, then the budget is:
- will increase fluctuations within the economic cycle;
2. From the listed possibilities for reducing the tax burden, determine legal:
A) taking into account the non-taxable minimum of the taxable object
B) exemption from taxation of individual elements of the tax object
B) tax exemption for individuals
E) use of certain benefits to reduce tax rates
3. The main source of formation off-budget funds (For example pension fund) are:
b) Income of legal entities
c) Income of individuals
4.Shortage state budget occurs when:
b) the amount of government expenses exceeds the amount of income
5. What to do if there is a budget deficit and you you do not want negative consequences for country:
B) Reduce government spending
D) Improve the tax collection system without changing tax rates.
6. Is it correct to say that covering the budget deficit increases inflation in the current period:
b) Correct only in certain cases, depending on the method of covering the deficit
7. What can lead to a state budget deficit:
a) high government spending
b) low tax rates;
c) rising unemployment
d) low incomes of the population
8. When a state has a budget deficit, it can be argued that:
b) it is possible for the state to pursue any type of fiscal policy
9. Public debt management includes:
A) efficient use borrowing funds
c) search for other means of payment
10. The most important source of income federal budget in a market economy is:
D) Value added tax
11. The most important direction of state budget expenditures (as a percentage of the amount of expenditures):
a) Financing of social programs
12. If the government intends to increase the level of real NNP through fiscal policy, it can:
- reduce taxes;
e) increase government spending
13. Pronounced anti-inflationary fiscal policy assumes:
- increasing the level of taxation and reducing government spending;
14. An annually balanced budget assumes that:
a) income must be equal to expenses
15. The advantage of built-in stabilizers is that they act:
a) automatically
16. Multipliers work in fiscal policy:
a) Government spending
c) Balanced budget
d) Tax
17. An increase in taxes leads to:
b) to a decrease in consumption and aggregate demand
18. Discretionary fiscal policy includes the following instruments:
a) government spending
b) change in tax rates
19. Balancing the budget over the cycle involves:
B) Equality of income and expenses during the industrial cycle
20. Principles of income taxation:
a) depending on income
21. Fiscal policy is:
A). The policy of manipulating taxes and government spending in order to maintain equilibrium NNP
22. The Laffer curve shows the relationship between the tax rate and:
B) The amount of profit of enterprises (tax base)
23. Balancing the state budget using the “Functional Finance” method involves:
C) Balancing the structure and increasing the efficiency of the national economy.
24. The main source of state budget revenue in a market economy is:
A) income tax
25. An increase in government spending equal to the amount obtained from an increase in taxes leads to an increase in NNP. This is the action of the multiplier:
D) Balanced budget
26. What functions do taxes perform:
A). Fiscal
b) Stimulating
c) Social
27. Decline tax rate on profit causes:
A) an increase in the budget deficit
B) increasing the level of output
B) increasing investment
28. Discretionary fiscal policy assumes:
d) conscious regulation of taxation and government spending
29. An increase in government spending allows:
d) increase the volume of GNP
30. The tax multiplier shows:
d) changes in GDP due to changes in taxes
31. An increase in taxes, other things being equal, leads to:
b) reduction in disposable income of the population
Topic: “Money market and state monetary policy”
1. Assume that each transaction dollar circulates on average 4 times a year and is used to purchase final goods and services. The nominal volume of GNP is $2 billion. Determine the amount of money demanded for transactions.
a) 0.5 billion dollars
2. If money for transactions makes an average of 5 revolutions per year, then the amount of money needed in circulation
b) is 20% of nominal GNP;
3. The basis for identifying aggregates M1, M2, M3 is:
A) The degree of their liquidity
4. If a ceiling is established by law interest rate below its equilibrium level, this will lead to:
a) lack of credit resources of banks;
5. If the nominal volume of GNP decreases, then:
b) The demand for money for transactions and the overall demand for money will decrease.
6. When the Central Bank sells government securities:
d) Credit resources of commercial banks are decreasing
7. In conditions of steady rising prices, the demand for money:
a) Increases
8. Which of the Central Bank operations increases amount of money in circulation?
d) The Central Bank buys government. bonds for open market.
9. Under the influence of what changes the value of money over time:
a) Inflation
10. Which listed means of payment are included in unit M1:
b) Metal money on hand
c) Banknotes on hand
d) Current bank account.
11. Which of the following refers to monetary policy?
b) control over the money supply;
d) controlling the terms and conditions of lending
e) impact on investment through changes in interest rates.
12. Central Bank sells government bonds commercial banks and the public. What happens to the credit resources of commercial banks:
b) decrease
13. Central Bank sells government bonds on the open market. What happens to the money supply:
B) decreases
14. Central Bank sells government bonds on the open market. What happens to the bank interest rate:
b) increases
15. The central bank reduces the discount rate. What happens to the demand for loans:
a) increases
16. The concept of “demand for money” means:
D) The totality of the demand for money for transactions and the demand for money as assets.
17. What will affect the demand for money for transactions:
A). Growth of nominal gross national product.
B). Increasing the velocity of money circulation.
18. Demand for money from assets:
b) inversely proportional to the interest rate;
19. What happens when using a dear money policy:
B) increase in the cost of credit;
D) rising production costs;
D) decrease in entrepreneurial activity
20. The real interest rate is:
B) Bank rate minus inflation rate.
21. The purpose of monetary regulation is to regulate:
a) Inflation
d) Bank interest
22. What will reduce amount of money in circulation:
B) Sale of government securities valuable papers to the population and banks
23. The term "open market operations" means:
c) purchase or sale by the Central Bank of government securities
24. The term "discount rate" means:
C) The interest rate at which the Central Bank provides loans to commercial banks.
25. The increase in the discount rate is aimed at:
A) to reduce the total amount of credit resources of commercial banks
26. If the Central Bank seeks to reduce money supply, then the discount rate:
b) Increases
27. The supply of money depends on:
B) aggregate demand for money
C) the rate of turnover of one monetary unit
28. Which of the listed items will correspond to the monetary aggregate M 1?
c) cash and checks
29. Credit system countries includes:
A) banking system
D) non-bank credit organizations
30. What functions does the Central Bank perform:
a) Money issue
c) Control over money circulation
d) Control over the activities of commercial banks
31. Basic tools monetary policy are:
a) Discount rate
d) Required reserve ratio
e) Central Bank operations on the open market.
32. The most rapid impact on the economy is exerted by:
c) open market operations
33. If it is necessary to reduce the multiplier value money supply, then you need:
b) increase the required reserve ratio
34. The term "open market operations" means:
d) sale or purchase by the Central Bank of government securities
Topic: “Social policy of the state and income distribution”
1. The level of inequality in a society increases if the Gini index:
1) tends to unity;
2. After the state collects taxes and pays social transfers to the population, what will happen to the Lorenz curve:
1) will approach the curve of absolute equality
3. If wage increased by 2 times, and prices by 3 times, then:
3) real income fell;
4. Social politics aims to:
A) implementation of social protection of a person
C) improving the income distribution system
5. To reflect inequality in income distribution in graphical form, the following is used:
A) Lorenz curve.
6. The Lorenz curve reflects:
4) distribution of income between families (individuals)
7. The level of inequality of income distribution in society is determined by:
8. Indicate the most accurate indicator of standard of living:
1) real income per capita;
9. Individual income depends on:
1) employee productivity;
3) profitability of the sphere of employment;
4) social policy of the state;
10. Sources of social assistance are:
A) State budget funds
B) Employers' funds
B) Funds of recipients of assistance
11. Distributive relations are relations regarding distribution:
c) income between production participants
12. Instruments for income redistribution include :
A). income tax on personal income;
b) wage regulation;
c) assistance and social security programs;
13. The following are used as means of income regulation:
a) taxes;
c) payment of benefits, pensions;
e) benefits
14. Minimum size wages are:
b) minimum bid wages
15. Among the effects of social policy listed below, highlight negative effects for future economic growth:
a) Separate social benefits and transfers reduce incentives to work
c) government spending increases;
d) taxes increase;
e) labor mobility decreases;
16. Social assistance is provided taking into account:
B) needs for help
17. The system of state guarantees includes:
3) the right to education and medical care;
4) the right to work and rest;
5) the right to labor and family protection
18. If income in a society is distributed absolutely evenly, then the Lorenz curve
4) bisector of the angle formed by the coordinate axes
19. The Gini coefficient is calculated:
3) dividing the area of the figure located between the line of absolute equality and the Lorenz curve by the area of the triangle located under the line of absolute equality
20. To the main ones economic methods State income regulation includes:
a) tax policy;
b) price regulation policy;
c) regulation of the minimum wage;
21. Transfers are social payments:
3) from the state budget in the form of pensions, benefits, scholarships provided free of charge unilaterally
22. Establish a correspondence between sources of income and types of income.
Source of income Type of income
B 1) income for work done A. transfer payments
or opening hours
D 2) income on loan capital B. entrepreneurial income
D 3) income from the use of land B. wages
and other natural resources
B 4) income on entrepreneurial activity, G. rent
enterprise
A 5) income not related to work D. percent
23. The absolute poverty line is:
3) living wage
24. Only to social infrastructure relate:
1) housing and communal services;
3) education;
4) healthcare;
25. Social policy of the state is an element:
A) social protection.
26. A socially oriented economy is an economy where:
C) Economic development is aimed at solving social problems.
27. Functional distribution of income involves distribution between:
D) Labor and capital
28. What distribution of income does a market economy consider fair:
a) distribution through market mechanisms
29. Public policy income distribution in a market economy is aimed at:
d) reducing income inequality through redistribution
30. The most important element of social protection should be:
A) pension
C) payment for temporary disability
D) minimum wage
D) benefits for low-income groups of the population
Topic: “The State in a Market Economy”
1. Which of the following is one of the reasons that determined the need for government intervention in market economy?
b) the presence of a number of areas whose activities fall outside the scope of the market mechanism;
2. Which of the following areas is not covered by the market mechanism?
c) maintaining public order;
3. Which of the following requires government intervention in economic processes?
b) the possibility of economic crises
c) protection economic interests countries on the world market;
4. What is the main purpose of government intervention in the economy?
d) increasing the efficiency of the economy and providing conditions for the development of the social sphere.
5. What are the areas of government intervention in the economy?
a) ensuring rational organization money circulation in the country;
b) providing the population with public goods;
c) the need to regulate external effects;
6. Which regulatory methods are monetarist:
b) impact on money circulation
7. State regulation of the economy in a market economy:
c) designed to solve problems that the market mechanism is not able to solve
8. Select which of the following applies to economic functions states?
b) implementation of income redistribution;
c) support for entrepreneurship;
9. Which of the following is the direction of state regulation of a market economy:
a) regulation of income distribution
d) stimulation of investments
10. The state supports entrepreneurship and competition. What should it do to perform this function?
a) fight monopolies;
b) support small and medium-sized businesses;
11. In which sectors of the economy is the public sector most often represented:
b) in infrastructure
e) in the extraction of raw materials
e) in research and development.
12. In what areas economic activity Can a state enterprise participate?
c) in all areas;
13. There is a shortage of goods in the country, prices are rising. What should the state do:
b) Stimulate private investment in the creation of new production capacities
14. Which of the following is within the competence of the state to regulate the economy?
a) support for small and medium-sized businesses and the fight against monopolism
15. Why is state intervention in the social sphere necessary:
c) to provide the population with equal starting opportunities in obtaining education;
d) for guarantees in the field of pension provision.
16. Why is government intervention in the economy necessary:
b) to carry out functions that complement and improve the operation of the market mechanism;
17. What methods are used by the state to regulate the economy:
b) economic methods;
c) administrative methods;
18. Which of the following are among the tools for implementing legal methods of state regulation of the economy?
a) the constitution of the country;
b) laws on property and business activities;
d) tax code.
19. Why does the process of economic legislation require periodic adjustments?
a) because economic relations change and improve;
20. What is included in the set of administrative methods of state regulation of the economy?
a) prohibitive measures;
b) restrictive measures;
c) incentive measures.
21. Which of the following forms relate to economic methods of state regulation of the economy:
b) taxes
d) discount rate.
22. Which of the following refers to the characteristics of administrative methods of state regulation of the economy?
b) these are measures to permit, prohibit, coerce and limit the activities of economic entities;
23. If the state sets a price for an essential commodity below the equilibrium market price for it, then:
c) there will be a shortage of this product;
24. The Keynesian version of regulation means influencing primarily:
b) aggregate demand
25. What objectives does the use of administrative regulatory measures meet:
d) adjusts the market mechanism where and to the extent where it is impossible or ineffective to correct it using economic methods
26. Which of the listed methods relate to economic methods of regulating the economy?
a) export duties;
c) tax incentives
27. Which of the following could be the main goal of the short-term economic policy states?
c) a decrease in the inflation rate.
28. Which of the following is the main goal of the state's long-term economic policy?
c) economic growth.
29. How should the state influence monopolies:
d) should only control prices
30. Which of the following is developed by the state in a market economy to implement its economic policy:
c) program for the socio-economic development of the country
31. The need for government intervention in the market economy is due to:
c) the market does not solve a whole range of socio-economic problems
32. Through the development of state property, the state regulates:
b) knowledge-intensive production
d) production of public goods
33. Economic policies include:
b) development and implementation of comprehensive programs
d) stimulation.
Liked? Click on the button below. To you not difficult, and for us Nice).
To download for free Tests at maximum speed, register or log in to the site.
Important! All Tests presented for free download are intended for drawing up a plan or basis for your own scientific works.
Friends! You have a unique opportunity to help students just like you! If our site helped you find the right job, then you certainly understand how the work you add can make the work of others easier.
If the Test, in your opinion, is of poor quality, or you have already seen this work, please let us know.
1. The circular flow model illustrates
process of market price formation
interaction between Central Bank, commercial banks, bank depositors and those who borrow money from banks
relationships between the main economic entities
interaction of economic growth factors
2. From the definitions of “gross domestic product” proposed below, choose the best one. Gross domestic product is
the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country during a calendar year
the cost of all final goods and services purchased at market prices within the country during a calendar year
the market value of final goods and services produced by a country's residents during a calendar year
market value of a country during a calendar year
3. The income received by the owners of factors of production totals
gross national product
gross domestic product
disposable income
national income
4. A family’s purchase of a new house outside the city will affect the amount
net exports
government spending
investment costs
expenses for the purchase of consumer durables
5. Indicate which of the following indicators is equal to the value obtained by adding the net national product, depreciation charges and indirect taxes:
gross domestic product
gross national product
added value
net national income
6. To the group of indicators characterizing economic security countries include
GNP, GDP, NNP, GNI
service life of fixed capital, resource potential, scientific and technical potential, share of investment in GDP, level of state budget deficit
rate of capital accumulation in the industry, industry rate of profit, economic growth rate
share of external government debt in GDP, state gold and foreign exchange reserves, share of imports in domestic consumption, share of external borrowings in covering the budget deficit
7. National wealth is
natural resources and cultural values
natural resources and human resources
means of production, accumulated property, natural resources, material and cultural values
8. Personal disposable income is
accrued wages
received total income(salary and other income)
real income
total income received minus tax and non-tax mandatory payments
9. Of the listed statements, the following is true
the AD curve has a negative slope
when the state tightens conservation requirements environment, this leads to an increase in production costs per unit of output and shifts the aggregate supply curve to the right
growth in real output cannot be accompanied by rising prices
10. In a situation where the potential volume of GNP has not yet been reached, not all resources have been used, demand growth leads
to increase the supply of goods
to rising prices with constant supply
11. If the price level rises and production falls, this is caused
shift of the aggregate demand curve to the right
shift of the aggregate demand curve to the left
shift of the aggregate supply curve to the left
shift of the aggregate supply curve to the right
12. Keynesian segment on the aggregate supply curve
has a positive slope
has a negative slope
represented by a vertical line
represented by a horizontal line
13. If prices rise, then:
holders of fixed-price securities increase their expenses
the demand for money and the level of interest rates increases
interest rate sensitive expenses increase
holders of fixed-price securities have increased purchasing power
14. When the economy is in a depression, then in the short run an increase in AD will lead to
to higher prices, but will not affect GDP dynamics in real terms
to an increase in GDP in real terms, but will not affect the price level
to an increase in both the price level and the volume of GDP in real terms
to higher prices and a reduction in GDP in real terms
15. If prices are imported goods have grown, it is most likely caused by
reduction in aggregate supply
growth in aggregate supply
decline in aggregate demand
1. What is economic rent
transfer income
the excess of income over its opportunity cost
2. What is gross domestic product (GDP)
the sum of all goods and services produced
the sum of all goods and services sold
sum of all finished goods and services
the market value of all final goods and services
3. Nominal GNP is the value of goods and services measured
at current prices
in real prices
in prices of the base period
in prices of the previous period
4. Which of the following income or expenses is not taken into account when calculating GNP for a given year
growth of company reserves
servants' wages
5. To determine the amount of national income it is necessary
subtract the amount of indirect taxes from GNP
reduce the amount of GDP by the amount of depreciation of fixed assets used
subtract from the GDP the amount of depreciation charges for a given period, the amount of indirect taxes and the amount of government subsidies
add the amount of government social transfer payments to GDP
6. The source of personal income is
property income
income from rental housing
transfer payments
wages, property income, rental payments, transfer payments
7. GDP value depends on
quantity of goods produced
the amount of resources used in the production of goods
quantities of goods produced and their prices
price dynamics
8. GDP increased from 500 billion rubles. up to 600 billion rubles. GDP deflator increased from 125 to 150%. Real GDP value
Will not change
will increase
will decrease
cannot be calculated based on these data
9. To move from gross national product (GNP) to net national product (NPP), it is necessary
add net investment expenses
subtract net investment from GNP
add depreciation to GNP
subtract depreciation of fixed assets
10. Of the following income or expenses are not taken into account when calculating the GNP of a given year
rent for an apartment
buying car company bonds
growth of company reserves
servants' wages
11. Personal income is
cost of goods and services produced per year
income received by households during a given year
all income available for personal expenses after taxes
GDP minus depreciation
12. To calculate the contribution of a company to the created GDP, calculated production method, necessary from market value products sold subtract
all indirect taxes
retained earnings
depreciation
volume of materials purchased from other companies
13. The following value is not included in GDP calculated based on the amount of expenses
investments
net exports
public procurement of goods and services
salary
14. An increase in government spending increases real GDP only if
government spending is directed towards the purchase of goods and services, rather than remuneration of officials
government spending is accompanied by an increase in the money supply
government spending does not crowd out an equal amount of spending in the non-state sector
government spending is financed by issuing government loans
15. GNP calculated by the flow of expenses and GNP calculated by the flow of income are related as follows
GNP by income is equal to GNP by expenses
GNP by income is greater than GNP by expenditure in conditions of economic growth
the ratio between GNP by income and GNP by expenditure depends on the inflation rate for the period under review
all answers are correct
Last year, the authorities adopted a number of laws that will directly or indirectly affect the construction and purchase of housing.
Some laws have already come into force, others are yet to take effect this year.
Real estate market analysts believe that, taken together, all these legislative innovations cannot but affect the most important aspect for the end consumer – housing prices.
Vestum.RU tried to understand the diversity of opinions and create a clear picture of what is happening with prices in the real estate market today and what awaits them in the future.
Today the situation is such that the purchasing power of the population has decreased, since people's incomes are not increasing, so they are forced to save. This also applies to purchasing a home. People choose cheaper real estate, look for offers with the lowest price, fortunately, the supply market is wide and there is plenty to choose from. In addition, the economic situation in the country has led to people no longer considering residential real estate as an investment option. Maintaining housing is becoming more and more burdensome, including rising taxes and utility bills.
Experts believe that with the abolition shared construction, large investments in housing will disappear altogether. If previously it was possible to buy an apartment cheaply at the initial stage of construction, and then, when the house is built, sell it at many times more expensive, then this opportunity will disappear when switching to project financing.
The only option left was to buy ready-made apartments without finishing. Many large businessmen buy such apartments, renovate them, furnish them and resell them. But this will soon come to an end, because the Ministry of Construction is preparing a bill that is designed to ban the sale of housing without finishing.
Mortgages are gaining momentum
It is natural that there is an increase in home purchases. The reason is lower mortgage rates. According to statistics for last year, 2017, the number of people who took mortgage loans, increased by 25%. The authorities are focusing on mortgages; according to calculations, by 2030, 60% of the population will be able to get a mortgage. So far this is where everything is going. Banks cut rates, reduce an initial fee, the state has launched a program for families with two or more children, under which you can take out a mortgage at 6%. However, not all experts think this is good.
Some analysts believe that overly affordable mortgages will lead to rising real estate prices. Plus, not all citizens pay their mortgage regularly. This is the economic situation: today you work and can take out a mortgage, tomorrow you are fired, and there is nothing to pay. Experts believe that in an unstable economic situation giving out loans is dangerous and they recall the mortgage crisis in the United States in 2007.
By the way, banks are already concerned about this problem. Already at the end of last year, experts noted, banks began to approve less frequently mortgage loans, arguing this precisely by the growing number of non-payment of loans. Long-term delays in payments over the past year increased by more than 20 percent.
In addition, according to Sberbank forecasts, the demand for mortgage loans will only grow this year. Moreover, the situation in the sphere of state policy on this issue is favorable. So it became known that, for example, they want to cancel the down payment altogether. True, only young families will have such an opportunity. Such a project was invented in the Youth Parliament, and the creators intend to send it to the State Duma, the Russian government and the regions.
Now, in order to buy housing with a mortgage, young families must make 30% of the cost of the apartment as a down payment. Not everyone can save that amount. Therefore, according to parliament, this contribution can be abolished by distributing it between payments or raising the rate.
The President of Russia, as we said above, approved the program for families with children. Plus, he instructed officials to develop a strategy that will allow half of the population to buy housing with a mortgage by 2025.
Against this background, the Bank of Russia, summing up the results of last year, reported that mortgages are breaking all records: rates have reached a minimum, and the amount of loans issued, on the contrary, has increased noticeably. Therefore, it is logical to assume that banks will tighten requirements for borrowers.