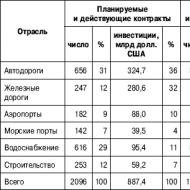
What is the main source of state income. Government revenues. characterize the concept of “property taxes”
Main sources of state revenue
Taxes are society's payment for the state's performance of its functions. This is the price we pay for the opportunity to live in a civilized country. We benefit from public goods.
Each of us relies on a state that can ensure national security, environmental protection, protection from external expansion, civil peace, good roads, access to education and healthcare and many other services. To perform its functions, the state needs funds, a significant part of which is generated from tax revenues.
Payment is made for the use of resources that belong to the state. The size of the fee depends on the size of the resources that are used. If the state loses ownership of them, then it also loses these incomes.
Deductions include special purpose payments. For example, enterprises contribute to road work, social insurance, the employment fund, and the fund for liquidating the consequences of the Chernobyl disaster.
This money must be used strictly for its intended purpose:
- maintenance and repair of roads,
-social insurance,
-liquidation of the consequences of the Chernobyl accident.
Budget revenues also include a group of so-called non-tax payments.
For example, income from the sale of confiscated property, from the privatization of state property, interest for the use of temporarily free budget funds, receipt of dividends from business activities carried out by enterprises formed with the participation of the state.
Taxes occupy a major place in the state revenue system, making up the largest portion of central budget revenues in all countries. Our state is no exception.
The social purpose of taxes is manifested through their functions:
fiscal and regulatory.
The fiscal function of taxes is to mobilize funds available to the state as centralized financial resources, used to perform government functions.
With the strengthening of the role of the state, the importance of the regulatory function of taxes increases. This function lies in the fact that taxes influence the activities of business entities. With an increase in taxes, the economic activity of business entities, as a rule, changes.
The use of taxes for regulatory purposes is a rather complex process, depending on the correct solution of many issues, in particular:
Establishing the size of tax rates, determining the timing of their payment, providing tax benefits, applying penalties for violation of tax legislation.
Income from all sources and activities is subject to income tax. But only income from hired labor and self-employment is subject to payroll tax. The proceeds from this tax are used to finance social measures protection of the population (old-age pensions, disability pensions, unemployment benefits, large families, etc.). This article budget revenues in all countries is, as a rule, second (after income tax) by the volume of resources brought to the budget. Income tax and payroll tax are direct taxes.
The payroll tax does not belong to the progressive, but to the proportional type of taxation. Proportional tax is a tax that is levied in an equal percentage on any level of income (for example, 20% on any amount - 100 rubles, 1 thousand rubles, 10 thousand rubles, 100 thousand rubles, etc. ).
Regressive taxation is tax withdrawal in which taxes take away a smaller and smaller portion of income as income increases. Since some taxes do not apply to certain low levels income, insofar as it turns out that, in percentage terms, a relatively smaller share is levied as tax on high incomes. Following the 1986 tax reform in the United States, for example, the marginal tax rate was 33%, applied to income between $71,900 and $149,250, and a rate of 28% applied to income above $149,250.
One of the universal taxes around the world is the sales tax, which is levied on a huge range of consumer purchases of goods and services. The tax imposed on certain specific goods (tobacco products, alcoholic beverages) is called excise tax. Excise taxes are a special case of sales tax. Sales tax and excise taxes are indirect taxes; they are “hidden” in the price of goods and services. Property tax is the main source of revenue for local authorities in many countries. This type of tax causes especially many social conflicts. Firstly, it is considered too onerous after the payment of income taxes, social taxes, sales taxes, etc. (like the last straw that overflows the cup of patience). Secondly, in order to collect it, you need to evaluate the property, which is done by a special service, which often allows a lot of abuse. This tax has one more feature - it is levied regardless of whether the owner of real estate and other property has any income or not. Consequently, it constitutes one of the foundations of the autonomous part of taxes (G - C1 T0), i.e. taxes that can be levied when there is no income at all.
Firms' accounting profits are subject to corporate income tax. Corporate income is generally subject to progressive taxation. This tax can stimulate investment through borrowed resources rather than through the firm's capital. This is because no adjustments are typically made for the factors of production owned by the firm itself and the equity capital invested by the firm's owners. A company that uses borrowed funds for investment will have to pay interest, which it will deduct as its costs from its accounting profit and the amount of its tax liability. If the same company uses its share capital for investment (that is, increases its share capital through additional issue of shares), then interest costs will not appear in the financial statements. Therefore, although there is an opportunity cost (lost benefit) of capital, whether it is created by investing through debt or issuing equity, only the interest on the debt reduces a firm's tax liability.
Some government revenue is not generated by taxes. The state can force consumers (individuals or legal entities) to pay for goods and services provided to them by the authorities. Local authorities provide utility, transport, medical, sanitary and other services that are produced by firms owned or licensed by the authorities, but in any case generating income from payments for these services by users. When choosing between taxes and direct payments for public goods provided by governments, economists prefer the latter because it provides better information about whether consumers value the value of those goods more than the costs of producing them.
Finally, a significant source of financial resources to cover government spending are government loans leading to the emergence and increase of public debt. Deficit is the difference between income and expenses in given year, i.e., an incremental variable. Public debt - the gross volume of unredeemed government valuable papers on this moment time, i.e. a variable reflecting the “stock” of unfulfilled obligations. Since the excess of government expenditures over revenues is equal to the amount of the new government loan (i.e., the increase in public debt), the deficit in a given year is equal to the increase in debt in the same year. Thus, the budget deficit is an increase that is equal to an increase in the “stock” of already accumulated debt.
Directions for spending funds from the Social Insurance Fund
Russian Federation
According to Art. 39 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation, everyone is guaranteed social security by age, in case of illness, disability, loss of a breadwinner, for raising children and in other cases established by law. Part of these payments is made from the Fund's funds social insurance of the Russian Federation, which carries out its activities in accordance with the Regulations on the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation, approved
by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 12, 1994 N 101.
The main task of the Fund is to provide state-guaranteed benefits for:
temporary disability;
pregnancy and childbirth;
at the birth of a child;
caring for a child until he reaches the age of one and a half years; for burial;
for sanatorium-resort treatment and health improvement of workers and members of their families.
The Fund's resources are generated from insurance contributions from employers (administrations of enterprises, organizations, institutions and other economic entities, regardless of their form of ownership). Federal law"On the tariff of insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation, the State Employment Fund of the Russian Federation and compulsory medical insurance funds for 1997" for employers and citizens using the labor of hired workers,
a single tariff for insurance contributions to the Social Insurance Fund has been established Russian Federation in the amount of 5.4 percent in relation to accrued wages for all reasons.
Unlike other extra-budgetary funds, the payment of all types of benefits from the funds of the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation is carried out directly through the accounting departments of policyholders at the place of work of citizens against the due insurance contributions. And only in certain exceptional cases, the assignment and payment of state social insurance benefits are made by the executive bodies of the Fund.
The standard for spending funds on paying all types of benefits to policyholders is not established. Expenses for sanatorium and resort services for employees and members of their families are made within the limits of the standard established for policyholders by the executive bodies of the Fund. The size of the standard cannot be less than 10 percent of accrued insurance premiums. To provide sanatorium and resort services, the funds of insurers with up to 300 employees are centralized in the executive bodies of the Fund without fail; more than 300 people - with the consent of the policyholder.
The balance of funds over actual social insurance expenses is transferred to the executive body of the Fund, where the organization is registered as an insurer, for subsequent redistribution among other policyholders who, for some reason, have overspent funds, that is, the principles of solidarity of policyholders in the formation and expenditure of funds apply state social insurance.
If actual expenses exceed the amount of accrued insurance premiums, the policyholder does not have the right to suspend the payment of state social insurance benefits. If policyholders do not have enough funds to pay benefits and resort treatment and rehabilitation, the executive bodies of the Fund cover the resulting deficit of funds.
In accordance with Art. 10 of the Regulations on the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation, responsibility for the correct accrual and expenditure of state social insurance funds rests with the administration of the policyholder represented by the manager and chief accountant. From representatives of the enterprise administration (personnel department employees, accounting department and others) and trade unions, members of the labor collective, on the basis of decisions of general meetings (conferences) of the labor collective, commissions for social
insurance or social insurance commissioners are elected to monitor the correct calculation and timely payment of social insurance benefits. Commissions or commissioners for social insurance also decide on the expenditure of funds for sanatorium treatment and recreation of workers and members of their families, and the distribution of insured vouchers.
All controversial issues between employees and employers regarding the provision of benefits are considered by the executive bodies of the Fund (department or its branch) at the place of registration of the employer as an insurer, by the central office of the Fund or in court.
State social insurance funds may be spent only for the purposes established by federal laws, the Regulations on the Fund, in accordance with the Fund’s budget, budgets and estimates of the Fund’s executive bodies, approved in the prescribed manner.
The bulk of the Fund's funds are used to pay benefits to working citizens:
for temporary disability;
for pregnancy and childbirth;
a one-time benefit for women registered in medical institutions in the early stages of pregnancy;
lump sum benefit for the birth of a child;
monthly benefit for the period of parental leave until the child reaches the age of one and a half years;
social benefit for funeral.
The most common type of social insurance provision is temporary disability benefits. It is issued in cases of illness or injury to an employee, caring for a sick family member, quarantine (when the employee is suspended from work by the sanitary and epidemiological service), placement in a hospital at a prosthetic and orthopedic enterprise, etc.
The intended purpose of this type of benefit is to compensate for earnings lost due to the onset of temporary disability. Currently, the amount of this benefit depends on the length of continuous work experience and ranges from 60 to 100 percent of actual earnings. For a number of categories of workers, it is issued in the amount of full earnings, regardless of continuous work experience. In the event of a work injury or occupational disease, temporary disability benefits are issued in the amount of 100 percent of earnings.
Maternity benefits are issued for the period the woman is granted leave for this reason. Unlike benefits for temporary disability, this benefit in all cases is paid to working women in the amount of full earnings, regardless of any conditions.
The fundamental document for the appointment and payment of these types of benefits is the Regulations on the procedure for providing benefits for state social insurance, approved by the resolution of the Presidium of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions of November 12, 1984 (with subsequent amendments and additions made by the Presidium of the Council of the All-Union Communist Party as of April 15, 1992) and currently in force, taking into account the regulations adopted in the subsequent period related to the provision of these types of benefits.
In addition to maternity benefits, women who register with medical institutions in the early stages of pregnancy (up to 12 weeks) are assigned and paid a benefit in the amount of the minimum wage established by federal law on the day maternity leave is granted.
In order to compensate, to a certain extent, for the costs of purchasing items to care for a newborn, a one-time benefit is paid upon the birth of a child in the amount of fifteen times the minimum wage established by federal law on the child’s birthday. One of the parents or a person replacing him has the right to this benefit. In the event that both parents do not work, this benefit is assigned and paid by the social protection authorities at the place of residence. But wherever these payments are made, that is, at the place of work or place of residence, the source of financing for these payments is the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation.
etc.................
State budget: concept, structure. Relationship state budget and GDP
An important tool government regulation economy is the state budget. The state budget - this is the balance of government income and expenditure for a certain period of time (usually a year), which represents the main financial plan of the country, which, after its adoption by the legislative body (parliament, State Duma, Congress, etc.) acquires the force of law and is binding.
In carrying out its functions, the state incurs numerous expenses. By purpose, state expenditures are divided into:
- political spending : ensuring national defense and security (maintaining the army, police, courts, etc.), maintaining the state administration apparatus;
- expenses for economic purposes : maintenance and ensuring the functioning of the public sector of the economy, assistance (subsidies) to the private sector of the economy;
- expenses for social goals : social security (payment of pensions, scholarships, benefits), education, healthcare, development of fundamental science, environmental protection.
From a macroeconomic point of view, all government expenditures are divided on the:
- state procurements goods and services (their value is included in GDP);
- transfers (their value is not included in GDP);
- interest payments on government bonds(servicing public debt).
The main sources of state revenue are :
- taxes (including social security contributions);
- profits of state-owned enterprises;
- seigniorage (income from the issue of money);
- proceeds from privatization.
The difference between government revenues and expenditures is government budget balance . Wherein, the state budget can be in three different states :
- when budget revenues exceed expenditures, the budget balance is positive, which corresponds to a surplus or surplus of the state budget;
- when revenues equal expenses, the budget balance is zero, that is, the budget is balanced;
- When budget revenues are less than expenditures, the budget balance is negative, that is, there is a government budget deficit.
There is an optimality interval - optimal budget share in gross domestic product (GDP) , the achievement of which ensures maximum rates of economic growth. With a high share of the state budget in GDP economics
However, this rule is only true up to a certain point. If the share of government spending in GDP is so small that it does not allow the government to effectively perform its functions, then this may have a negative impact on economic development.
Budget is a specific detailed plan for the collection and use of resources by economic agents for a certain period.
- a document describing the income and expenses of a particular state, usually for the year (from January 1 to December 31).
Functions of the state budget:
- Regulates the cash flows of the state, strengthens ties between the center and the subjects of the federation
- Legally controls government actions
- Provides information about government intentions to economic participants
- Defines parameters economic policy and sets the framework for possible government actions
Due to the special importance of the state budget for all areas economic life its drafting, approval and implementation take place at the level of laws. At the same time, the state budget itself is law.
Almost every economic institution (enterprise, firm, sector of the economy, bank, economic and financial funds, etc.) has a plan for collecting income and using expenses. All socio-political institutions (government organizations, political parties, etc.) also have budgets.
The state budget serves as a prerequisite and financial base functioning of the state and its implementation of those functions that society has authorized it to perform. With the help of the budget, issues of financial regulation are resolved at the macro level and throughout the economy. Economic significance The budget lies in the fact that it forms a significant part of the final demand (at the expense of its funds, most of the income from the population is generated, large volumes of products are purchased, and state reserves are created). Significant financial flows pass through the budget; it directly influences the formation of important economic indicators(Fig. 27):
State budget revenues - final stage cash flows, coming from the real sector and other large areas financial relations, and state budget expenditures are the starting point for the movement of state resources for the needs identified by the state and society (Fig. 28).

- Volume of production
- Investments
- Real income

The state budget is the country's basic financial plan, which has the force of law.
Budget is a way of redistribution cash income population, enterprises and others legal entities in the interests of financing government and other public expenditures.
State budget revenues:
- Taxes on income of legal entities and individuals
- Revenues from the real sector (income tax)
- Receipt of indirect taxes and excise taxes
- Duties and non-tax charges
- Regional and local taxes
State budget expenditures:
- Industry
- Social politics
- Agriculture
- Public Administration
- International activity
- Defense
- Law enforcement
- The science
- Healthcare
Balanced Budget- a budget in which the ratio of income and expenses is equal.
If income and expenses in the budget differ, then there is a budget deficit or surplus.
State budget funds are spent in areas and in amounts determined by federal law, laws and other regulatory legal acts of government entities. State budget expenditures can be classified according to various signs, the most important of which is financing state of their functions: economic, social, defense etc.
From federal budget The following expenses are financed:- maintenance of government bodies;
- national defense;
- science funding;
- financing of the real sector;
- formation of state reserves;
- servicing and repayment of public debt (internal and external);
- regulation of the financial potential of state entities (federal or unitary).
- state support for industries (construction, Agriculture, transport, communications);
- ensuring law enforcement activities;
- ensuring fire safety;
- science and socio-cultural events.
The basic principle of delimiting expenses between budgets is their adequacy with the powers assigned to the corresponding level of government.
Budget expenditures are also divided according to the principle of their participation in the process of expanded reproduction.
Based on the principle of participation in the process of expanded reproduction budget expenses are divided into current And capital expenditures.
Current expenses- This:
- maintenance of government, management and law enforcement agencies;
- current expenditures on defense, science, social sphere;
- separate compensation expenses by economic sectors.
Capital expenditures are divided into:
- New construction;
- reconstruction of important state and municipal property.
Among priority State budget expenditures are divided into:
- social expenses;
- military spending;
- maintenance of the judicial system;
- education and healthcare.
Therefore, part of the country is transferred to the ownership and disposal of the state in the form of various cash payments and receipts. As a result, it has its own and, i.e. government revenues. They are the property of the Federation and its subjects. They are administered by the relevant government authorities. In addition, they have their own income municipalities. These are municipal (local) revenues, the disposal and management of which is carried out by.
State revenues- this is part of the country’s national income, circulated in the process of its distribution and redistribution through different kinds cash receipts into the ownership and disposal of the state in order to create the financial base necessary to fulfill its tasks in implementing socio-economic policy, ensuring the defense and security of the country, as well as for the functioning of government bodies.
Municipal(local) income are also part of the national income and serve to create a financial basis local government, are used to resolve issues of local importance based on the interests of the population of the relevant territory.
Government revenues are credited to various state monetary funds - in different levels, off-budget target government funds. Municipal (local) revenues go, accordingly, to municipal monetary funds - and. Part of the income remains at the disposal of state or municipal enterprises.
Classification of state revenues
The current system of state and local revenues in the Russian Federation is based on the principle of unity. It is expressed in the fact that the legislation of the Russian Federation defines the types of state and local revenues, the principles of their distribution between the Federation, its constituent entities and municipalities. Therefore, if appropriate sources are available, the same types of cash receipts are used everywhere in the country.
Composing unified system, government and local revenues classified into groups. The classification can be based on various characteristics that reflect the most significant features of state and local revenues.
Thus, the classification of state revenues by socio-economic basis gives the most complete picture of their sources, the connection of income with various forms of ownership, and the effectiveness of the latter in generating state revenues. In accordance with this feature, the following revenues are distinguished in the revenue system of the state and municipalities:
- from the state or municipal economy, resulting mainly from the production activities of state or municipal enterprises, as well as from the use of property and natural resources state or municipal entities (for example, forests, reservoirs, other natural resources, from the privatization of state and municipal property);
- from enterprises and organizations of non-state forms of ownership (taxes, fees, other payments);
- from joint ventures, foreign enterprises and organizations operating in the Russian Federation;
- from the personal income of citizens.
Depending on the territorial level income is divided into:
- federal;
- income of the subjects of the Federation;
- local revenues of municipalities.
Depending on the legal features and legal form Among the income of the state and municipalities, one can distinguish payments and receipts:
- tax;
- non-tax.
There are signs of obligation and individual gratuitousness in legal form, regularity of receipts from a certain taxable object. However, more diverse in forms and methods of collection are not tax payments and receipts. As mentioned above, they can be mandatory or voluntary.
If we take into account procedure for the formation and use of state and municipal (local) revenues, then they can be divided into two groups:
- centralized;
- decentralized.
Decentralized state (and local) revenues - These are the incomes of state (and municipal) enterprises and organizations that remain at their direct disposal and are used by them independently for production and social needs. Mainly, this is part of the profits of enterprises. The funds of enterprises related to state or municipal property are assigned to such enterprises and belong to them by right economic management or operational management, as well as other property assigned to them (Articles 114, 115 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). After paying taxes, the enterprise independently disposes of its profits and other income at its disposal.
TO centralized(at different territorial scales) income include income concentrated in state and local budgets and the same extra-budgetary funds. It is these incomes that the Civil Code of the Russian Federation refers to the federal state treasury, the state treasury of the constituent entities of the Federation, the municipal treasury, and distinguishes them from the funds assigned to state and municipal enterprises.
Revenue sources of government and local budgets, as a rule, do not have a special purpose. This allows them to be directed at the appropriate time to the most important, priority needs of society to finance the planned programs.
Features of the formation of state revenues
Non-tax revenues play an important role in the formation of state and municipal revenues. They differ from taxes in the peculiarities of the forms of payments and methods of attracting them to the disposal of the state and municipalities, the content of the rights and obligations of payers, on the one hand, and state authorities and local self-government, on the other.
Non-tax revenues states and municipalities - this is the income received at their disposal from the use of state and municipal property and the activities of state authorities and local self-government, payments of an equivalent and punitive nature, as well as funds raised on a voluntary basis.
Unlike taxes, non-tax revenues can be not only mandatory, but also voluntary payments. In particular, state and municipal lotteries are held on a voluntary basis, serving as a source of income for the state and municipalities, issuing state and municipal securities, raising funds for state and municipal extra-budgetary funds and institutions in the form of charitable activities, etc.
Non-tax payments of a mandatory nature, unlike taxes, are characterized by a certain remuneration, since their collection is conditioned by granting the payer the right to carry out any activity (license fees), receive legally significant services (registration fees), to use public or municipal property(rent), etc. Therefore, payers have the right to demand from government or municipal authorities performing actions, providing services, etc. related to this payment. Moreover, such payments may have a specific purpose, i.e. be spent on the object for the use of which they were paid (payments for the use of natural resources).
Attracting funds at the disposal of the state and municipalities on a contractual, voluntary and repayable basis is becoming increasingly important. Among them, an important role belongs to the institutions of state and municipal credit, including state and municipal loans, and insurance institutions.
On a voluntary basis, the state and municipalities raise funds through lotteries.
Lottery- a form of voluntary attraction of funds from the population through sales lottery tickets, in which part of the funds raised is played out in the form of cash or in-kind winnings and paid to the owners of the winning tickets.
Legal regulation of lotteries in the Russian Federation is carried out in accordance with the Federal Law of the Russian Federation of November 11, 2003 “On Lotteries”, which came into force on January 1, 2004. According to this Law lottery - a game that is held in accordance with the agreement and in which one party (the lottery organizer) draws the lottery prize fund, and the second party (the lottery participant) receives the right to win if it is recognized as a winner in accordance with the terms of the lottery.
State revenues are represented by that part of financial relations that is associated with the formation of financial resources at the disposal of the state (represented by its various structures) and state enterprises.
Financial resources accumulated by the state are classified as centralized income, while those remaining at the disposal of state-owned enterprises are classified as decentralized.
- Centralized state revenues are formed mainly from tax revenues, income from foreign economic activity, payments from the population.
- Decentralized government revenues are formed from cash income and savings of the enterprises themselves.
In the composition of centralized state revenues, the main place is occupied by budget revenues, through which the solution of economic and social problems of the development of society is ensured.
Centralized state revenues also include government resources off-budget funds: social insurance, pension, employment fund, etc.
Objects budgetary relations are profit and wage, tax payments from which are the source of budget revenues. The object of state credit relations are the temporarily free financial resources of enterprises (organizations, institutions) and the savings of the population.
The main source of government revenue is national income. But sometimes, especially during periods of emergency (war, major natural disaster, etc.), previously accumulated national wealth can act as a source of government revenue.
All sources of government revenue can be divided into two groups - internal and external.
- Internal government revenues include national income and national wealth created within the country and used by the state to perform its inherent functions.
- External government revenues include national income, and in exceptional cases, the national wealth of another country if they are borrowed in the form of government loans or received in the form of reparation payments.
Income composition
The composition of government revenues is largely determined by the methods by which the state accumulates the necessary funds. cash. In conditions market economy The main methods of mobilizing government revenues are taxes (in their various forms), loans and emissions. The totality of all types of state revenues makes up the state revenue system, which is designed to solve not only fiscal, but also economic problems - to stimulate the growth of production and increase its efficiency, influence the distribution of productive forces throughout the country, and help accelerate scientific and technological progress.
Taxes
They occupy a central place in the state revenue system. They are a universal and at the same time initial category that expresses the basic properties of finance. It is in the conditions of functioning of a market economy tax form becomes predominant in common system financial relationships. Taxes have fiscal, economic and social significance.
Government loans
Not only used for coating budget deficit, but also to ensure various capital expenditures, especially in terms of investing funds in the public sector of the economy. Between taxes and government loans There is a close connection, determined by the fact that the financial basis for repaying loans is taxes.
Emission
It is the third method of mobilizing government revenues, and not only paper money, but also credit. The state resorts to emission only if tax and loan revenues do not cover growing government expenses, and financial market a situation is developing that is unfavorable for issuing new loans.