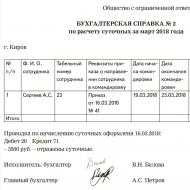
The procedure for calculating local taxes and fees is established. The procedure, methods and timing of tax payment. General characteristics of local taxes
Today the state uses the most different ways collection of compulsory tax payments, such as a pledge of property, seizure of taxpayer's property, penalty interest, suspension banking operations, surety, etc. However, not everyone knows what these methods can generally be, how they are accepted and in what situations they are used.
Below are the main methods that are used today.
- Source of income. Here, the payer does not receive the entire amount of income in his hands, but only part of it - what remains after withholding the payment established by the tax office.
- Declaration. When using such methods, the payer in deadlines submits to the official tax return, where he indicates all his obligations.
- The cadastral method has nothing to do with profitability. Who does not know, the cadastre is a special register. It includes a list of typical objects that are classified according to various external characteristics. The main function of the inventory is to establish the average profitability of the taxable object.

Tax payment procedure
All payment methods and procedures are regulated by Article 58 of the RF Tax Code. So, you can pay the entire amount at once or apply some other procedure provided for in this article and others. legislative actsthat relate to tax charges. In doing so, it is important that the amount to be paid is transferred by you or your authorized person within the specified period. The calculation itself can be either non-cash or cash.
Article 58 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The procedure for paying taxes and fees. Article text for download

Tax return
This is a written statement drawn up by the payer in order to indicate all his income and expenses, list the sources of profit, available benefits, the amount of tax and other important information regarding taxation. 
Order dated November 25, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11 / [email protected] Download text
Typically, you must submit such a return separately for each of the taxes payable, provided that nothing else is required by law. The tax inspectorate does not have the right to demand anything other than compliance with the requirement for the payment procedure, so you should not indicate something in the declaration that is not directly related to the issue. 

Note! The declaration should be submitted within the timeframes specified in Article 229 of the Tax Code - that is, before April 30 of the year that follows the reporting year. In other words, for the 2015 reporting year, for example, the declaration must be submitted by the end of April 2016.

Property pledge
When the timing of the fulfillment of obligations related to taxation is changed, it is possible to secure such an obligation through a pledge. A pledge agreement can be drawn up between you, that is, the taxpayer, and the relevant authority. Although it should be added that, according to the legislation, the pledger can be not only a citizen who is obliged to pay taxes, but also his authorized representative. If the payer fails to fulfill its obligations, the tax authorities have the right to resort to measures that are approved by the current Civil Code of the Russian Federation. 
What property can be mortgaged?
Any property in respect of which, according to civil law, it (pledge) can be established can serve as a pledge. The only exceptions are those items that are already a pledge in other contracts (in other words, you cannot use, say, a car as a pledge for a bank and tax office simultaneously). 
Note! After the conclusion of the pledge agreement, the property can be held by both the payer and tax service... What is typical, the transfer of property should be carried out only at the expense of the mortgagor, moreover, only he is responsible for its safety.
And all transactions related to the pledged property, until the full repayment of the debt, can be carried out exclusively by mutual agreement.
Surety

When changing the deadlines for which you should have time to use one of the payment methods, a surety can act as a guarantee that the obligations will be fulfilled. In such cases, the guarantor is responsible to the fiscal authorities for the payment of tax fees if the payer has not paid the required amount and the corresponding penalty within the specified time frame. A surety can only be issued in accordance with the requirements of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
If the payer fails to comply with his tax obligations, that is, if he does not pay the required amount on time, he will bear responsibility together with the guarantor, and the debt will be collected forcibly in court. But if the obligations of the surety are fulfilled in accordance with the contract, then he has the right to recover from the payer the refund of the money paid and penalties on them, as well as losses incurred during the surety.
Basic requirements for a surety
The role of the guarantor can be played by physical. or legal. a person, and for a specific duty there may be several of them at once. The procedure for surety in in this case regulated by the same The Civil Code, although it should be added that the provisions of this normative act may also apply to the payment of fees.
Penalty
Penalty interest means a certain accrued amount of money that the payer undertakes to pay in case of late payment tax contributions (by the way, this also includes payments that are obligatory when transporting various goods across the border of the Russian Federation).
Note! According to the law, penalty interest must be paid in addition to the main tax amount, regardless of what other measures to ensure the fulfillment of obligations are used, or from the liability provided for various kinds of violations of the law.
Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Penalty. Download file
In what cases is the default interest not charged?
It is calculated for each day of delay, and the calculation is made from the next after the last day of payment established by the authorities. However, for such arrears that the person did not pay due to the freezing of transactions on his bank accounts according to a court decision, or fiscal authority, penalty interest cannot be charged. The same applies to situations where the payer's property is seized. Here, the penalty will not be charged until these circumstances cease to exist.
However, a penalty will be charged if:
- you have applied for an installment plan;
- you are / are seeking to obtain an investment loan.
Features of the accrual procedure
Penalty is charged as a percentage of the amount owed, and separately for each overdue day. The interest percentage should be 1/300 of the Central Bank refinancing rate that is in effect at the time of accrual. 
Penalty interest can be paid both at one time, together with tax, and after all debts have been paid in full. In addition, the penalty is actively used as a way to collect customs taxes by collecting money from the payer's accounts or his property. We also add that the provisions of Article 48 apply to individuals, and Article 46 of the Tax Code applies to individual entrepreneurs, organizations and tax agents.
Is it possible to evade taxes?
There are many sophisticated methods by which you can evade taxes. Let's take a quick look at the most common methods. 
The most popular way is considered to be the use of fly-by-night businesses, which provide organizations with significant tax benefits. Such enterprises are created with the aim of obtaining deductions for some taxes or fictitious expenses, or, alternatively, to increase the added value of products and reduce the total tax burden.
Another option is that the entire product is driven through a series of such fly-by-night, as a result of which its value increases, and the fictitious firms immediately disappear along with their tax liabilities... If you carefully read the practice of the Higher arbitration court, then we can conclude: in most cases, the management of a one-day company, which has abdicated responsibility, is completely released from it (provided that due diligence has been exercised); which means that the responsibility will therefore fall on the end user.
As a result, we emphasize that any tax fraud is almost always a violation existing laws... People who use the methods described above or other methods must understand what the consequences of such actions may be.  Be aware of liability for fraudulent activities and tax evasion
Be aware of liability for fraudulent activities and tax evasion
Video - What can be the threat of tax evasion?
The procedure for calculating and paying taxes of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is provided for taxpayers-organizations, individual entrepreneurs and individuals.
Taxpayer organizationscalculate the tax base based on the results of each tax period based on register data accounting and (or) on the basis of other documented data on objects subject to taxation or related to taxation.
Individual entrepreneurscalculate the tax base based on the results of each tax period on the basis of data on the accounting of income and expenses and business transactions in the manner determined by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of the Russian Federation for Taxes and Duties.
Other taxpayers are individualscalculate the tax base on the basis of data on taxable income received in accordance with the established procedure from business entities, as well as data own accounting taxable income, carried out in arbitrary forms.
Deadlines for payment of taxes and fees are set for each tax and charge. (Article 57 of the Tax Code) The deadlines for the payment of taxes and fees are determined by the calendar date (for example, land tax - September 15, November 15) or the expiration of a period of time calculated in years, quarters, months, weeks and days, as well as an indication of an event that should occur or occur, or an action that should be performed.
Payment of taxmade by a one-time payment of the entire amount of tax or in another manner provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and other legislative acts on taxes and fees within the established time frame.
When paying a tax (due) in violation of the payment deadline, the taxpayer pays a penalty interest in accordance with the legally established procedure.
In the practice of most states, the following forms of tax collection have been formed:
1) at the source;
3) at the time of spending the income;
4) in the process of consuming goods and services.
Withholding tax is levied prior to the receipt of income by the taxpayer. Responsibility for the incorrect calculation of the tax amount, as well as its untimely payment, lies with the tax agent. An illustrative example: the established practice of withdrawing personal income tax at the time of receiving wages.
Tax collection on tax return involves the taxpayer filling out the declaration on his own.
A vivid illustration of the principle of levying taxes at the time of spending income is the payment by the buyer as part of the price of the goods of indirect taxes: sales tax (USA, Russia), value added tax (Russia, France, Italy), excise taxes.
An example of the implementation of the principle - in the process of consuming a product or service - is the transport tax.
Federal taxes.
All taxes of the Russian Federation in accordance with the state and budget device by level of action are divided into: federal; regional; local.
In addition to being attached to the relevant budget, the following are the signs of tax classification by exemption levels: the level of tax legislation, the scale of territorial applicability.
It is the last two criteria that are used when dividing taxes in the tax system of the Russian Federation according to the levels of exemption into federal, regional and local taxes.
Federal - these are taxes and fees established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (at the federal level) and obligatory for payment throughout the territory of the Russian Federation.
In accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, federal taxes and fees include:
1) value added tax (VAT);
2) excise taxes;
3) corporate income tax;
4) personal income tax;
5) water tax;
6) unified social tax;
7) state duty;
8) tax on the extraction of minerals;
9) fee for the right to use objects of animal world and aquatic biological resources.
The main ones are: VAT, income tax, personal income tax.
Main federal tax - VAT (indirect tax).
His payers are both organizations and individual entrepreneurs... Are not payers who have switched to special regimes (simplified tax and imputed tax).
Object of taxation - sale of goods (works, services) on the territory of the Russian Federation.
The tax base - the cost of goods sold.
Tax rates - 0% (for export operations), 10% (main food products and children's products), 18% (other, until 2004 - 20%)
Taxable period - quarter.
Calculation and payment procedure - calculated based on the results of each tax period as the difference between the total tax calculated on the basis of the tax base and the corresponding tax rate minus the amount of tax deductions (the amount of VAT paid when purchasing goods - "input VAT").
Payment terms - by the 20th day of the next month after the tax period.
Income tax.
His payers only organizations, including foreign ones, act. Are not payers who have switched to special regimes (simplified tax and imputed tax).
Object of taxation - profit (financial result).
The tax base - the difference between income and expenses.
Tax rates - 24%
Taxable period- calendar year; reporting period - 1st quarter, 1st half, 9 months.
Calculation and payment procedure - calculated based on the results of reporting periods, advance payments are made.
Payment terms - by the 20th day of the next month for the reporting period.
Personal income tax.
Taxpayers - all individuals, including residents and non-residents (less than 183 days a year in the Russian Federation). Are not payers of ind. entrepreneurs who have switched to special regimes (simplified n / a and imputed tax).
Object of taxation - income received by an individual.
The tax base - monetary value of income subject to taxation minus tax deductions (standard, social, property, professional).
Tax rates - 13% basic, 30% on dividends, income received by non-residents, 35% on winnings and material benefits.
Taxable period- calendar year.
Calculation and payment procedure - for hired employees, it is calculated, withheld and transferred to the budget at the source of payment (by the employer - tax agent); ind. entrepreneurs pay on their own according to the declaration.
Payment terms - by a tax agent no later than the day of actual receipt of funds from the bank for salary payments; an individual entrepreneur - no later than July 15 of the year following the expired tax period.
Taxes of the subjects of the Russian Federation.
By regional taxes and fees established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation are recognized, which are binding on the territories of the corresponding constituent entities of the Russian Federation and are credited to regional and local budgets.
When establishing a regional tax, the legislative bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation determine the following elements of taxation: tax rates within the limits established by the Tax Code, the procedure and terms payment of tax, as well as reporting forms for this regional tax. Other elements of taxation are established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. When establishing a regional tax by the legislative bodies of the subjects Russian Federation tax benefits and grounds for their use by the taxpayer may also be provided.
In accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, regional taxes include:
1) tax on property of organizations;
2) transport tax;
5) tax on gambling business.
Corporate property tax.
Tax payers - organizations, incl. foreign ones with a separate balance sheet and fixed assets on the balance sheet.
Tax object - movable and real estate organizations accounted for as property, plant and equipment.
The tax base - the average annual cost of fixed assets.
Tax rate - up to 2.2 percent.
Taxable period - calendar year; reporting period - 1st quarter, 1st half, 9 months.
Calculation procedure: OS cost per 01.01.+01.02.+….+01.12.+31.12 *2,2%
Payment term - quarterly, no later than 30 days after the reporting period.
Privileges - Privileges are granted to public organizations of disabled people, religious organizations, housing and communal services facilities and the social sphere, etc.
Transport tax.
His payers - organizations and individuals with registered vehicles.
Object of taxation - vehicles: cars, motorcycles, buses, airplanes, helicopters, motor ships, yachts, snowmobiles, snowmobiles, motor boats, and other water and air vehicles. Not subject to taxation: fishing sea and river vessels; passenger and cargo sea, river and aircraft, for the implementation of passenger and (or) cargo transportation; agricultural machinery used in agricultural work for the production of agricultural products; etc.
The tax base - 1) in relation vehiclehaving engines - as engine power in horsepower;
2) in relation to water vehicles for which the gross tonnage is determined - as the gross tonnage in registered tons; 3) in relation to water and air vehicles not specified in subparagraphs 1 and 2 of this paragraph - as a unit of a vehicle.
Tax rates - fixed rates in absolute value (rubles) to horse power etc.
Taxable period- calendar year.
Calculation and payment procedure - organizations calculate the amount of tax on their own, tax authorities calculate the amount of tax for individuals on the basis of information from the authorities that carry out state registration of vehicles in the territory of the Russian Federation.
Payment terms - payment is made by n / payers at the location of vehicles in the manner and terms established by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (in the Omsk region - for organizations - until March 15 of the next year (with advance payments on a quarterly basis), for individuals - until July 15.
Privileges - established for certain categories of payers.
Gambling business tax.
Taxpayers - organizations or individual entrepreneurs operating in the gambling business.
Object of taxation - a gaming table, a slot machine, a sweepstakes office, a bookmaker's office.
The tax base - the total number of relevant objects n / a.
Taxable period- calendar month.
Tax rates - fixed rates in absolute value (rubles) per unit of the object n / a (for 1 machine, table, etc.).
Calculation procedure - the tax amount is calculated by the payer independently as a product tax base, established for each object of n / a, and the tax rate established for each object of taxation.
Payment terms - no later than the deadline for filing a tax return for the relevant tax period (by the 20th day of the next month).
Local taxes and fees.
Local taxes and fees are established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and regulatory legal acts of the representative bodies of local self-government, operate on the territory of the corresponding MO and go to local budget.
When the local tax is established by the representative bodies of local self-government, the following elements of taxation are determined in regulatory legal acts: tax rates within the limits established by the Tax Code, the procedure and terms for paying the tax, as well as reporting forms for this local tax. Other elements of taxation are established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. When establishing a local tax, representative bodies of local self-government may also provide for tax benefits and grounds for their use by the taxpayer.
Regional or local taxes and (or) fees that are not provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation cannot be established.
Local taxes and duties include:
1) land tax;
2) tax on property of individuals.
Local taxes and fees are the MO budget's own revenues.
Individual property tax.
Taxpayers - individuals, owners of property recognized as an object of taxation.
Object of taxation - residential buildings, apartments, summer cottages, garages and other buildings, premises, structures.
The tax base - the total inventory value of the property.
Tax rate - established by local governments in the form of% differentiated from the value of the property within the limits set by federal law (up to 300 thousand rubles - 0.1%, from 300 to 500 thousand rubles - from 0.1 to 0.3%, over 500 thousand rubles - from 0.3 to 2.0%).
Taxable period - calendar year.
Calculation procedure - the tax authorities calculate on the basis of information from the authorities that carry out state registration of property in the territory of the Russian Federation, as of January 1 of each year.
Privileges - established for certain categories of payers.
The tax is credited to the local budget at the location (registration) of the taxable object (property).
1. The payment of tax is made by a one-time payment of the entire amount of tax or in another manner provided for by this Code and other acts of legislation on taxes and fees.
2. The amount of tax to be paid shall be paid (transferred) by the taxpayer or tax agent within the established time frame.
3. In accordance with this Code, it may be envisaged to pay preliminary tax payments - advance payments during the tax period. The obligation to pay advance payments is recognized as fulfilled in the manner similar to the payment of tax.
In the event that advance payments are made at a later date than those established by the legislation on taxes and fees, penalties shall be charged on the amount of untimely paid advance payments in the manner prescribed by Article 75 of this Code.
Violation of the procedure for calculating and (or) making advance payments cannot be considered as grounds for bringing a person to responsibility for violation of the legislation on taxes and fees.
4. Tax payment is made in cash or without cash.
In the absence of a bank, taxpayers (tax agents) who are individuals, can pay taxes through the cashier of the local administration or through the organization of the federal postal service.
In this case, the local administration and the organization of the federal postal service must:
accept funds for payment of taxes, correctly and timely transfer them to budget system Of the Russian Federation to the corresponding account of the Federal Treasury for each taxpayer (tax agent). In this case, the admission fee money not charged;
keep records of the funds received for payment of taxes and transferred to the budgetary system of the Russian Federation for each taxpayer (tax agent);
to issue receipts to taxpayers (tax agents) when receiving funds, confirming the receipt of these funds. Form of receipt issued local administration, approved by the federal executive body authorized for control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees;
submit to the tax authorities ( officials tax authorities), at their request, documents confirming the receipt from taxpayers (tax agents) of monetary funds for payment of taxes and their transfer to the budget system of the Russian Federation.
Funds received by the local administration from a taxpayer (tax agent) in cash, within five days from the date of their receipt, must be deposited with a bank or a federal postal organization for transfer to the budget system of the Russian Federation to the appropriate account of the Federal Treasury.
In the event that, due to a natural disaster or other force majeure circumstance, the funds received from the taxpayer (tax agent) cannot be deposited within the prescribed period in the bank or the federal postal organization for their transfer to the budget system of the Russian Federation, the specified period extended until such circumstances are eliminated.
For non-fulfillment or improper fulfillment of the obligations provided for in this paragraph, the local administration and the organization of the federal postal service are liable in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The application of measures of responsibility does not relieve the local administration and the organization of the federal postal service from the obligation to transfer to the budgetary system of the Russian Federation the funds received from taxpayers (tax agents) for the payment and transfer of taxes.
5. The specific procedure for paying the tax is established in accordance with this article with respect to each tax.
Payment procedure federal taxes established by this Code.
The procedure for paying regional and local taxes is established, respectively, by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and regulatory legal acts of representative bodies municipalities in accordance with this Code.
6. The taxpayer is obliged to pay tax within one month from the date of receipt of the tax notification, unless a longer period of time for tax payment is specified in this tax notification.
In case of recalculation tax authority of the previously calculated tax, the payment of tax is carried out according to the tax notification within the time period specified in the tax notification. Wherein tax notice must be sent no later than 30 days before the due date specified in the tax notification.
Article 58. Procedure for payment of taxes, fees, insurance premiums
1. The payment of tax is made by a one-time payment of the entire amount of tax or in another manner provided for by this Code and other acts of legislation on taxes and fees.
2. The amount of tax to be paid shall be paid (transferred) by the taxpayer or tax agent within the established time frame.
3. In accordance with this Code, it may be envisaged to pay preliminary tax payments - advance payments during the tax period. The obligation to pay advance payments is recognized as fulfilled in the manner similar to the payment of tax.
In the event that advance payments are made at a later date than those established by the legislation on taxes and fees, penalties shall be charged on the amount of untimely paid advance payments in the manner prescribed by Article 75 of this Code.
Violation of the procedure for calculating and (or) making advance payments cannot be considered as grounds for bringing a person to responsibility for violation of the legislation on taxes and fees.
4. Payment of tax is made in cash or non-cash form.
Individuals can pay taxes through the cash office of the local administration or through the organization of the federal postal service in the absence of a bank, as well as through the multifunctional center for the provision of state and municipal services, in which, in accordance with the decision of the supreme executive body of state power of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation, the possibility of receiving from the specified persons of funds for the payment of taxes and their transfer to the budgetary system of the Russian Federation.
Information about changes:
Article 58 is supplemented with clause 4.1 from January 1, 2019 - Federal Law of July 29, 2018 N 232-FZ
4.1. In the case specified in paragraph two of clause 4 of this article, the local administration, the organization of the federal postal service and the multifunctional center for the provision of state and municipal services are obliged to:
1) accept monetary funds from individuals for the payment of taxes, transfer them correctly and in a timely manner, taking into account the provisions provided for in paragraph 4.2 of this article, to the budget system of the Russian Federation to the corresponding account of the Federal Treasury for each taxpayer (tax agent). At the same time, no fee is charged for receiving funds and transferring them to the budgetary system of the Russian Federation;
2) keep records of monetary funds accepted for payment of taxes and transferred to the budgetary system of the Russian Federation for each taxpayer (tax agent);
3) issue receipts or other documents confirming the receipt of these funds upon receipt of funds. The form of the receipt issued by the local administration is approved by the federal executive body authorized for control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees;
4) submit to the tax authorities (officials of the tax authorities), upon their requests, documents confirming the receipt of monetary funds from individuals in payment of taxes and their transfer to the budgetary system of the Russian Federation.
Information about changes:
Article 58 is supplemented with clause 4.2 from January 1, 2019 - Federal Law of July 29, 2018 N 232-FZ
4.2. Funds received from an individual in cash by the local administration, within five days from the date of their receipt, must be deposited with a bank or a federal postal organization for transfer to the budget system of the Russian Federation to the appropriate account of the Federal Treasury.
Funds received from an individual in cash by a federal postal service organization or a multifunctional center for the provision of state and municipal services, as well as received from a local administration in cash by a federal postal service organization, within five days from the date of their receipt, must be deposited with the bank for their subsequent transfer to the budgetary system of the Russian Federation to the corresponding account of the Federal Treasury.
In the event that, due to a natural disaster or other force majeure circumstance, the funds received from an individual cannot be deposited within the prescribed period in a bank or a federal postal service for their transfer to the budget system of the Russian Federation, the specified period is extended until elimination such circumstances.
Information about changes:
Article 58 is supplemented by clause 4.3 from January 1, 2019 - Federal Law of July 29, 2018 N 232-FZ
4.3. For non-fulfillment or improper fulfillment of the duties provided for in clauses 4.1 and 4.2 of this article, the local administration, the organization of the federal postal service, the multifunctional center for the provision of state and municipal services are liable in accordance with this Code and other legislative acts of the Russian Federation.
The application of measures of responsibility does not relieve the local administration, the organization of the federal postal service, the multifunctional center for the provision of state and municipal services from the obligation to transfer to the budget system of the Russian Federation the funds accepted for the payment and transfer of taxes.
Information about changes:
Article 58 is supplemented with clause 4.4 from January 1, 2019 - Federal Law of July 29, 2018 N 232-FZ
4.4. In case of failure to transfer to the budget system of the Russian Federation to the appropriate account of the Federal Treasury within the prescribed period of time, the funds of an individual received by the local administration, the federal postal organization or the multifunctional center for the provision of state and municipal services, to the local administration, the organization of the federal postal service, the multifunctional center for the provision of state and municipal services, measures are taken to collect the unlisted amount of tax in accordance with subparagraph 1 of paragraph 2 of Article 45 of this Code, as well as in a manner similar to the procedure established by this Code.
The requirement to transfer the tax to the budgetary system of the Russian Federation (hereinafter in this article - the requirement to transfer the tax) must be sent to the local administration, the organization of the federal postal service or the multifunctional center for the provision of state and municipal services no later than three months from the date of identification of the non-transferred to the budget the system of the Russian Federation of the amount of tax and the preparation by the tax authority of a document on the identification of the amount of tax not listed by the local administration, the organization of the federal postal service or the multifunctional center for the provision of state and municipal services to the budget system of the Russian Federation.
The requirement to transfer the tax by the local administration, the federal postal organization or the multifunctional center for the provision of state and municipal services is recognized as the notification of the relevant body, organization about the unlisted amount of tax, as well as about the obligation to transfer this amount of tax within the prescribed period.
5. The specific procedure for paying the tax is established in accordance with this article with respect to each tax.
The procedure for paying federal taxes is established by this Code.
The procedure for payment of regional and local taxes is established, respectively, by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and regulatory legal acts of the representative bodies of municipalities in accordance with this Code.
The taxpayer is obliged to pay tax within one month from the date of receipt of the tax notification, unless a longer period of time for paying tax is specified in this tax notification.
In case of recalculation by the tax authority of the previously calculated tax, the tax shall be paid on the basis of the tax notification within the time period specified in the tax notification. In this case, the tax notification must be sent no later than 30 days before the due date specified in the tax notification.
PROCEDURE FOR PAYMENT OF TAXES (Dues) - the procedure for making or transferring tax payments to the budget; one of the main elements of taxation that must be defined in an act of legislation on taxes and fees in order to be considered established. The rules for establishing the procedure for paying tax (collection) are established in Art. 58 NK. The payment of tax is made by a one-time payment of the entire amount of tax or in another manner provided for by the Tax Code and other acts of legislation on taxes and fees. The amount of tax to be paid is paid (transferred) by the taxpayer or tax agent within the established time frame. Tax payment is made in cash or non-cash form. In the presence of a bank, a taxpayer or individuals who are individuals can pay taxes through the cash office of a village or settlement local government body or through the communications organization of the RF State Committee for Communications and Informatization. The specific procedure for the payment of tax is established in relation to each tax. The procedure for paying federal taxes is established by the Tax Code. The procedure for paying regional taxes and local taxes is established, respectively, by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and regulatory legal acts of representative bodies of local government in accordance with the Tax Code. These also apply to the procedure for paying fees.
Encyclopedia of Russian and International Taxation. - M .: Jurist... A. V. Tolkushkin. 2003.
See what the "TAX PAYMENT PROCEDURE" is in other dictionaries:
Procedure and conditions for granting a deferral in payment of tax and duty - a deferral or installment plan for the payment of tax is a change in the deadline for paying the tax, if there are grounds provided for by this article, for a period of one to six months, respectively, with a lump sum or step-by-step payment ... ...
The procedure and conditions for the beginning and termination of the application of the simplified taxation system (STS), established in Art. 346.13 NK. Organizations and individual entrepreneurs who have expressed a desire to switch to the simplified tax system submit from October 1 to November 30 ... ...
PAYMENT OF TAXES - (English tax payment) - the fulfillment of obligations imposed on the taxpayer to pay taxes (fees) in the manner prescribed by the current legislation. The taxpayer is obliged to independently execute the CC, unless otherwise provided ... ...
COLLECTION OF TAXES - (English collection of taxes) - the procedure for payment and collection of taxes (fees) established by tax legislation. Payment of tax in accordance with Art. 23 and Art. 52 part one Of the Tax Code RF (1998 with amendments 1999 and 2000) is imputed to ... ... Financial and credit encyclopedic dictionary
Payment of taxes and fees - is made by a one-time payment of the entire amount of tax or in another manner provided for by the Tax Code of Russia and other acts of legislation on taxes and fees. The amount of tax to be paid is paid (transferred) by the taxpayer or tax ... ... Encyclopedic dictionary of the head of the enterprise
HARMONIZATION OF TAXES - (English tax harmonization) - systematization and unification of taxes, coordination of tax systems and tax policies of countries belonging to international regional groupings and associations. G.N. first began to be carried out in the late XIX - early. XX century ... Financial and credit encyclopedic dictionary
Old order - History of France Portal France ... Wikipedia
Defined in Art. 12 15 parts of the first NK. These articles are introduced from the date of the entry into force of part two of the Tax Code, before that the types of taxes and fees in the Russian Federation are determined by Art. 19 21 of the Law on the Basics tax system... In accordance with the Tax Code in the Russian Federation, ... Encyclopedia of Russian and International Taxation
The criteria used to group taxes (fees, duties and other mandatory payments) and tax revenues in order to develop tax policies of states, tax and budget statistics, analyze the structure of tax ... ... Encyclopedia of Russian and International Taxation
CLASSIFICATION OF TAXES - (English tax classification) - grouping of taxes by type. Due to decomp. the basics of classification: by the method of collecting taxes, by the subject of the taxpayer; the nature of the rates applied, tax incentives; source and object of taxation; ... ... Financial and credit encyclopedic dictionary
Books
- Regional and local taxes. Tutorial. Grif UMC Professional textbook, Kosov Mikhail Evgenievich. The existing in the Russian Federation procedure for the calculation and payment of regional and local taxes by organizations and individuals has been generalized and systematized from the standpoint of the current tax ...