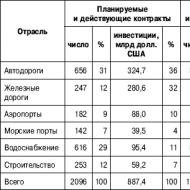
For which Sberbank withdraws 450 rubles. Sberbank is quietly stealing money from the card. How much does it cost to service a Sberbank Visa Classic card?
Description of the pharmacy warehouse operation
The pharmacy warehouse is located inside the warehouse terminal and is part of it. The warehouse is divided into several boxes (each box is intended for a specific Client). Each box has the following rooms:
· main storage area (at room temperature);
· cool room (temp. +12+15);
· refrigerator (+2+8);
· acceptance and unpacking room (goods are accepted, inspected, counted and prepared for transportation to the required storage area);
· forwarding area (goods selected for shipment are placed here, they are also inspected and counted).
Directly at the entrance to the pharmacy, electric catchers for flying insects are located above the ceiling. Rodent traps are distributed around the perimeter of each box. Thermo-hygrometers are also distributed along the perimeter of the main storage area (to take into account temperature and humidity conditions). According to the thermohygrometer, it is located in the cool zone, refrigerator, reception and unpacking area and expedition area.
The main subprocesses performed by personnel in a pharmaceutical warehouse when working with medicines the following:
· Upon acceptance of goods: unloading the vehicle, inspection and counting of goods, paperwork, preparation of goods for movement to storage areas, movement through storage areas;
· When shipping the goods: inspection and registration of a vehicle arriving for loading, moving goods to the loading area, checking the selected order, loading goods into a vehicle, preparing shipping documents.
· When completing an order: acceptance of the “request for cargo transportation”, execution of the commission sheet, selection of the order, verification of the order, movement to the expedition zone.
· During storage: cleaning premises, maintaining cleanliness on pallets with products, checking temperature and humidity conditions, participating in inventories.
The technological flow diagram for the circulation of medicines in the warehouse can be seen in Fig. 1.5.1.
Requirements for pharmacy wholesale warehouses
From the regulatory documents listed in section 1.3., the main requirements for wholesale pharmacy warehouses were identified, failure to comply with which poses a threat to the safety of storage of medicines, that is, low-quality goods may fall into the hands of the end consumer.
Fig.1.5.1
A. Requirements for warehouse premises.
· be spacious for unpacking and storage;
· provide reliable protection against theft and pollution/contamination;
· be provided with sufficient illumination to create normal working conditions;
· have separate rooms for storing disinfectants, detergents, materials and equipment for cleaning;
· operate at a certain temperature and humidity (check frequency at least once a day, records must be kept in logs);
· be provided with the required number of racks, pallets, cabinets.
· include areas: reception and main storage, which are separated from each other, rooms for medicines that require special conditions storage, forwarding.
B. When receiving finished products.
· Protection of incoming medicines from exposure to precipitation, dust, solar radiation, and mechanical damage;
· medicines requiring special storage conditions are identified and stored in the prescribed manner;
· defective medicines are placed in a special area;
· returned products are accepted only into the quarantine zone.
B. Storage of finished products.
· must be carried out in such a way as to minimize the possibility of reducing the risk of deterioration in quality;
· must be provided in appropriate conditions;
· storage of medicines without a marketing authorization must be carried out under the conditions established by the manufacturer ( finished products placed in “quarantine”);
· defective products must be marked accordingly and stored in a special area;
· storage should be carried out depending on the physical and physico-chemical properties, method of application, pharmacological group, physical state, taking into account expiration dates;
· carrying out continuous visual monitoring during storage of the condition of the container and external changes in medicines (at least once a month);
· carrying out measures to combat rodents and insects;
· stacking of goods on pallets should not exceed 1.5 meters.
D. Release of finished products/transportation.
· it is prohibited to dispense medicines that have become unusable and are illegal copies;
· transport containers must protect medicines from exposure to precipitation, dust, solar radiation, and mechanical damage;
· in closed Vehicle ah/containers, taking into account the rules for the transportation of goods in force on the relevant mode of transport;
· taking into account the requirements specified in the documentation for specific types of medicines.
D. Personnel requirements.
· must take part in classes on topics related to personal hygiene, industrial sanitation, and safety;
· must wear special clothes and shoes;
· Must be trained to properly follow process instructions.
In the process of moving goods from the manufacturer of pharmaceutical products to the consumer, most of the time (approximately 80 - 90%) is spent on the storage process. Therefore, the organization of warehouses occupies an important place in the system of movement of goods. A pharmacy warehouse is organized for the purpose of supplying pharmaceutical organizations, medical institutions and other organizations and enterprises with medicines, medical products and other goods.
The main tasks of a pharmaceutical warehouse are receiving, storing and dispensing to pharmacies, medical institutions and other organizations, as well as pharmaceutical manufacturing enterprises Medicines, medical devices, pharmaceutical equipment and supplies that meet all quality requirements and current legislation.
In accordance with the main objectives, the pharmacy warehouse performs the following functions:
concludes contracts with suppliers;
purchases pharmaceutical goods and medical products;
conducts claims and lawsuits, imposes penalties on suppliers in case of violation of contractual obligations;
accepts drugs and medical devices from suppliers in terms of quality, quantity and cost;
organizes the storage of drugs and medical devices, taking into account their physical and chemical properties and the requirements of the State Fund;
ensures the safety and accepts orders from pharmacies, treatment and prevention and other institutions, as well as pharmaceutical enterprises, completes and timely delivers medicines and medical products;
organizes strict adherence to the procedure for accounting and dispensing pharmaceutical, parapharmaceutical and other goods;
exercises control at all stages of production activities using its various types;
ensures control over expiration dates during storage and shipment of medicines and medical devices, over their timely sale taking into account expiration dates, as well as over compliance with price discipline during delivery and settlements with suppliers and consumers;
complies with occupational health and safety requirements.
To perform the main functions, managers and personnel of a pharmacy warehouse are required to comply with regulatory documents regulating its activities, study supply and demand in the pharmaceutical market, comply with the procedure for certification of drug quality control, and preparation of relevant documentation.
Regulatory documents determined pharmaceutical requirements requirements for a pharmacy warehouse:
general provisions, where the conditions for wholesale sales are given (availability of premises, equipment, inventory, licenses, etc.);
requirements for premises and equipment for wholesale trade, which list the warehouse requirements for composition and size, as well as the main groups of equipment and instruments, placement of shelving in the warehouse; the procedure for receiving medicines into the warehouse and releasing them from the warehouse, which provides recommendations for organizing the work of the warehouse receiving department, the acceptance area, and preparing accompanying documentation for the shipment of goods; procedure for organizing the storage of drugs;
ensuring quality at a drug wholesale trade enterprise, the need for regular internal inspections and the appointment of a person responsible for compliance with the rules for the wholesale trade of drugs (quality officer).
Regulatory documents define the pharmaceutical requirements for a pharmacy warehouse: certain room sizes; appropriate layout of premises; organization of goods movement; organization of packaging works; storage organization various groups Medicines and medical devices. The pharmacy warehouse must be located in a room that meets the volume of work performed, sanitary, hygienic and fire safety requirements, ensuring the complete safety of valuables. The warehouse can be located in a separate building (structure), in the structure of the building (except for pharmacies of medical institutions) on a lease basis or other rights that do not contradict the law. A pharmacy warehouse should be an isolated block of premises with a separate entrance and access roads.
The warehouse must have a centralized water supply, sewerage, heating and supply and exhaust ventilation systems. The external design must contain a sign indicating the organizational and legal form and operating hours of the warehouse.
pharmacy warehouse sign
JSC "PHARMA-XXI century"
PHARMACY WAREHOUSE
Opening hours: daily
from 9-00 to 19-00
seven days a week
A wholesale trade enterprise can be located in separate buildings or in isolated premises within the structure of the building included in non-residential fund. In this case, the warehouse must be isolated from other premises, have separate entrance, access area and ramp for unloading goods. When a warehouse is located in a medical or pharmacy building, administrative and amenity premises may be shared with hospital or pharmacy buildings.
Composition and dimensions of pharmaceutical warehouse premises
To organize the movement of medical goods within a pharmacy warehouse, it is necessary to have main production premises and zones: reception (reception department);
main storage (including cold room and picking area); expeditionary.
To unload incoming goods, it is advisable to have a loading and unloading ramp that provides protection for cargo and loading and unloading mechanisms from precipitation. The length and width of the ramp must correspond to the cargo turnover and capacity of the warehouse. It is advisable to provide insulated boxes and doorways with air thermal protection for unloading vehicles.
Loading and unloading operations in the reception area (reception department) are carried out using overhead cranes and electric forklifts. It is advisable to install a conveyor belt extending from the receiving department to the body of the unloading vehicle. In the reception department it is necessary to provide areas:
unloading, unpacking and sorting of arriving goods;
temporary storage of domestically produced medicines;
temporary storage imported goods;
movement and placement of mechanization and transportation means;
checking medicines (solutions, including injections) for the absence of mechanical impurities;
temporary storage of goods for which a complaint has been made;
storage of containers (empty pallets).
Reception department must be isolated from other premises, but be interconnected with the main storage areas for medicines.
In storage rooms, drugs can be placed: on racks, on standard pallets in factory containers, on stockpiles, in containers of elevator racks (small goods).
The number of storage rooms depends on the groups of medicines that require isolated placement. Traditionally, regardless of the volume of work of the warehouse, it provides the following storage departments: dry medicines, liquid medicines, finished medicines, sanitary and hygiene products, dressings, poisonous and narcotic drugs (if there is a license for their storage).
On an expedition The following main areas must be provided:
To place goods prepared for shipment;
for the movement of mechanization equipment (transport);
for storing internal warehouse vehicles;
sanitary and household.
Completed orders must be shipped through a special area (box). In this case, doorways should be equipped with a thermal curtain to create comfortable working conditions.
Administrative and service premises are calculated according to current regulatory materials depending on staffing table with inclusion:
office of the head of the pharmacy warehouse;
operational accounting premises;
wardrobe
The pharmacy warehouse must be provided with equipment and inventory in accordance with the functions performed.
Exemplary equipment list pharmaceutical warehouse:
racks, pallets, stockpiles;
refrigeration chambers;
means of mechanization of loading and unloading operations;
instruments for recording air parameters;
wooden and metal cabinets (safes);
work tables and chairs;
cabinets for separate storage of special and outerwear and shoes;
disinfectants and equipment to ensure sanitary conditions.
The warehouse is managed by a specialist with a pharmaceutical education (certified) and with at least three years of work experience. The number of specialist jobs depends on the nature of the work performed. Production activities (purchase, reception, storage, wholesale sales of drugs and medical devices, etc.) are carried out by specialists with pharmaceutical education (at least two years).
On March 1, 2017, the new “Rules of Good Practice for the Storage and Transportation of Medicines for Medical Use” came into force, approved by order Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 646n dated August 31, 2016. These rules also apply to drug wholesale trade organizations, that is, for pharmaceutical(wholesale) warehouses. The new requirements cover several aspects.
Firstly, the number of zones into which the warehouse must be divided has increased. Now there are six of them:
a) area for receiving medications;
b) main storage area;
c) expedition zone;
d) storage area for medicines requiring special conditions;
e) storage area for identified falsified, substandard, counterfeit medicines;
f) quarantine zone (for medicines returned to the organization, for medicines received in damaged containers, without accompanying documents, and also subject to withdrawal from civil circulation).
Also if you want to store and carry out wholesale trade dietary supplements, then it is necessary to allocate a seventh storage zone.
One of the main and serious innovations is the introduction of mandatory temperature mapping. At its core, warehouse mapping is about identifying the coldest and hottest spots, as well as the point where the maximum temperature fluctuation occurs. These measurements are initially carried out in an empty warehouse for at least 24 hours at intervals of 5–15 minutes; the number of temperature sensors is determined individually for each warehouse. That is why doesn't seem to be it is possible to carry out the procedure without specialized equipment. Based on the mapping results, critical control points for the empty warehouse are determined, where equipment used to record temperature and humidity is placed. The second stage involves mapping the warehouse loaded with products. Repeated measurements are carried out within 72 hours. The warehouse fill volume should be as large as possible to simulate the worst case in terms of obstructing air flow distribution, usually more than 60%. Based on the results of repeated measurements, critical control points for a warehouse with products are determined, at which, if they differ from those previously determined in an empty warehouse, additional equipment is placed to record temperature and humidity.
Also unchanged is the constant maintenance of temperature conditions in the zones, carried out by the warehouse manager or pharmacist. Temperature and humidity are recorded daily, including weekends and holidays. It must be remembered that the registration log is stored for 2 years. Therefore, you are required to provide 2 years of records of daily temperature records in the warehouse at any inspection
from Roszdravnadzor. Also during periodic inspection from territorial Roszdravnadzor body checks the procedure for drawing up accompanying documents for medicinal
drugs. The new rules established a list of information required to be present in each accompanying document. The list of required equipment has also increased in pharmaceutical warehouse Now it includes not only security and fire alarms, refrigerators, air conditioners and thermohygrometers (psychrometers) or other equipment used to record temperature and humidity. Now the equipment includes a ventilation system (which means the presence technical passport and permanent
Maintenance
) and access control systems.
The second main innovation of the new rules is the introduction of a quality system. The warehouse manager ensures the implementation of the quality system (QMS), which should ensure that:
a) the movement of medicinal products between subjects of circulation of medicinal products, including within a warehouse, ensures storage and (or) transportation in compliance with all requirements;
b) the responsibility of warehouse workers for violation of requirements for the reception, transportation, and placement of medicines (hereinafter referred to as standard operating procedures (SOPs)) is determined;
c) medicinal products are delivered by the subject of medicinal products circulation within the time period agreed with the recipient of medicinal products in compliance with all requirements; d) documentation of any actions in the warehouse and the results achieved is carried out during the implementation or immediately after completion of the SOPs; e) in relation to each violation of the requirements established by SOPs, internal audit
The head of the warehouse is a person responsible for implementing and ensuring the quality management system, monitoring the effectiveness of the quality system and bringing SOPs into compliance.
If after reading this article you still have any questions about preparing a pharmaceutical warehouse for the licensing procedure, you can always contact the experienced team of United lawyers. We can help not only in obtaining a license for the wholesale trade of medicines from Roszdravnadzor, but also in obtaining a sanitary certificate from Rospotrebnadzor!
Asafieva Polina,
lawyer, licensing specialist
United Lawyers group.
Lecture No. 1. Pharmacy warehouse - as a wholesale trade enterprise. Tasks and functions of a pharmacy warehouse. Structure of a pharmacy warehouse. Features of pharmaceutical wholesalers. Consignment warehouse
Pharmacy warehouse
Wholesale trade of drugs - professional activity organizing wholesale trade for the provision of pharmaceutical work and services, and the stage of bringing drugs and medical devices from the manufacturer to pharmaceutical organizations.
A pharmacy warehouse is a pharmaceutical division of a wholesale trade organization designed to perform pharmaceutical work and services.
The main tasks of a pharmacy warehouse are:
Reception of goods.
Storage and distribution to pharmacies, medical organizations and other organizations of pharmaceutical products.
Distribution of equipment and supplies for pharmaceutical production.
To accomplish the main tasks facing the wholesale distribution chain, pharmacy warehouses are created, which operate independently or are structural divisions distributor.
The pharmacy warehouse performs the following functions:
Concludes supply agreements with suppliers.
Purchases pharmaceutical goods and medical devices.
Conducts claims and lawsuits (in case of loss of goods during transportation).
Submits penalties to suppliers (in case of violation of contractual obligations).
Receives drugs and medical devices from suppliers based on quality, quantity and cost.
Organizes the storage of drugs and medical devices, taking into account their physical and chemical properties.
Ensures safety.
Receives orders from pharmacy organizations. Health care facilities, pharmaceutical enterprises. Provides packaging and timely delivery of drugs and medical devices.
Organizes strict adherence to the procedure for accounting and release of goods, exercises control at all stages of production activities using its various types.
Ensures control over expiration dates, timely sale of goods taking into account expiration dates, pricing during delivery and settlements with suppliers and consumers.
Compliance with occupational health and safety requirements.
Warehouses are designed for receiving, placing and storing goods received at them, preparing them for consumption and release to the consumer. They are one of the most important elements in logistics channels, since the objective need for specially equipped places for storing inventories exists at all stages of the movement of material flow.
Pharmacy warehouses are located in separate buildings that meet sanitary requirements, as well as licensing requirements for the wholesale trade of drugs.
A pharmacy warehouse must be located in a room that meets the volume of work performed, sanitary, hygienic and fire safety requirements, ensuring the complete safety of valuables; it must have centralized water supply, sewerage, heating, and supply and exhaust ventilation systems.
A warehouse is a specially equipped isolated room for the main production, utility and auxiliary purposes of a wholesale trade enterprise.
A pharmaceutical warehouse must be isolated from other premises, have a separate entrance, an access area and a ramp for unloading goods.
The part of the warehouse intended for receiving, sorting, storing, assembling, issuing and shipping goods belongs to warehouse premises for the main production purpose. These premises include receiving rooms, storage departments, refrigeration chambers, packaging, picking, and forwarding (delivery of goods to the pharmacy).
Utility warehouses are designed to accommodate auxiliary services and perform maintenance work on the technological process. The utility rooms include rooms for storing packaging materials, technological equipment, inventory and containers.
Auxiliary warehouse premises are used to house control apparatus and utility premises:
Offices of the control apparatus.
Dining room.
Health center
Sanitary facilities.
Stairwells.
Tambours.
The area of all premises constitutes the total area of the warehouse.
During the movement of goods from producer to consumer, most of the time, approximately 90%, is spent on the process of storing goods. A pharmacy warehouse is organized for the purpose of supplying drugs, medical devices and other goods to pharmacy organizations, medical organizations, other organizations.
In accordance with the Law of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 1222n “On approval of the rules of wholesale trade,” organizations can sell drugs or transfer them in the manner prescribed by law:
Drug wholesale trade organizations.
Pharmacy organizations with a license for pharmaceutical activities.
Individual entrepreneurs with a license for pharmaceutical activities.
Medical organizations.
Pharmaceutical manufacturers.
All drugs registered in the Russian Federation are subject to wholesale trade.
Trade in counterfeit drugs is prohibited. Wholesale trade of drugs is carried out in the presence of a license for pharmaceutical activities with the indication “wholesale trade of drugs”. The license for wholesale trade is issued by Roszdravnadzor.