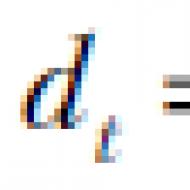Codes of standard social tax deductions
For example, the amendments introduced new code 2002 for awards, paid for production results and other similar indicators provided for by the norms of the legislation of the Russian Federation, labor or collective agreements. IN in this case We are talking about bonuses that are not paid out of funds net profit organization, and not at the expense of special purpose funds or targeted revenues. Also, a new income code 2003 was introduced for remunerations paid from the organization’s net profit, special purpose funds or earmarked proceeds.
In addition, the order introduced new codes for standard deductions.
Federal Tax Service Order No. ММВ-7-11/633@ came into force on December 26, 2016 and this means that from this date (December 26, 2016) you can use new income codes and it is not advisable to use excluded deduction (income) codes. At the same time, the order is not a direct indication that the tax agent must urgently make changes to the accounting policy regarding personal income tax accounting, since only the Tax Code of the Russian Federation contains the responsibilities of a tax agent.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation requires the tax agent to independently classify the payments he makes, i.e. Whether a specific amount should be taken into account with income code 2002 (or 2000) is determined by the tax agent in his accounting policy. Therefore, you should change the classification of income or information about the right to deductions from the moment a new one appears. accounting policy, which is usually approved for the next year.
Thus, in the 2-NDFL certificates for 2016, based on the amendments to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation effective from January 1, 2016 and the new order of the Federal Tax Service:
- deductions for guardians of disabled children should be separated from deductions for parents of disabled children and shown with new codes (133, ...)
- previously taken into account deductions for “parents” are, if possible, shown with new codes (126, ...)
In addition, based on the new order of the Federal Tax Service, in certificates for 2016 it is allowed to use separate deduction codes for guardians of “healthy” children (130, 131, etc.) and new income codes (2002, 2003, ...).
According to experts from the 1C company, revision of accounting data registered before December 26, 2016 is not required.
How to change personal income tax codes in the 1C: Salaries and Personnel Management 8 program in 2017
In 2017, it is imperative to change the bonus coding. You can do the following:
1. define in local regulations expected bonuses and introduce new types of payment with new codes
2. leave the previous accruals, changing the income codes in them, having previously protected the documents from re-posting by the date of prohibition of editing.
The new income code is indicated in the payment type card on the tab Taxes, contributions, accounting ( Fig.1 )

As for deduction codes, in 1C accounting solutions, deduction codes for parents are replaced automatically when updating the program while maintaining the history (Fig. 2).
For example, instead of 114, code 126 is set. Similarly, deduction codes for guardians of disabled children will be automatically changed if these codes were introduced in the programs at the beginning of 2016 (code 117 will be replaced by 133, etc.). Only the deduction codes for guardians of children (non-disabled) indicated in the directory need to be reviewed and corrected manually Employees – Applications for personal income tax deductions information about deductions.

The program will add new codes for children's deductions to 2-NDFL certificates for 2016.
Personal income tax deduction codes in 2015–2016: table
To make the task easier for accountants who keep records of employee income, personal income tax amounts withheld and transferred to the budget, and who carry out the procedure for calculating preferential amounts for income tax from employees, we have placed a current table in our article deduction codes for personal income tax, which you can download and study.
Correct display of codes will help subsequently avoid errors when drawing up 2-NDFL certificates, which are a reporting form for tax agents on the one hand and a document that confirms the income of citizens.
Tax agents, upon application from their employees and upon receipt of supporting documents, take into account standard tax deductions when calculating tax.
In addition to the standard ones at the place of work, it is now possible to receive other personal income tax benefits, including social ones.
Classification of tax deductions in the code table
To the table of deduction codes for reduction purposes tax base For personal income tax (IP), the following categories of deductions provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are included:
- Standard. Currently, codes 104, 105, 114–125 are in effect according to Art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- Social. Codes 320, 321, 324–328 are used, applied in accordance with Art. 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- Property. For codes 311 and 312 based on Art. 220 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- Professional. Codes 403–405 are used in accordance with Art. 221 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- Investment. Codes 617, 618 and 620 are provided for them (Article 219.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, a number of articles provide for benefits or a special taxation procedure for certain types of income of individuals.
Since this article is aimed at tax agents for personal income tax, information on deductions applied on the basis of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, for which codes are assigned from 501 to 510.
What changes have affected tax deduction codes since 2015?
Along with the abolition of outdated codes, the Federal Tax Service of Russia introduced new ones and replaced a number of old ones codes tax deductions , and also adjusted the decoding for some deductions.
In general, the structure of the table remained the same, although an innovation was added in the form of investment deductions.
Exactly which codes and what changes have undergone are shown in the table below.
Code change table
|
Excluded |
New codes |
Replacing one code with another |
Description changed |
|
Standard deductions |
|||
|
Transfer from transactions with the Central Bank and FISS to REPO transactions with the Central Bank |
|||
|
REPO operations with the Central Bank |
|||
|
Property deductions |
|||
|
Social deductions |
|||
|
320, 321, 324–328 |
|||
|
Non-taxable income |
|||
|
Actually 607 by 510 |
|||
|
Investment deductions |
|||
Main sections of the updated tax deductions table
The 13 sections of the table of deduction codes, which came into force at the end of 2015, are a document structured by type of tax preferences.
It is a guide for taxpayers and tax agents for the correct selection of the digital code assigned to a particular benefit provided tax legislation, when filling out 2-NDFL certificates about income received by individuals for the period from November 29, 2015.
The table includes sections that include the deductions presented below.
Table of sections of tax deduction codes
|
Name of deduction |
Number of sections allocated for deduction |
Assigned code numbers |
Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which is the basis for the deduction |
|
Standard |
104,105, 114–125 |
||
|
Reducing the base |
201–203, 205–207, 209, 210 |
||
|
Property |
|||
|
Social |
Subp. 2 p. 1 art. 219 |
||
|
Subp. 3 p. 1 art. 219 |
|||
|
Subp. 4 paragraphs 1 art. 219 |
|||
|
Subp. 5 p. 1 art. 219 |
|||
|
Professional |
|||
|
Non-taxable income |
|||
|
Reduce the base |
|||
|
Investment |
|||
Who uses deduction code 104 in the 2-NDFL certificate
As mentioned above, codes 104 and 105 reflect benefits for categories of persons who have special merits to the Fatherland or who have this benefit for other reasons.
Tax deduction by code 104 reduces monthly tax base on ND to a specific person from the list below for 500 rubles. Among them:
- Heroes of the USSR and Russia.
- Participants of the Second World War.
- Siege survivors of Leningrad during the Second World War.
- Civilian employees who took part in defensive activities in a number of cities during the Second World War.
- Persons who were prisoners of concentration camps and ghettos during the Second World War.
Among others, deductions under code 104 can be applied:
- Disabled people of the first 2 groups and persons who have been disabled since childhood.
- Persons who were exposed to radiation during accidents involving radioactive releases.
- Persons who become bone marrow donors in the name of saving other people.
- Persons evacuated from exclusion zones who were exposed to radioactive contamination in different years.
- Other persons listed in sub. 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Who has the right to deduction with code 105 in the 2-NDFL certificate
Tax deduction with code 105 is provided in the amount of 3,000 rubles. And if code 104 is used mainly by those who have been exposed to radiation, then the deduction under code 105 is provided to the following persons:
- those directly involved in the liquidation of the consequences of the accidents at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant and the Mayak PA, who were at the epicenter of the events and in the exclusion zones, including civilian and military personnel called up for training;
- other persons who, over the years, participated in various types of nuclear tests, listed in subparagraph. 1 clause 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In addition, this benefit is available to:
- persons who suffered radiation sickness or became disabled as a result of these global man-made disasters;
- disabled people of the Second World War and persons who became disabled due to wounds or shell shock during the defense of the USSR or Russia;
- other persons named in Art. 218.
Deduction codes 114, 118 and 122 in the 2-NDFL certificate
Tax deduction by code 114 is provided to individuals as part of standard deductions for the first-born child in the family until he reaches the age of majority or 24 years old, if he receives full-time education for a fee (upon presentation of a certificate from an educational institution).
In addition to the parents themselves, persons who have a foster child, who have taken guardianship or trusteeship over him or who have adopted him have the right to take advantage of this deduction.
Deductions for codes 118 and 122 are provided on the same basis in double the amount (in 2015–2016 - 2,800 rubles):
- according to code 118 - a single parent (adoptive parent, trustee and guardian (UPO));
- 122 - to one of the spouses in case the second parent refuses the deduction.
Deduction codes 115, 119 and 123
By analogy with codes 114, 118 and 122 and in the same amount, deductions are allowed if there is a 2nd child in the family. The conditions for the deduction completely coincide with the conditions for its provision according to the codes described in the previous section.
Deduction codes 116, 120 and 124
The 3rd and all other children are entitled to deductions for children similar to those described in the previous 2 sections in accordance with the codes:
- 116 - for the 3rd, 4th, etc. child (in the amount of 3,000 rubles);
- 120 - to the parent (UPO), who is the only one, and 124 - in case of refusal of the 2nd parent from the tax benefit (double the amount - 6,000 rubles).
Deduction codes for disabled children (117, 121 and 125)
If there is a disabled child in the family (confirmation is required in the form of a certificate with a specified validity period), then he is entitled to the following deductions until he reaches the age of 18, and in case of paid full-time education - up to 24 years:
- by code 117 - 12,000 rub. not only to parents, but also to the UPR;
- 121 - for single parents and UPR, 125 - in the case of receiving a deduction by only one of the spouses (the amount of the deduction is also doubled and is equal to 24,000 rubles in such situations).
Deduction codes for property expenses
Currently, after a documentary check and receipt of approval from the tax office, it is allowed to take into account the full amount of personal income tax benefits associated with the place of work:
- with the purchase of housing or its construction (code 311);
- on interest paid on the mortgage (code 312).
Digital symbols for social tax deductions
Starting this year, social deductions for personal income tax related to the payment of education (up to the age of 24) and treatment (if for children, then until the 18th birthday) can also be taken into account by the tax agent without waiting for the end of the year in which they were received. It is enough to present documents confirming these expenses to the tax office for verification, and after a positive response from the tax authorities in the form of a notification, the deduction can be used at the place of work.
Digital codes of social deductions and their brief descriptions are as follows:
- For training (in total expenses no more than 50,000 rubles):
- 320 - for yourself, brother and/or sister.
- 321 - for children (their own and/or in relation to whom the payer is the UPR).
- For treatment:
- 324 - your own, as well as immediate family members;
- 325 - as listed VHI contributions for yourself and family members;
- 326 is expensive.
- Other:
- 327 - for paid contributions to non-state pension funds or contracts voluntary insurance the lives of your own and your closest relatives;
- 328 - expenses for additional savings contributions to the pension fund.
Deductions for non-taxable income received from a tax agent
For a number of deductions, which, in accordance with Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not subject to income tax in full or in part; in the table of tax deduction codes for personal income tax since 2015, codes from 501 to 510 are highlighted.
Codes 501 to 506 are reserved for deductions associated with receiving gifts, prizes, winnings, as well as financial assistance and reimbursement of the cost of purchased medications.
NOTE! The amount of deductions for codes 501 to 506 is limited to 4,000 rubles. and applies for each reason listed in paragraph 28 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, separately.
That is, if an employee received a gift in the amount of 4,000 rubles, it is for the same taxable period may also claim a deduction for the medications he actually paid for in the same amount.
The deduction under code 508 for the birth of a child in the family is limited to the amount of 50,000 rubles.
The deduction under code 510 in connection with the payment of additional insurance contributions for an employee for the funded part of the pension is limited to 12,000 rubles.
Deduction code 501 in certificate 2-NDFL
Most often, employers reward their employees on the occasion of various holidays or anniversaries with gifts, for which a tax deduction is provided for income tax under code 501 within an amount not exceeding 4,000 rubles.
Gifts for this amount are not subject to personal income tax. If the value of the gift is more than the non-taxable limit, then the entire amount in excess of it is taxed at a rate of 13%, which is reflected in the 2-NDFL certificate.
NOTE! The gift can be made in in cash. In this case, a gift agreement must be drawn up between the employer-donor and the employee being gifted so that this amount is not counted as a cash bonus by the regulatory authorities.
Deduction code 503
Financial assistance not subject to income tax up to 4,000 rubles. per year per 1 employee - this is the most often used hidden form of employee incentives by employers, which makes it possible not to withhold personal income by showing deduction code 503 in 2-NDFL certificates.
Amounts of financial assistance in excess of this established limit are subject to taxation in full if it is not due to the birth of a child and is not related to the death of a family member of the employee.
Deduction code 2012
This deduction code is often found in search queries on the Internet. In fact, there is no such tax deduction code. Code 2012 refers to the income code of individuals for paid vacation pay.
Any accountant should be well acquainted with tax deduction codes in order to correctly reflect them in the 2-NDFL certificate. And we must not forget that the right to apply any tax deductions must be documented.
The Tax Service has changed the codes for children's personal income tax deductions. The child is subject to the new deduction code 126 in the 2-NDFL certificate for 2016.
Enter deduction code 126 on the certificate if you provided a deduction for the first child in a single amount to the parent, spouse or adoptive parent. Previously, code 114 was used for this deduction.
The Federal Tax Service of Russia approved new codes in order dated November 22, 2016 No. ММВ-7-11/633@. Changes in appendices No. 1 and 2 to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 10, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11/387@ came into force on December 26.
What codes have changed
The new codes are 126-149, and codes 114-125 have been cancelled. The amendments are due to the fact that since 2016, the Federal Tax Service has adjusted the rules for providing deductions for children to a guardian, trustee, adoptive parent, or spouse of an adoptive parent.
Thus, for guardians, trustees and adoptive parents there is a tax deduction for personal income tax of 6,000 rubles. Parents and adoptive parents of a “special” child receive an updated standard deduction for personal income tax of 12,000 rubles. every month. The employee income threshold, above which companies do not have the right to apply a deduction, has increased to RUB 350,000 since 2016. from 280,000 rub. This required changing the codes.
On December 26, 2016, the Federal Tax Service Order No. ММВ-7-11/633 dated November 22, 2016 “On introducing amendments and additions to the appendices to the Russian Federal Tax Service order No. ММВ-7-11/387@ dated September 10, 2015 “On approval” came into force codes for types of income and deductions.” In this regard, from December 26, 2016, new codes must be reflected in 2-NDFL certificates issued to employees. Also, updated income and deduction codes will need to be indicated in 2-NDFL certificates for 2016, which tax agents will submit to the Federal Tax Service in 2017. We'll tell you how the income and deduction codes have changed.
When to enter new codes
Organizations and individual entrepreneurs (who are tax agents) are annually required to submit to the Federal Tax Service information on employee income for the past calendar year in the form of a 2-NDFL certificate. You must submit 2-NDFL certificates for 2016:
- with sign 2 – no later than March 1, 2017;
- with sign 1 - no later than April 3, 2017 (since April 1, 2017 falls on a Saturday, certificates can be submitted on the coming Monday, clause 7 of article 6.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Cm. " ".
Also, 2-NDFL certificates may need to be given to employees “in their hands” if they apply for them. They may need the certificate, for example, to apply for a loan. The 2-NDFL certificate form stipulates that 2-NDFL certificates must show income and deduction codes that are associated with a specific individual. The list of new income codes and deductions for personal income tax was approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service dated November 22, 2016 No. ММВ-7-11/633. New deduction codes should be used when filling out 2-NDFL certificates from December 26, 2016. Now let's see what exactly has changed.
The form of a certificate of income of an individual (2-NDFL) and the procedure for filling it out were approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 30, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11/485. This form applies in 2017. New form certificate 2-NDFL for 2017 was not approved.
New revenue codes
In the 2-NDFL certificate, tax agents (organizations or individual entrepreneurs) reflect only those incomes for which they themselves are the source of payment. Moreover, the type of income paid to the employee is reflected in personal income tax certificate 2 in the form of a special code.
What income to consider
The certificate in form 2-NDFL must include all income that is taxed. Thus, take into account all the amounts that were paid to the citizen, both under the employment and civil law contracts (clause 3 of Article 226, Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Income individuals are reflected in section 3 of the 2-NDFL certificates. The title of this section reflects tax rate applied to income. If during 2016 the same person received income subject to personal income tax under different rates, then section 3 will need to be completed separately for each tax rate.
When filling out the table in section 3 of the 2-NDFL certificate, you need to apply appendices 1 “Income Codes” and 2 “Deduction Codes” to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 10, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11/387. Each type of income and each type of tax deduction are assigned special codes. For example, income in the form of wages corresponds to code 2000. When paying remuneration under other civil contracts - code 2010, when paying benefits for temporary disability - code 2300. If there is no special code for income - code 4800. Income codes are reflected in section 3, for example like this:
Read also Standard children's deductions: is everything so standard?

The main income codes have not changed. However, as of December 26, 2016, the meaning of some income codes has been updated and some codes have been added. In particular, two new codes have appeared that many people will need to indicate in their certificates. tax agents, namely:
New deduction codes
From December 26, 2016 excluded from application standard deductions with codes 114 - 125. Instead, new deduction codes were introduced for the 2-NDFL certificate in 2017 from 126 to 149. This was done due to the fact that previously there were uniform deduction codes for parents, adoptive parents, guardians, trustees and adoptive parents. However, from December 26, 2016, the codes for parents (adoptive parents) and codes for guardians, trustees, adoptive parents are separated, since a deduction of 12,000 rubles is established for parents of disabled children, and for guardians (trustees, adoptive parents) - in the amount 6000 rubles.
note
You should submit child deductions only to those employees whose income is taxed at a rate of 13%. To exercise their right, the employee must write an application, to which must attach a copy of the child’s birth certificate.
| Deduction code | A comment | Deduction amount |
| 126 | For the first child under 18 years of age, as well as for each student full-time training, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to the parent, spouse of the parent, adoptive parent who is supporting the child. | 1400 rubles |
| 127 | For the second child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to the parent, spouse of the parent, adoptive parent who is supporting the child. | 1400 rubles |
| 128 | For the third and each subsequent child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to the parent, spouse of the parent, adoptive parent who is providing for the child | 3000 rubles |
| 129 | For a disabled child under the age of 18 or a full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student under the age of 24, who is a disabled person of groups I and II to the parent, spouse of the parent, adoptive parent who is providing for the child. | 12,000 rubles |
| 130 | For the first child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to the guardian, trustee, adoptive parent, spouse of the adoptive parent, who is supported by child. | 1400 rubles |
| 131 | For the second child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to the guardian, trustee, adoptive parent, spouse of the adoptive parent, who is supported by child | 1400 rubles |
| 132 | For the third and each subsequent child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24, a guardian, trustee, foster parent, spouse of a foster parent, for provided for by the child. | 3000 rubles |
| 133 | For a disabled child under the age of 18 or a full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student under the age of 24, who is a disabled person of groups I and II, to a guardian, trustee, foster parent, spouse of a foster parent, supported where the child is located | 6000 rubles |
| 134 | Double the amount for the first child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to a single parent, adoptive parent | 2800 rubles |
| 135 | Double the amount for the first child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to the sole guardian, trustee, foster parent. | 2800 rubles |
| 136 | Double the amount for the second child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to a single parent or adoptive parent. | 2800 rubles. |
| 137 | Double the amount for the second child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to the sole guardian, trustee, foster parent | 2800 rubles |
| 138 | Double the amount for the third and each subsequent child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to a single parent, adoptive parent | 6000 rubles |
| 139 | Double the amount for the third child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to the sole guardian, trustee, foster parent. | 6000 rubles |
| 140 | In double the amount for a disabled child under the age of 18 or a full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24, who is a disabled person of group I or II to the only parent, adoptive parent. | 24,000 rubles |
| 141 | In double the amount for a disabled child under the age of 18 or a full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24, who is a disabled person of groups I and II to the sole guardian, trustee, foster parent. | 12,000 rubles |
| 142 | In double the amount for the first child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to one of the parents of their choice based on an application for refusal of one of the parents receiving a tax deduction. | 2800 rubles |
| 143 | In double the amount for the first child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to one of the adoptive parents of their choice based on an application for refusal of one of the adoptive parents parents from receiving a tax deduction. | 2800 rubles |
| 144 | In double the amount for the second child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to one of the parents of their choice on the basis of an application for refusal of one of the parents from receiving a tax deduction. | 2800 rubles |
| 145 | In double the amount for the second child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to one of the adoptive parents of their choice based on an application for refusal of one of the adoptive parents parents from receiving a tax deduction. | 2800 rubles |
| 146 | In double the amount for the third and each subsequent child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to one of the parents of their choice based on an application for refusal of one from parents from receiving a tax deduction. | 6000 rubles |
| 147 | In double the amount for the third child under the age of 18, as well as for each full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24 to one of the adoptive parents of their choice based on an application for refusal of one of the adoptive parents parents from receiving a tax deduction. | 6000 rubles |
| 148 | In double the amount for a disabled child under the age of 18 or a full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24, who is a disabled person of group I or II, to one of the parents of their choice on the basis of an application for refusal of one of the parents to receive a tax deduction. | 24,000 rubles |
| 149 | In double the amount for a disabled child under the age of 18 or a full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student, cadet under the age of 24, who is a disabled person of group I or II, to one of the adoptive parents of their choice based on an application about the refusal of one of the adoptive parents to receive a tax deduction. | 12,000 rubles |
Child deduction codes and some income codes have changed. Therefore, fill out the 2-NDFL certificates for 2016 in a new way. Move the icon left and right on the samples and compare the codes.
From December 26, 2016, new codes for income and deductions for personal income tax are in effect. The Federal Tax Service updated them by order No. ММВ-7-11/633 dated November 22, 2016.
Put new codes in the 2-NDFL certificates that you issue to employees for the past and this year, as well as in the certificates that you will submit to the inspection at the end of 2016. There are two more changes due to which 2-NDFL for 2016 needs to be filled out in a new way.
Reflect children's deductions and bonuses in 2-NDFL for 2016 with new codes
Production bonuses must now be shown separately from wages with the new code 2002. Previously, they were reflected together with wages under code 2000.
For bonuses based on net profit, a new code 2003 has been introduced. Place it opposite bonuses for holidays, anniversaries and other similar payments. Previously, they were included in certificates under code 4800 “Other income.”
All standard child deduction codes have been updated. We have listed them in the table below. The old child deduction codes 114-125 have now been eliminated.
To compare old and new child deduction codes, move the icon left and right on the sample.


In section 4, show the social deduction
An employee has the right to receive in your company social deduction for education or treatment only since 2016, so you did not show such deductions in the certificates for 2015.
If the employee paid for routine treatment, enter code 324 in section 4 of the certificate. Show expensive treatment with code 326.
Under the table in section 4, write down the details of the notification from the tax office, which confirms the right to the deduction.
Recalculate personal income tax from January if the employee submitted an application for property deduction in the middle of the year
Recalculate personal income tax from January, even if the employee brought a notice to property deduction in another month. Officials stopped arguing with this (letter of the Russian Ministry of Finance dated October 6, 2016 No. 03-04-05/58149).
Before this, the Federal Tax Service and the Ministry of Finance more than once changed their opinion on which month to provide the deduction from. But now they have agreed and resolved this issue in favor of individuals.
Return the difference to the employee within three months at the expense of upcoming personal income tax payments (clause 1 of article 231 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the accruals are not enough, the inspectorate will return the tax.
Example. How to return Personal income tax for the employee
Employee salary - 30,000 rubles. From January to November he was credited with 330,000 rubles. Personal income tax was transferred from these incomes - 42,900 rubles. (RUB 330,000 × 13%).
On December 15, the employee brought a notice of deduction in the amount of 1 million rubles. He has the right to receive 130,000 rubles from the company. (RUB 1,000,000 × 13%). This is more than the amount withheld (130,000 > 42,900). This means that the employee must return all 42,900 rubles. Personal income tax for December - 3900 rubles. (RUB 30,000 × 13%) - no need to withhold.
The accountant transferred 42,900 rubles to the employee. In January and February, personal income tax is 20,000 rubles each. in each month - they were not transferred to the budget. And in March, instead of 20,000 rubles. sent 17,100 rubles. (20,000 – (42,900 – 20,000 – 20,000)).
The rest of the deduction is RUB 83,200. (130,000 – 42,900 – 3900). The employee can receive it from the inspection or postpone it to the next year. To do this, you need to bring a notice for 2017.
In the certificate, enter the deduction code 311 if the employee paid for housing, 312 if he paid off the interest on the mortgage.
Sample of 2‑NDFL certificate for 2016, filled out in a new way
Move the icon on the sample to the right and you will see how you would format this certificate for 2015.