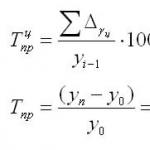
How to avoid fines for late payment of personal income tax. Accountable amounts. how to avoid personal income tax and contributions. Supporting documents must be attached to the costs.
In 2019, a procedure for submitting Form 6-NDFL was introduced for employers. It allows you to control the timely payment of taxes. Indeed, in accordance with Article 123 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, fines are provided for non-payment of personal income tax in 2019. The amount will be 20% of the overdue amount and additional penalties. The number of days during which the payment was overdue is not taken into account.
There are no mitigating circumstances when determining the amount of the fine. Therefore, even if the tax authorities did not send the receipt on time, sanctions will be applied.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to know how solve exactly your problem- contact a consultant:
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and FOR FREE!
According to experts, the measure is considered legal. But sometimes unfair decisions are noted. After all, citizens may suffer due to shortcomings of the tax inspectorate.
To avoid such situations, it is important to know the deadline for paying taxes. If you deposit funds before a certain date, you will not have to pay any fines.
Provisions by law
Personal income tax must be paid within the time limits specified in Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. If the date is missed, the Federal Tax Service has the right to fine the violator. The amount of sanctions will be 20% of the payment amount. This rule applies to all taxpayers.
More severe penalties apply to tax agents. They can be legally held accountable even under criminal law.
The deadlines for payment for employers are prescribed in Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. At the same time, they do not need to rely on the norms of Articles 227 and 228.
The collection of a fine can be carried out by the inspectorate in two cases. In the first, a fine is applied if there is no tax withholding from the funds transferred to the employee. Sanctions are also applied to organizations that do not transfer fees to the state budget in a timely manner.
Such norms are reflected in Article 123 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In addition, the payment rules are prescribed in Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-02-07/1/8500, which was issued on March 19, 2013.
Despite the accrued fine, the tax agent must still deduct personal income tax. Based on paragraph 1 of Article 46 and paragraph 1 of Article 47 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, collection can be carried out by tax authorities forcibly. If payment deadlines are violated, the organization will be required to pay a penalty. The amount is determined in accordance with the duration of the delay.
Central questions
Fines for non-payment of personal income tax in 2019 are provided for many categories of taxpayers. It is important to know how much the violator of the law will have to pay and what changes have been introduced to the legislation since the beginning of the year.
Who should pay
Personal income tax is withheld from each employee by the employer. It is 13%, which is set at the state level.
If a citizen is a resident of the country, then when calculating it is important to know the full amount of income within the state and beyond. For non-residents, the tax base is determined only on the basis of Russian income.
Taxes for the labor activity of employees are paid by employers. The status of the institution and its organizational form are not taken into account. Foreign citizens pay patent tax in advance in the established amount.
If specialists carry out private practice, their income is obtained through independent labor activity. The procedure for withholding tax is prescribed in Articles 226 and 227 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
When the tax period ends, organizations must send information to the tax office for each employee. The document reflects the amount of total income and withheld tax. Submission of reports is scheduled for April 1 of the following reporting year.
Onset of liability
Sometimes employers do not pay taxes, but the inspection does not detect violations. It is important to know how long you can hold him accountable.
The period may vary depending on the method of receiving income:
- cash;
- natural goods;
- in the form of material benefit;
- non-cash way.
Some employers use an envelope system for paying salaries to avoid paying taxes. In this case, the amount of taxes and insurance contributions is reduced.
If tax inspectors reveal violations, the employer will have to pay 40% of the debt. But violators are often not afraid of this. Therefore, the issue of not only increasing penalties, but also other countermeasures is being resolved by law.
After committing an offense, the employer will need to pay a fine. It is calculated depending on certain circumstances. It is important to know the situations when additional funds cannot be withheld, as well as the powers of tax authorities in calculating such payments.
When paying a fine, it is important to fill in the details correctly. A special one is provided for each taxpayer.
Last changes
Fines in 2019 remained unchanged, but adjustments were made to the procedure for withholding personal income tax:
- Tax on vacation payments is calculated together with the direct calculation of benefits.
- A certificate in form 2-NDFL is submitted if the tax is fully withheld until April 3, 2019, and if the tax is incomplete, until March.
- Previously, the transfer of personal income tax had to be carried out on the day of payment of wages. Now the employer is allowed to do this the next day.
- Social benefits can be transferred at the place of work. Previously, taxpayers had to visit the territorial office of the Federal Tax Service directly.
It is worth remembering that income is allocated to which taxation does not apply.
These include:
- state benefits related to maternity, childhood, unemployment;
- scholarships;
- pension payments;
- one-time transfers for the birth of a child or for burial;
- inherited or gift income;
- interest on deposits;
- gifts and prizes received, the value of which does not exceed four thousand rubles;
- certificate for receiving maternity capital.
What is the amount of the fine for non-payment of personal income tax in 2019?
Failure to pay personal income tax will result in severe penalties.
It may occur in accordance with Article 123 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation when:
- lack of transfer of funds to the budget;
- partial payment;
- violation of tax payment deadlines.
The fine will be 20 percent of the total amount of the debt.
There are cases in which the employer may not be held accountable. They are reflected in Article 109 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
These include:
- lack of corpus delicti;
- availability of evidence that the tax agent or payer is not guilty;
- the offender is under 16 years of age;
- the statute of limitations has expired.
Penalty may be applied within three years from the date of violation. This norm is prescribed in Article 113 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If the employer has not submitted reports or has not paid tax, the Federal Tax Service may initiate an on-site inspection.
Once violations are identified, the following may occur:
- a penalty has been charged;
- a fine is provided;
- The case was referred to the prosecutor's office for consideration.
In the latter case, there is a high probability of bringing the employer to criminal liability. Then the fine will increase to 500 thousand rubles. If the act is particularly serious, imprisonment for a term of up to six years is provided.
In some cases, employers want to reduce the tax amount or avoid penalties. To do this, they need to learn practical tips. It is also important to find out in advance the terms during which the debt is repaid.
How to avoid or reduce
In some situations, even when an illegal act is committed, there is no liability.
This is possible with:
- paying personal income tax in advance, before receiving income;
- transfer of tax to the budget before payment of wages to employees;
- transfer of funds to the NFS of the head office instead of the inspectorate supervising the branch;
- non-payment of tax, since the acquisition was made from extra-budgetary funds.
In such situations, the employer can defend its rights and avoid administrative liability.
There are situations when it is possible to legally reduce the amount of penalties.
When determining a fine, it is important to take into account mitigating circumstances:
- technical program errors;
- change of leadership of the organization;
- admission of guilt by the employer;
- no debt on other fees;
- social sphere of the institution's activities.
If at least one of the signs is present, the fine can be halved. If this point is ignored by the tax authorities, the tax agent may appeal to the judicial authorities.
Getting the date right
To avoid a fine, you need to know the date when taxes must be transferred to the budget.
For each type of income, special deadlines are provided:
| Income | Receipt time | Date of retention and transfer |
| Wage | The last day of the month or the first day of the next month during which work was carried out | No later than the date of funds transfer |
| Cash as income | Date of transfer or payment of funds | Date on which the transfer is made |
| Holiday pay payments | ||
| Benefit provided for temporary disability | Last date for payment of income | No later than the last date of the month in which the payment was made |
In the absence of personal income tax withholding, a fine is assessed, and the arrears cannot be recovered.
Sanctions for agents, individuals and payers
The withholding and transfer to the budget of 13% of the tax is provided for by employers, as well as private practitioners and foreign firms.
If obligations are not met, a fine of 20% of the debt will be applied. The exception is income in kind.
Ordinary individuals must also make deductions when they receive income from selling property, receiving a prize or winning a lottery. If they ignore the requirements of the law, then a fine is provided for them in a similar amount.
For particularly large violations, the amount increases to 40%. Such situations include reducing the amount of income by illegal means, as well as the use of illegal deductions.
Individual entrepreneurs deduct taxes on certain types of income. If the tax base is reduced, an individual entrepreneur may be subject to a fine of 20% of the debt amount. Tax crimes are punishable by a 40% fine of the amount owed.
Payment deadlines
Payment of personal income tax is made within the time limits established by law. Despite the payment of wages in the form of an advance and the main payment, deduction is made once at the end of the month.
Terms vary depending on the payment method:
Individual entrepreneurs and individuals pay personal income tax at the end of the reporting period. Funds must be received no later than July 15 of the following year.
Personal income tax is a tax that a company withholds from an employee’s salary. The personal income tax rate is 13%. The company transfers the withheld amount to the health and social insurance funds, as well as to the pension fund.
Personal income tax is calculated using the following algorithm:
- the income of company employees is summed up;
- deductions for benefits are calculated. They are standard, when their amount depends on the number of children, property (sale of residential houses, apartments, etc.) and social (expenses for study, treatment of yourself and your relatives, for charity);
- the value that was obtained when calculating deductions is subtracted from the total amount of employee income;
- The resulting amount is then multiplied by 13%.
There are two personal income tax certificates that the company is required to submit to the tax office. The first is 2-NDFL. This document contains the details of the enterprise, information on wages and withheld income taxes for each employee. The company must submit a 2-personal income tax certificate to the tax office before April 1 of the following year after the reporting year.
The second certificate is 6-NDFL. It indicates the summary amount of income and withheld taxes for all employees. The company is required to submit this certificate to the department for the following periods:
- for the reporting year - no later than April 1 of the following year;
- for the first quarter - no later than May 3;
- for six months - no later than July 31;
- nine months - no later than October 31.

By law, the company must transfer the personal income tax withheld from wages to the tax office on the day the employee received his salary. An enterprise can also transfer the withheld personal income tax on the next working day after the employee receives earnings. If the company does this later, it will receive a fine. Its size is 20% of the amount that was transferred to the tax service late. If the company did not transfer the full amount to the government agency, it will also be fined.
The reason that changed the law
In some past, one company was fined by the tax office for late submission of personal income tax. The fine amounted to 300 thousand rubles. However, the company challenged this decision in court: company representatives argued that it had no personal income tax debts when it submitted reports to the tax service. The company managed to pay off the arrears along with penalties even before submitting reports to the state body.
As a result, the court sided with the company, and later amendments were made to Article 123 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which allow a legal entity to avoid a fine for late payment of personal income tax.
How is this possible?
It is possible to avoid personal income tax fines if the company has paid off the debt and penalties before submitting the update to the tax service. However, she must pay off the debt and penalties before the tax office finds out about it. Tax specialists can find out about it using the primary 6-NDFL: the document indicates payments for which the company has debts. The company will be forced to pay a fine if the department has identified tax debts.
What will help you avoid fines for non-payment of personal income tax?
With the help of the VLSI electronic reporting program, you will submit correct reports to regulatory authorities in a timely manner. The system allows you to conduct financial analysis and assess tax risks, generate reports and check them in accordance with regulatory requirements for format and content. Thanks to the VLSI electronic reporting program, you will be able to receive certificates and extracts from the tax office, statements of reconciliation of payments online, check partners and affiliates for reliability, and much more.
The system is constantly updated in accordance with all changes in legislation. It can also be integrated with most accounting programs.
Please note that to submit reports via the Internet, you will definitely need an electronic digital signature. Thanks to the EDS Center service, you will purchase an electronic digital signature at the best price.
All your questions related to personal income tax, reporting and VLSI products will be answered by ours. At our events you will also find answers to questions related to electronic trading, accounting, optimization and automation of business processes.
There is just over a month left until the tax return filing deadline. Go Banking Rates has found that a small segment of the population has discovered loopholes to avoid paying some income tax - legally.
1. A drunk driver turns a DUI into a tax deduction.
Justin Rohrs managed to get his truck off the embankment in 2005 only to collect insurance payouts after driving while intoxicated. He claimed insurance on his $33,629 pickup truck. After the insurance company denied his claim, he attempted to claim the loss of his vehicle as a tax deduction.
Rohrs filed a lawsuit in U.S. Tax Court, arguing that he deserved to have the loss of the truck deducted from his tax return. The judge agreed and allowed him to do so.
2. Cats are very expensive
Jan Van Dusen is a cat lover. She has more than 70 cats in her house. She cared for the animals, but then released some of them into the wild. Although most often I left my furry friends at home.
The cost of caring for cats began to mount for Van Dusen, so she filed a 2004 tax return trying to write off $12,068 in cat rescue items such as food, vet bills, paper towels and more. After the IRS told her that these expenses were considered personal and the service could not deduct them, she sued the IRS. After a long battle, Van Dusen proved that caring for the cats was a charity, resulting in the IRS finally providing deductions for most of her claims.
3. An exotic dancer's breast implants are a business expense.
Cynthia Hess, also known by her stage name Tonda Marie, was an exotic dancer who wanted to improve her business by eliminating her "hereditary defect." In other words, she needed bigger breasts. After she had breast augmentation, her business began to grow.
Hess, now known as Chesty Love, decided to deduct her implants as a business expense. The IRS denied her request, saying that business deductions only work in circumstances that are ordinary and necessary.
Hess sued the IRS, arguing that her new breasts should be considered a business uniform. She continued to say that she planned to have them removed immediately after leaving the business and only had her breasts enlarged for business purposes.
4. Even drug dealers get tax deductions
Drug dealer Jeffrey Edmondson may be giving master classes on how to legally avoid paying taxes. He got into trouble with the law after he was arrested and accused of drug trafficking. In an effort to get even more from the dealer, the IRS fined him $17,000 in back taxes because he failed to declare his drug income.
Edmondson decided the government would not “have the last laugh.” In summing up his trial, he filed a tax return showing his taxable net income along with a list of business deductions. After looking at the tax refund, the IRS rejected the deductions. But Edmonson decided to go even further.
He filed a claim in tax court where he claimed to have founded a home-based business and claimed a deduction for home office expenses, including drugs. Surprisingly, the judge agreed to allow him to deduct expenses, which included a $50 scale, more than 19,000 miles on his car and 100 pounds of marijuana.

3 Easy Ways to Legally Avoid Taxes
You may not want to sue the IRS every time you give up a tax deduction, but you can benefit by learning how to legally avoid paying taxes. Here are three options to legally avoid paying taxes:
1. Qualification for tax credits
Many people don't realize that a tax credit is the equivalent of free money. Tax deductions reduce the amount of taxable income you can claim, and tax credits reduce the tax you owe and, in many cases, result in a nice refund.
The IRS offers a large number of tax credits that cover everything from purchasing energy-efficient products for your home to a low-cost, moderate-income home. The key to benefiting from them is to look at all the purchases you made throughout the year.
2. Use adjusted deductions
Most people take the standard deduction available to them when they file their taxes to avoid having to provide proof of all the purchases they made during the year.
But if you've made significant payments for mortgage interest, property taxes, medical expenses, local and state taxes, or made large charitable contributions, it might be worth it. These tax deductions are subtracted from your adjusted gross income, which reduces your taxable income.
3. Enroll in college
One way to take advantage of tax credits or credits is to enroll in college.
Students who are not eligible for credits must consider tax deductions. The government allows students to deduct up to $4,000 from the cost of tuition, fees and course materials. Although it is not as valuable as a loan, deductions can significantly reduce taxes.
Also, keep in mind that financial assistance in the form of grants and work study offers tax-free money that is not considered taxable income. Scholarships also help pay for school and are not taxable if the money is used for educational purposes.
There's no doubt that it's legally impossible to evade taxes, but by taking advantage of credits and deductions, you can improve your chances of doing so.
When selling a car, personal income tax is required to be paid by the owners of the cars that were sold, that is, the individual received a benefit from this in the form of cash. But tax is not always paid - only under certain circumstances, which are extremely rare. Typically, car owners can avoid paying sales tax or reduce the interest rate, which is currently 13 percent of the sale proceeds.
- this is income tax (mandatory collection of funds from citizens of the Russian Federation when they receive profit or income). In the case of the sale of a car, the income is the money received by the seller (the person who sold the car).
Currently, the tax rate on sales is 13 percent. But it is the most general and primitive, since in some cases the percentage increases significantly. The money from the payment goes to the tax authorities, and then is distributed to the budget (usually a small percentage goes to the Federal Budget, and the majority of the amount goes to the budget of the region where the owner of the car is registered).
For example, if the car according to the documents was sold for 700 thousand rubles, then the citizen who sold it is obliged to pay 91 thousand rubles (13 percent of the cost) to the budget, only on condition that the car was previously received free of charge (about this and other conditions will be written later). But, as mentioned earlier, personal income tax is not always paid when selling a car, but only in some cases. Typically, the tax amount is either reduced or no tax is collected at all.
How to calculate income tax on the sale of a car?
Many people think that tax is paid only on the amount specified in the purchase and sale agreement. But the tax is levied only on profits. And the car was previously purchased by the owner (or transferred by inheritance or gift). That is, income tax is calculated not on the sale price, but on the profit that the owner will receive (if he receives it at all).
So, for example, the current owner, who is going to sell the car, bought it for 1,000,000 rubles. And he decided to sell it for 1,100,000 rubles. That is, the profit he will receive will be 100,000 rubles. And it will be paid from this amount. That is, the tax will be only 13,000 rubles. But if the car was received as a gift, then the profit from its sale will be the same as the amount for which it is sold. But even in this case there are some peculiarities that allow you to reduce the amount of tax.
This is interesting! It is also worth noting the case when the seller bought a car for more than he was selling it for. For example, a car cost half a million rubles, but the owner decided to sell it for 300,000 rubles. That is, he will not receive any profit from this. Therefore, no income tax is paid.
There are other ways to reduce your tax amount. For example, . It is written about in detail below.
Tax deduction when drawing up a purchase and sale agreement
A tax deduction is another way to reduce your tax bill. It applies under the following conditions:
- The seller owned the car for less than 3 years.
- The maximum deduction amount is 250 thousand rubles.

A tax deduction is applicable if the seller has not retained information about the cost of the car at the time of its purchase. That is, the initial price paid by the seller cannot be determined.
Note! Sometimes tax deductions are used in other circumstances.
Calculation of deductions and its features
As mentioned earlier, the deduction amount is 250,000 rubles. It is deducted from the profit from the sale if you have owned the car for less than three years, and there are no documents remaining about the cost of its acquisition. That is, the profit is equal to the amount for which you sell the car.
For example, a car is sold for 500,000 rubles, it has been owned for less than three years, and there are no documents on the cost of the car at the time of purchase. The deduction amount is 250,000 rubles, which is deducted from the profit. That is, 500,000 – 250,000 = 250,000 (rubles). Consequently, income tax of 13 percent is paid on an amount of 250,000 rubles.
Important! However, there is one main feature - the tax deduction must be indicated in the declaration when submitting it to the tax authorities at the place of residence.
How to avoid tax payments?
A tax deduction is a wonderful gift from the state. But there are circumstances in which personal income tax is not paid at all when selling a car:
- The cost of selling a car is less than the cost of buying it. That is, the seller will not receive any profit from this transaction. This happens very often, because over time the car loses its former qualities. Everyone knows that after buying a car at a car dealership, its value decreases by 20 percent. Therefore, no income tax is paid on the sale of such a car.
- The period of ownership is more than three years. This is enshrined in law - personal income tax is not paid on sales for less than 3 years. But there are some caveats. Personal income tax is not paid only if the car was not used for business purposes.
Moreover, owning a car for more than three years allows you not to apply for a sale. In all other cases, even if you do not need to pay tax, you must submit a return.
The video discusses in detail the points that are worth paying attention to:
Deadlines for filing a declaration and paying personal income tax
The application must be submitted to the tax authorities no later than April 30 of the following year. That is, if you sold the car in 2017 (the date is not important), then you must submit a declaration no later than April 30, 2019. But in this case the tax can be paid until July 15, 2019. That is, the tax is paid until July 15 of the year following the year in which the car was sold.
This is interesting! It is also worth noting that if documents are filled out incorrectly, criminal or administrative liability is intentionally provided.
Now the penalty for paying personal income tax late can be avoided. Companies will no longer have to resort to the trick of submitting an updated 6-NDFL in order to avoid paying a fine. The resolution of the Constitutional Court dated 02/06/2018 No. 6-P will help.
How do tax authorities find late personal income tax?
If a company delays payment of personal income tax, the tax office assesses a fine instantly (Article 123 of the Tax Code). Officials consider even one day of missing a payment to be grounds for a fine.
To calculate fines, inspectors use data from form 6-NDFL and budget settlement cards. In line 120 of form 6-NDFL you show the date no later than which the personal income tax must be transferred. In line 140 - the amount that should go to the budget. From it, tax authorities deduct the returned personal income tax from line 090.
If the company transferred the personal income tax later than the date in line 120, the tax office sees the delay in the budget settlement card. It is maintained by the department for accounting of accruals and payments at the tax office. The inspector of the desk audit department enters information about taxes paid based on the company's invoices.

What trick have companies used in the past to avoid fines?
Previously, in order to avoid a fine, companies submitted an updated Form 6-NDFL. Before submitting the update, the organization transferred penalties and the missing amount of tax if there was arrears.
If the accountant managed to do this before the tax authorities found the mistake or ordered an on-site audit, the company could avoid a fine (subclause 1, clause 4, article 81 of the Tax Code). The court supported this approach of the companies.
Example
Resolution of the Supreme Arbitration Court of March 18, 2014 No. 18290/13. In this case, the tax agent company replaced technical information in the original report, not even the tax. However, she was exempted from fines for late payment of taxes.
Ambiguous judicial practice after the decision of the Supreme Arbitration Court
After the SAC ruling was issued, judges made decisions both in favor of tax agent companies and in favor of inspectors.
Arbitrage practice
|
Details of the resolution |
The Judges' Arguments |
|
The tax inspectorate won the case |
|
|
Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Volga-Vyatka District dated October 30, 2017 No. F01-4709/2017 in case No. A29-246/2017 |
The absence of personal income tax debt on the date of drawing up the inspection report does not exempt from a fine for paying personal income tax later than the due date. The court did not exempt the company from the fine. |
|
Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the West Siberian District dated December 21, 2016 in case No. F27-1017/2016 |
The company admitted its guilt and compensated for budget losses by paying penalties. The court reduced the fine by 2 times. |
|
The company won the case |
|
|
Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Moscow District dated 02/08/2017 No. F05-22322/2016 in case No. A40-81345/2016 |
The company paid taxes and penalties before submitting the initial report. This demonstrates conscientious behavior. The court released the company from the fine. |
|
Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Moscow District dated October 7, 2016 No. F05-14968-2016 in the case “A40-14266/2016” |
|
The Constitutional Court simplified the work of an accountant
Do I need to file an updated report for the tax agent to receive an exemption from the late tax penalty? According to the Constitutional Court, a fine can be avoided even if the company repays the arrears and pays penalties before submitting the initial report. Otherwise, it has a less advantageous position than an organization that made errors in the report and submitted an amendment (Resolution of the Constitutional Court dated 02/06/2018 No. 6-P).

After the decision of the Constitutional Court No. 6-P, there will be fewer problems with personal income tax. You won’t have to waste time searching for errors in 6-NDFL, which may not exist, or preparing clarifications.
The Constitutional Court obliged everyone to apply Resolution No. 6-P. If suddenly your tax inspector tries to charge a fine, show him paragraph 2 of this resolution.
The penalty for an error in SZV-M can be removed completely
SZV-M indicate the reporting month code. Companies often make mistakes in the period code - instead of the month for which they submit the report, they put the month in which it is sent. For example, in the report for March, instead of code 03, they put code 04. The fine for such a violation can be challenged in full in court.
Example
The company noticed an error in the reporting period code when the deadline for submitting the report had already passed. The accountant sent a new report with the correct code, and in response the Pension Fund issued a fine of 500 rubles. for each person in the report (Article 17 of the Federal Law of April 1, 1996 No. 27-FZ). The result was 48 thousand rubles. The company challenged the fine, but the court of first instance only reduced its amount. And the “appeal” canceled the fine in full.
Arguments that work in court to protect the company:
- The fund has already received information for a specific month earlier. Therefore, there is no question of being late;
- the original report with an error in the field for the reporting period number was submitted with the code “output”;
- the organization submitted objections to the inspection report with explanations of why it corrected the error.
The Supreme Court completely agrees with these arguments (Decision of the Supreme Court dated January 22, 2018 No. 301-KG17-20650).
If you incorrectly indicated the period code in SZV-M, try to cancel the fine before the trial. To do this, prepare your objections. Perhaps the Pension Fund will take into account your explanations, reduce the fine or cancel it. Then you won't have to go to court.
If this does not help, file a claim with the Pension Fund. The right to challenge the fine in court is given by Article 18 of Law No. 27-FZ. In the statement of claim, demand that the fine be canceled in full. The court can reduce the punishment as much as possible. In any case, you can at least reduce the fine.
Next, you need to understand how to report for a month that was indicated by mistake, for example, if you mistakenly indicated the month code 04, but it should have been 03. If, after your objections, the fund corrected the reporting period code from 04 to 03, send a new report for April to the Pension Fund of Russia with code "Ikhd".
If the fund refused to accept the amendment, see if your composition of employees and contractors changed in April. If not, then there is no need to fix anything. It will turn out that you have reported for April in advance. It's not a mistake.
If new employees arrived in April, then submit the supplementary SZV-M. In the line “Reporting period” put 04, in the line “Form type” - “additional”. If someone quit in March, then submit a canceled SZV-M for April. In the line “Reporting period” put 04, and in the line “Form type” - “cancel”. Since you are correcting data for April, it is safer to submit the cancellation and addition forms no later than May 15th.
If you need advice and assistance from qualified specialists,First BIT experts will help you in solving any problems.